|
Charbagh
''Charbagh'' or ''Chahar Bagh'' ( ''chahār bāgh'', ''chārbāgh'', ''chār bāgh'', meaning "four gardens") is a Persian and Indo-Persian quadrilateral garden layout based on the four gardens of Paradise mentioned in the Quran. The quadrilateral garden is divided by walkways or flowing water into four smaller parts. They are found in countries throughout Western Asia and South Asia, including Iran and India. Persian garden concept of chahar bagh The quadrilateral Charbagh concept is interpreted as the four gardens of Paradise mentioned in Chapter (Surah) 55, Ar-Rahman "The Beneficient", in the Qur'an: One of the hallmarks of Charbagh garden is the four-part garden laid out with axial paths that intersect at the garden's centre. This highly structured geometrical scheme, called the chahar bagh, became a powerful method for the organization and domestication of the landscape, itself a symbol of political territory. The concept of chahar bagh is not only mentioned in Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradise Garden
The paradise garden is a form of garden of Old Iranian origin, specifically Achaemenid which is formal, symmetrical and most often, enclosed. The most traditional form is a rectangular garden split into four quarters with a pond in the center, a four-fold design called ''chahar bagh'' (“four gardens”). One of the most important elements of paradise gardens is water, with ponds, canals, rills, and fountains all being common features. Scent is an essential element with fruit-bearing trees and flowers selected for their fragrance. It is also often referred to as an Islamic garden. The form of garden spread throughout Egypt and the Mediterranean during the Muslim Arabic conquests, reaching as far as India and Spain. Etymology Originally denominated by a single noun denoting "a walled-in compound or garden", from "''pairi''" ("around") and "''daeza''" or "''diz''" ("wall", "brick", or "shape"), philosopher and historian Xenophon of Athens borrowed the Old Iranian ''*p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humayun's Tomb
Humayun's tomb ( Persian: ''Maqbara-i Humayun'') is the tomb of the Mughal Emperor Humayun in Delhi, India. The tomb was commissioned by Humayun's first wife and chief consort, Empress Bega Begum under her patronage in 1558, and designed by Mirak Mirza Ghiyas and his son, Sayyid Muhammad, Persian architects chosen by her. It was the first garden-tomb on the Indian subcontinent,Humayun's Tomb, Delhi , . and is located in , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charbagh, Isfahan
Chahar Bagh Boulevard (, translation: ''Four Gardens'') is a historical avenue in Isfahan constructed in the Safavid era of Iran. This histories street is very similar to the Champs-Élysées in Paris, which some visitors called the Champs-Élysées of Isfahan. The avenue, historically, is the most famous in all of Persia. It connects the northern parts of the city to the southern sections and is about 6 kilometers long. On the east side of this street, there are the Hasht Behesht and Chehel Sotoun gardens. History Shah Abbas I was the king who changed his capital from Qazvin to Esfahan and decided to pour all the country's artistic wealth into that central spot which has been dubbed for centuries "Nisfi Jahan" or "Half the World". The chief architect of this task of urban planning was Shaykh Bahai (Baha' ad-Din al-'Amili), who focused the programme on two key features of Shah Abbas's master plan: the Chahar Bagh avenue, flanked at either side by all the prominent institutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
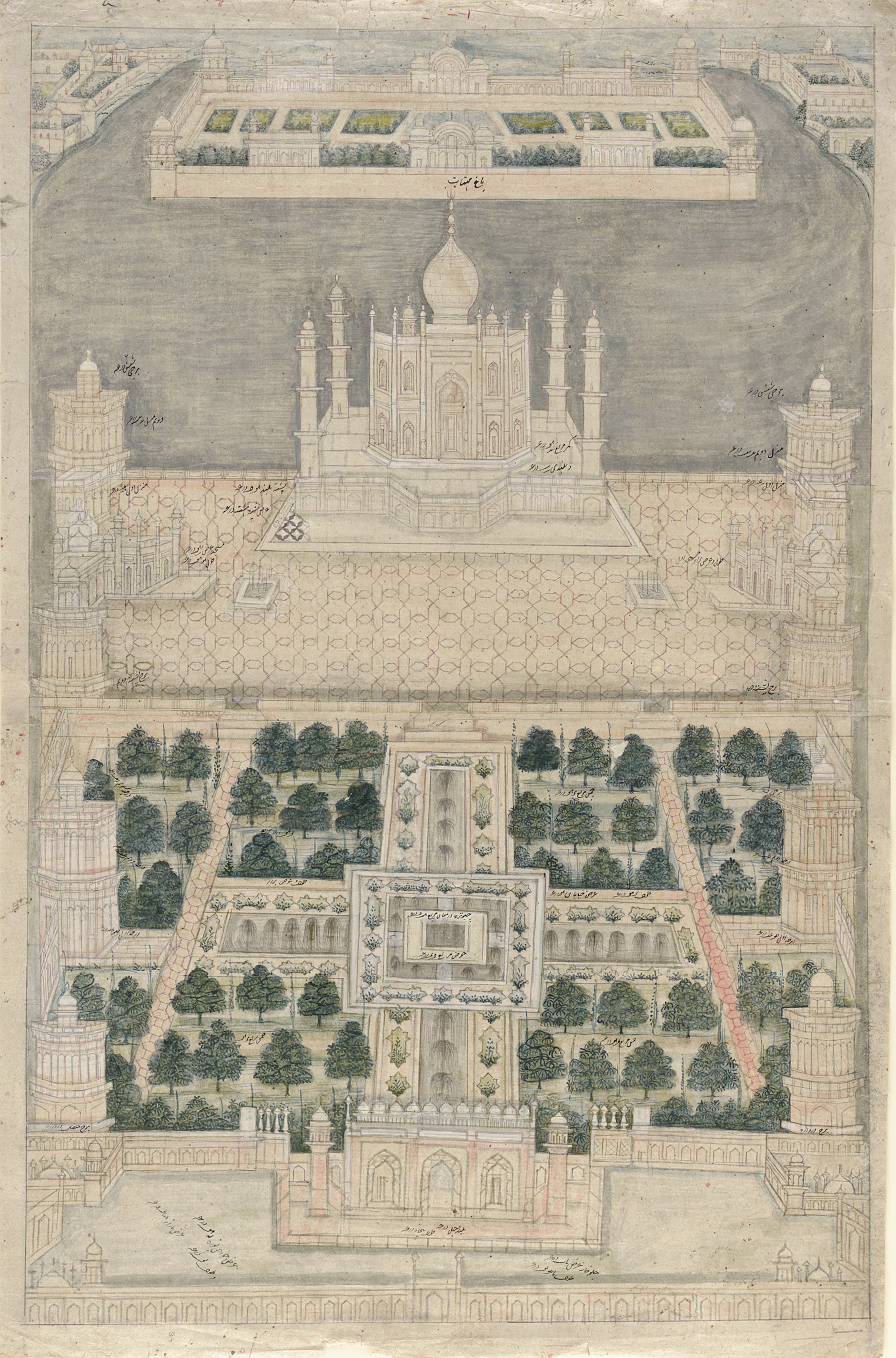
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal (; ) is an Islamic ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his favourite wife, Mumtaz Mahal; it also houses the tomb of Shah Jahan himself. The tomb is the centrepiece of a complex, which includes a mosque and a guest house, and is set in formal gardens bounded on three sides by a crenellated wall. Construction of the mausoleum was essentially completed in 1643, but work continued on other phases of the project for another 10 years. The Taj Mahal complex is believed to have been completed in its entirety in 1653 at a cost estimated at the time to be around ₹32 million, which in 2020 would be approximately 70 billion (about US $1 billion). The construction project employed some 20,000 artisans under the guidance of a board of architects led by the court architect to the emperor, Ustad Ahmad Lahauri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismaili Centre, London
The Ismaili Centre, London is one of six such centres world-wide. Established in South Kensington more than thirty years ago, it is a religious, social and cultural meeting place for the Ismaili Muslim community in the United Kingdom and is the first such centre to be specially designed and built for Ismailis in the Western world. Establishment The Ismaili Centre, London was inaugurated on 24 April 1985 by then Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, in the presence of His Highness the Aga Khan, the 49th Imam (spiritual leader) of the Ismaili Muslims. It was the first religious, cultural and social space specifically designed for the Ismaili community in the Western world. The Ismaili community had been in the United Kingdom since as early as 1951, when they established a religious, cultural and social centre at Kensington Court. It was moved to Palace Gate in 1957, but the needs of the growing community increased over time, and a site at Cromwell Gardens was acquired in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isfahan Garden Carpet
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its Achaemenid empire, ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in Sassanian Empire, middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Region, Isfahan Province, Iran. It is located south of Tehran and is the capital of Isfahan Province. The city has a population of approximately 2,220,000, making it the third-largest city in Iran, after Tehran and Mashhad, and the second-largest metropolitan area. Isfahan is located at the intersection of the two principal routes that traverse Iran, north–south and east–west. Isfahan flourished between the 9th and 18th centuries. Under the Safavids, Safavid dynasty, Isfahan became the capital of Achaemenid Empire, Persia, for the second time in its history, under Shah Abbas the Great. The city retains much of its history. It is famous for its Perso–Islamic architecture, grand boulevards, covered bridges, palaces, tiled mosques, and mina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
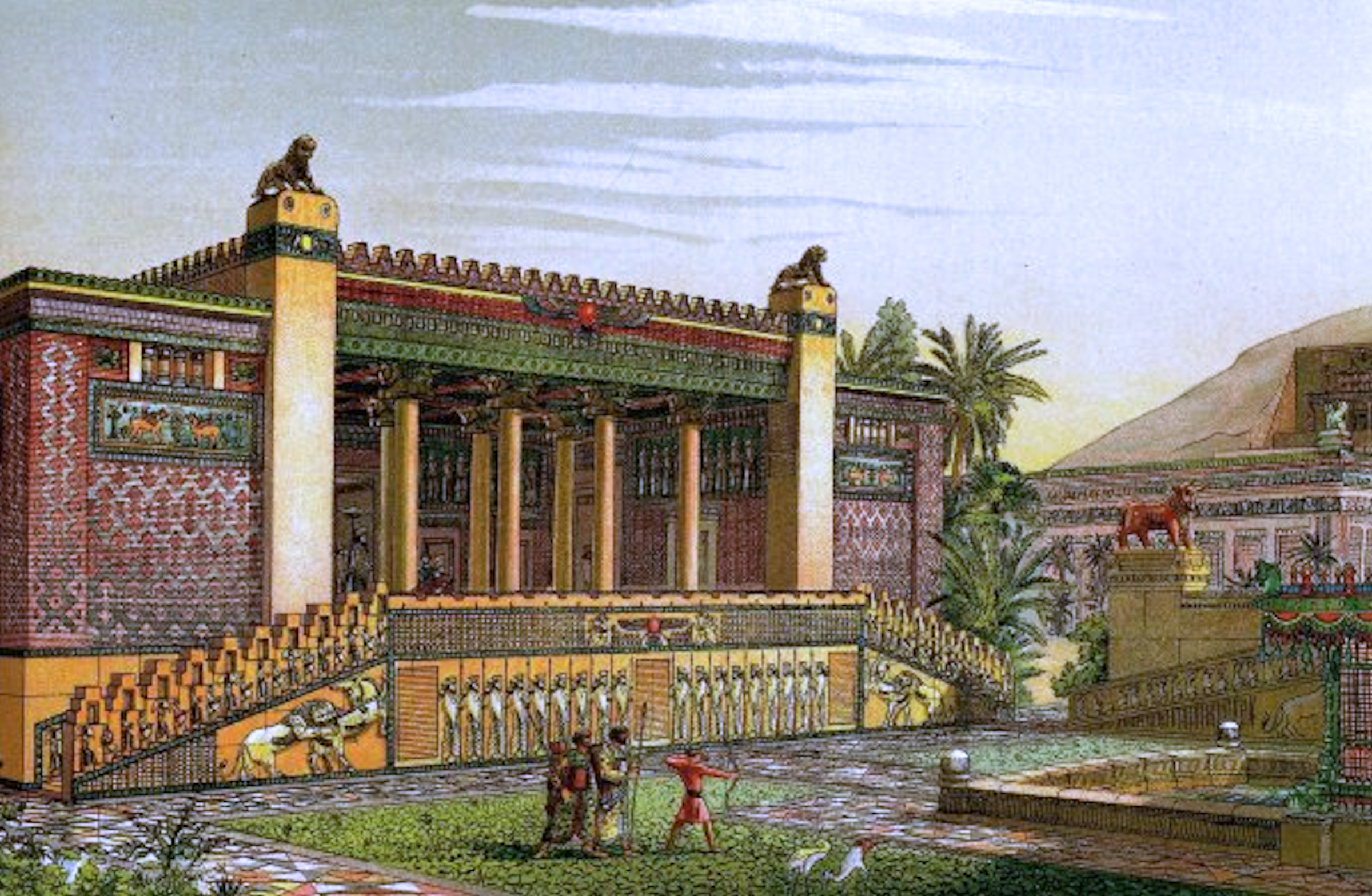
Persian Gardens
The tradition and style of garden design represented by Persian gardens or Iranian gardens ( fa, باغ ایرانی), an example of the paradise garden, has influenced the design of gardens from Andalusia to India and beyond. The gardens of the Alhambra show the influence of Persian garden philosophy and style in a Moorish palace scale, from the era of al-Andalus in Spain. Humayun's Tomb and the Taj Mahal have some of the largest Persian gardens in the world, from the era of the Mughal Empire in India. Concept and etymology From the time of the Achaemenid Empire, the idea of an earthly paradise spread through Persian literature and example to other cultures, both the Hellenistic gardens of the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemies in Alexandria. The Avestan word ''pairidaēza-'', Old Persian *''paridaida-'',Although the genuine Old Persian form must have been *''paridaida-'', Modern Persian ''palīz'' 'garden' from Middle Persian ''palēz'' presupposes a variant *''pardaiza-'' (wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehtab Bagh
Mehtab Bagh () is a charbagh complex in Agra, North India. It lies north of the Taj Mahal complex and the Agra Fort on the opposite side of the Yamuna River, in the flood plains. The garden complex, square in shape, measures about and is perfectly aligned with the Taj Mahal on the opposite bank. During the rainy season, the ground becomes partially flooded. History The Mehtab Bagh garden was the last of eleven Mughal-built gardens along the Yamuna opposite the Taj Mahal and the Agra Fort. The garden was built by Emperor Babur (d. 1530). It is also noted that Emperor Shah Jahan had identified a site from the crescent-shaped, grass-covered floodplain across the Yamuna River as an ideal location for viewing the Taj Mahal. It was then created as "a moonlit pleasure garden called Mehtab Bagh." White plaster walkways, airy pavilions, pools and fountains were also created as part of the garden, with fruit trees and narcissus. The garden was designed as an integral part of the Taj Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Gardens
Mughal gardens are a type of garden built by the Mughals. This style was influenced by the Persian gardens particularly the Charbagh structure, which is intended to create a representation of an earthly utopia in which humans co-exist in perfect harmony with all elements of nature. Significant use of rectilinear layouts are made within the walled enclosures. Some of the typical features include pools, fountains and canals inside the gardens. Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan have a number of Mughal gardens which differ from their Central Asian predecessors with respect to "the highly disciplined geometry". History The founder of the Mughal empire, Babur, described his favourite type of garden as a charbagh. The term '' bāgh'', ''baug'', ''bageecha'' or ''bagicha'' is used for the garden. This word developed a new meaning in South Asia, as the region lacked the fast-flowing streams required for the Central Asian charbagh. The Aram Bagh of Agra is thought to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the fourth-most populous city in Uttar Pradesh and twenty-third most populous city in India. Agra's notable historical period began during Sikandar Lodi's reign, but the golden age of the city began with the Mughals. Agra was the foremost city of the Indian subcontinent and the capital of the Mughal Empire under Mughal emperors Babur, Humayun, Akbar, Jahangir and Shah Jahan. Under Mughal rule, Agra became a centre for learning, arts, commerce, and religion, and saw the construction of the Agra Fort, Sikandra and Agra's most prized monument, the Taj Mahal, built by Shah Jahan as a mausoleum for his favourite empress. With the decline of the Mughal empire in the late 18th century, the city fell successively first to Marathas and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isfahan
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Region, Isfahan Province, Iran. It is located south of Tehran and is the capital of Isfahan Province. The city has a population of approximately 2,220,000, making it the third-largest city in Iran, after Tehran and Mashhad, and the second-largest metropolitan area. Isfahan is located at the intersection of the two principal routes that traverse Iran, north–south and east–west. Isfahan flourished between the 9th and 18th centuries. Under the Safavid dynasty, Isfahan became the capital of Persia, for the second time in its history, under Shah Abbas the Great. The city retains much of its history. It is famous for its Perso–Islamic architecture, grand boulevards, covered bridges, palaces, tiled mosques, and minarets. Isfahan also has many historical buildings, monument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |