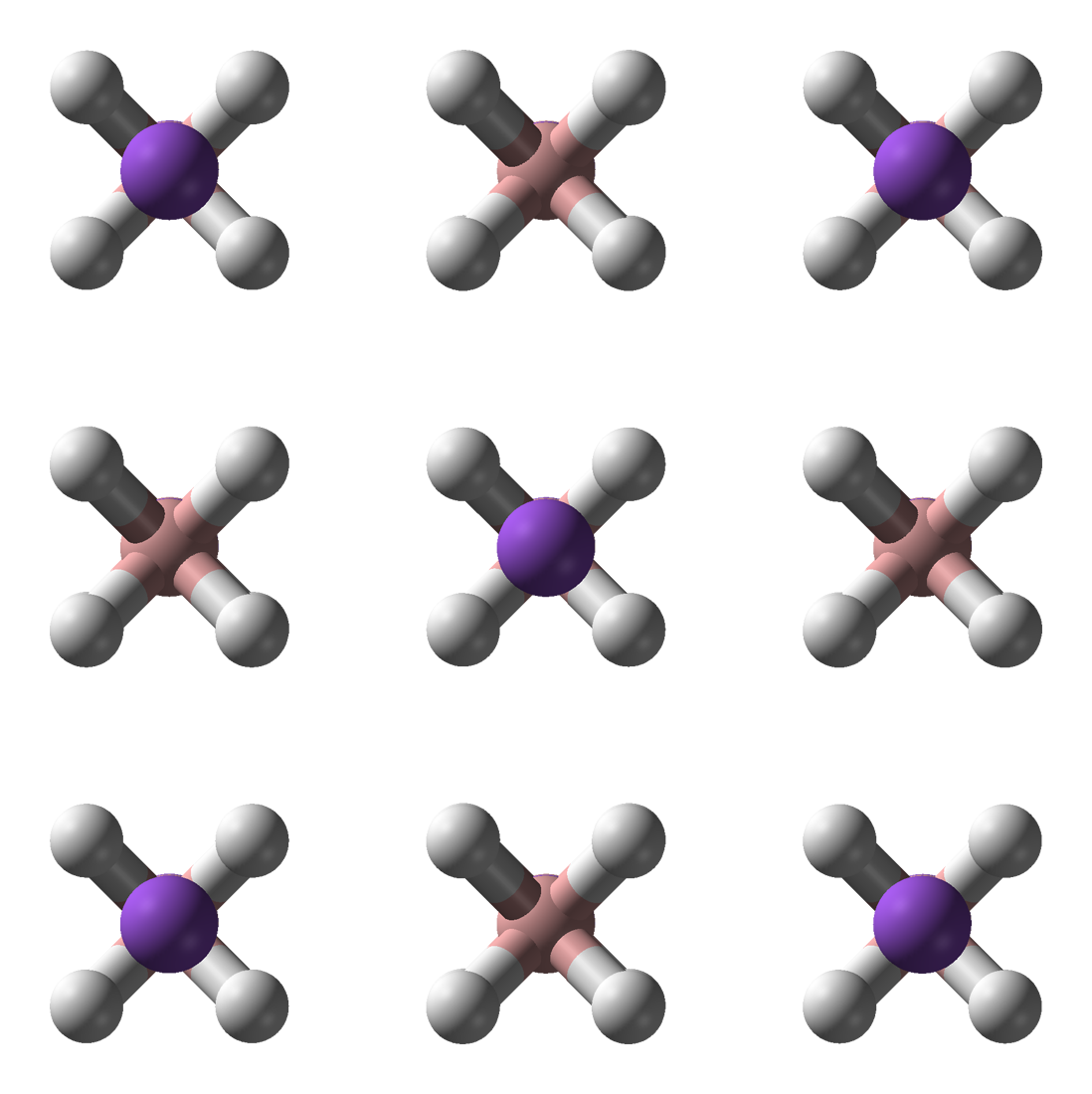
|
Chlorohydridobis(bis-1,2-(diphenylphosphino)ethane)iron(II)
Chlorobis(dppe)iron hydride is a coordination complex with the formula HFeCl(dppe)2, where dppe is the bidentate ligand 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane. It is a red-violet solid. The compound has attracted much attention as a precursor to dihydrogen complexes. Structure The complex exhibits octahedral molecular geometry. The chloride and hydride ligands are mutually trans. The bond distances between the iron metal atom and the coordinating ligands are given by the following: Synthesis and reactions The compound is synthesized according to the following idealized reaction: :FeCl2 + 2 dppe + Na H4→ NaCl + ½ B2H6 + HFeCl(dppe)2 In the course of this conversion, high-spin complex FeCl2(dppe)2 converts to low-spin HFeCl(dppe)2. The complex HFeCl dppe)2 exhibits a number of reactions associated with the remaining Fe-Cl bond. Reaction of the complex with sodium borohydride gives the dihydride complex: :HFeCl(dppe)2 + NaBH4 → H2Fe(dppe)2 + NaCl + "BH3" Removal of chl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Compounds
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or Metallurgical furnace, furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelting, smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC, 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace list of copper alloys, copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as '' ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dppe
1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (PhPCH) (Ph = phenyl). It is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Preparation The preparation of dppe is by the alkylation of NaPPh: :P(CH) + 2 Na → NaP(CH) + NaCH NaP(CH), which is readily air-oxidized, is treated with 1,2-dichloroethane (ClCHCHCl) to give dppe: :2 NaP(CH) + ClCHCHCl → (CH)PCHCHP(CH) + 2 NaCl Reactions The reduction of dppe by lithium to give PhHP(CH)PHPh has been reported. :PhP(CH)PPh + 4 Li → PhLiP(CH)PLiPh + 2 PhLi Hydrolysis gives the bis(secondary phosphine): :PhLiP(CH)PLiPh + 2 PhLi + 4HO → PhHP(CH)PHPh + 4 LiOH + 2 CH : Treatment of dppe with conventional oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide (HO), aqueous bromine (Br), etc., produces dppeO in low yield (e.g., 13%) as a result of non-selective oxidation.Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd Select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrogen Complex
Dihydrogen complexes are coordination complexes containing intact H2 as a ligand. They are a subset of sigma complexes. The prototypical complex is W(CO)3( PCy3)2(H2). This class of compounds represent intermediates in metal-catalyzed reactions involving hydrogen. Hundreds of dihydrogen complexes have been reported. Most examples are cationic transition metals complexes with octahedral geometry. Upon complexation, the H−H bond is extended to 0.81–0.82 Å as indicated by neutron diffraction, about a 10% extension relative to the H−H bond in free H2. Some complexes containing multiple hydrogen ligands, i.e. polyhydrides, also exhibit short H−H contacts. It has been suggested that distances 1 Å are better described as dihydride complexes (see figure). Characterization The usual method for characterization is 1H NMR spectroscopy. The magnitude of spin-spin coupling, ''J''HD, is a useful indicator of the strength of the bond between the hydrogen and deuterium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix '' octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na BH4. This white solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution, is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis. The compound was discovered in the 1940s by H. I. Schlesinger, who led a team seeking volatile uranium compounds.Hermann I Schlesinger and Herbert C Brown (1945)Preparation of alkali metal compounds. US Patent 2461661. Granted on 1949-02-15; expired on 1966-02-15. Results of this wartime research were declassified and published in 1953. Properties The compound is soluble in alcohols, certain ethers, and water, although it slowly hydrolyzes. Sodium borohydride is an odorless white to gray-white microcrystalline powder that often forms lumps. It can be purified by recrystallization from warm (50 °C) diglyme. Sodium borohydride is soluble in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Complex
Transition metal dinitrogen complexes are coordination compounds that contain transition metals as ion centers the dinitrogen molecules (N2) as ligands. Historical background Transition metal complexes of N2 have been studied since 1965 when the first complex was reported by Allen and Senoff. This diamagnetic complex, 2+.html" ;"title="u(NH3)5(N2)sup>2+">u(NH3)5(N2)sup>2+, was synthesized from hydrazine hydrate and ruthenium trichloride and consists of a u(NH3)5sup>2+ centre attached to one end of N2. The existence of N2 as a ligand in this compound was identified by IR spectrum with a strong band around 2170–2100 cm−1. In 1966, the molecular structure of u(NH3)5(N2)l2 was determined by Bottomly and Nyburg by X-ray crystallography. The dinitrogen complex ''trans''- rCl(N2)(PPh3)2is made by treating Vaska's complex with aromatic acyl azides. It has a planar geometry. The first preparation of a metal-dinitrogen complex using dinitrogen was reported in 1967 by Yam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Hydrides
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. For inorganic chemists, hydrides refer to compounds and ions in which hydrogen is covalently attached to a less electronegative element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Pm, Os, Ir, Rn, Fr, and Ra. Exotic molecules such as positronium hydride have also been made. Bonds Bonds between hydrogen and the other elements range from highly to somewhat covalent. Some hydrides, e.g. boron hydrides, do not conform to classical electron-counting rules and the bonding is described in terms of multi-cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloro Complexes
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride salts like ammonium chloride ( sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However, the nature of free chlorine gas as a separate substance was only recognised around 163 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine Complexes
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air (pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine, PH3, is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavoisier, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |