|
Chlorantraniliprole
Chlorantraniliprole (Rynaxypyr) is an insecticide of the ryanoid classes. Chlorantraniliprole was developed world-wide by DuPont and belongs to a class of selective insecticides featuring a novel mode of action to control a range of pests belonging to the order Lepidoptera (moth) and some other Coleoptera (beetle), Diptera (fly), and Isoptera (termite) species. Chlorantraniliprole opens muscular calcium channels,in particular the ryanodine receptor, rapidly causing paralysis and ultimately death of sensitive species. The differential selectivity chlorantraniliprole has towards insect ryanodine receptors explains the outstanding profile of low mammalian toxicity. Chlorantraniliprole is active on chewing pest insects primarily by ingestion and secondarily by contact. Chlorantraniliprole is an active ingredient An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticides
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repellen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryanoid
Ryanoids are a class of insecticides which share the same mechanism of action as the alkaloid ryanodine Ryanodine is a poisonous diterpenoid found in the South American plant ''Ryania speciosa'' (Salicaceae). It was originally used as an insecticide. The compound has extremely high affinity to the open-form ryanodine receptor, a group of calcium cha .... Ryanodine is a naturally occurring insecticide isolated from '' Ryania speciosa''. Ryanoids include natural chemicals which are closely related to ryanodine, such as ryanodol and 9,21-didehydroryanodol, and also chemically distinct synthetic compounds such as chlorantraniliprole (Rynaxypyr), flubendiamide, cyantraniliprole, cyclaniliprole, and tetraniliprole, which are called diamide insecticides. Ryanoids exert their insecticidal effect by interacting with ryanodine receptors, a type of calcium channel. This causes loss of muscle function leading to paralysis and death. References {{insecticides Insecticides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in the development of Delaware and first arose as a major supplier of gunpowder. DuPont developed many polymers such as Vespel, neoprene, nylon, Corian, Teflon, Mylar, Kapton, Kevlar, Zemdrain, M5 fiber, Nomex, Tyvek, Sorona, Corfam and Lycra in the 20th century, and its scientists developed many chemicals, most notably Freon (chlorofluorocarbons), for the refrigerant industry. It also developed synthetic pigments and paints including ChromaFlair. In 2015, DuPont and the Dow Chemical Company agreed to a reorganization plan in which the two companies would merge and split into three. As a merged entity, DuPont simultaneously acquired Dow and renamed itself to DowDuPont on August 31, 2017, and after 18 months spin off the merged en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order of insects that includes butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 families and 46 superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described species of living organisms. It is one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. The Lepidoptera show many variations of the basic body structure that have evolved to gain advantages in lifestyle and distribution. Recent estimates suggest the order may have more species than earlier thought, and is among the four most speciose orders, along with the Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Coleoptera. Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scales that cover the bodies, wings, and a proboscis. The scales are modified, flattened "hairs", and give butterflies and moths their wide variety of colors and patterns. Almost all species have some form of mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleoptera
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal life-forms; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ladybugs) eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Beetles typically have a particularly hard e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described. Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great maneuverability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoptera
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blattodea (along with cockroaches). Termites were once classified in a separate order from cockroaches, but recent phylogenetic studies indicate that they evolved from cockroaches, as they are deeply nested within the group, and the sister group to wood eating cockroaches of the genus ''Cryptocercus''. Previous estimates suggested the divergence took place during the Jurassic or Triassic. More recent estimates suggest that they have an origin during the Late Jurassic, with the first fossil records in the Early Cretaceous. About 3,106 species are currently described, with a few hundred more left to be described. Although these insects are often called "white ants", they are not ants, and are not closely related to ants. Like ants and some bees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
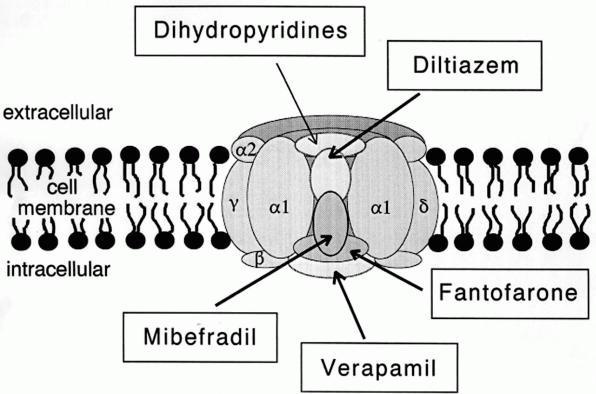
Calcium Channels
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) **P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hyperten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryanodine Receptor
Ryanodine receptors (RyR for short) form a class of intracellular calcium channels in various forms of excitable animal tissue like muscles and neurons. There are three major isoforms of the ryanodine receptor, which are found in different tissues and participate in different signaling pathways involving calcium release from intracellular organelles. The RYR2 ryanodine receptor isoform is the major cellular mediator of calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) in animal cells. Etymology The ryanodine receptors are named after the plant alkaloid ryanodine which shows a high affinity to them. Isoforms There are multiple isoforms of ryanodine receptors: * RyR1 is primarily expressed in skeletal muscle * RyR2 is primarily expressed in myocardium (heart muscle) * RyR3 is expressed more widely, but especially in the brain. * Non-mammalian vertebrates typically express two RyR isoforms, referred to as RyR-alpha and RyR-beta. * Many invertebrates, including the model organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryanodine
Ryanodine is a poisonous diterpenoid found in the South American plant ''Ryania speciosa'' (Salicaceae). It was originally used as an insecticide. The compound has extremely high affinity to the open-form ryanodine receptor, a group of calcium channels found in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and heart muscle cells. It binds with such high affinity to the receptor that it was used as a label for the first purification of that class of ion channels and gave its name to it. At nanomolar concentrations, ryanodine locks the receptor in a half-open state, whereas it fully closes them at micromolar concentration. The effect of the nanomolar-level binding is that ryanodine causes release of calcium from calcium stores as the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the cytoplasm, leading to massive muscle contractions. The effect of micromolar-level binding is paralysis. This is true for both mammals and insects. See also * Ryanoid, a class of insecticides with the same mechanism of action as ryano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Ingredient
An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body of humans or animals. The similar terms active pharmaceutical ingredient (also abbreviated as API) and bulk active are also used in medicine, and the term active substance may be used for natural products. Some medication products may contain more than one active ingredient. The traditional word for the active pharmaceutical agent is pharmacon or pharmakon (from el, φάρμακον, adapted from ''pharmacos'') which originally denoted a magical substance or drug. The terms active constituent or active principle are often chosen when referring to the active substance of interest in a plant (such as salicylic acid in willow bark or arecoline in areca nuts), because the word "ingredient" in many minds connotes a sense of human agency (that is, something that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamides
Benzamide is a organic compound with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid. In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents. It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa. Chemical derivatives A number of substituted A substitution reaction (also known as single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction) is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reactions ar ... benzamides are commercial drugs, including: See also * References External links Physical characteristics {{Authority control Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(10144905255).jpg)