|
Carruca
The carruca or caruca was a kind of heavy plow important to medieval agriculture in Northern Europe. The carruca used a heavy iron plowshare to turn heavy soil and may have required a team of eight oxen. The carruca also bore a coulter and moldboard. It gave its name to the English carucate. The heavy iron moldboard plow was developed in China's Han Empire in the 1st and 2nd century. Based on linguistic evidence, the carruca may have been employed by some Slavs by AD 568.White Jr., Lynn, The Life of the Silent Majority, pg. 88 of Life and Thought in the Early Middle Ages, ed. Robert S. Hoyt, University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis. 1967 It was present in Italy's Po Valley by 643 and—judging from the terminology in the '—in southwestern Germany by 720. The carruca may have been introduced to the British Isles by the Viking invasions of England in the late 9th century. The carruca was able to turn over a furrow and it gave an opportunity to utilize the heavier soils of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carucate
The carucate or carrucate ( lat-med, carrūcāta or ) was a medieval unit of land area approximating the land a plough team of eight oxen could till in a single annual season. It was known by different regional names and fell under different forms of tax assessment. England The carucate was named for the carruca heavy plough that began to appear in England in the late 9th century, it may have been introduced during the Viking invasions of England.White Jr., Lynn, The Life of the Silent Majority, pg. 88 of Life and Thought in the Early Middle Ages, ed. Robert S. Hoyt, University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis. 1967 It was also known as a ploughland or plough ( ang, plōgesland, "plough's land") in the Danelaw and usually, but not always, excluded the land's suitability for winter vegetables and desirability to remain fallow in crop rotation. The tax levied on each carucate came to be known as "carucage". Though a carucate might nominally be regarded as an area of 120 acres (49 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scratch Plow
The ard, ard plough, or scratch plough is a simple light plough without a mouldboard. It is symmetrical on either side of its line of draft and is fitted with a symmetrical share that traces a shallow furrow but does not invert the soil. It began to be replaced in China by the heavy carruca turnplough in the 1st century, and in most of Europe from the 7th century. In its simplest form it resembles a hoe, consisting of a ''draft-pole'' (either composite or a single piece) pierced with a nearly vertical, wooden, spiked ''head'' (or ''stock'') which is dragged through the soil by draft animals and very rarely by people. The ard-head is at one end a ''stilt'' (handle) for steering and at the other a ''share'' (cutting blade) which gouges the surface ground. More sophisticated models have a composite pole, where the section attached to the head is called the ''draft-beam'', and the share may be made of stone or iron. Some have a cross-bar for handles or two separate stilts for han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carucate
The carucate or carrucate ( lat-med, carrūcāta or ) was a medieval unit of land area approximating the land a plough team of eight oxen could till in a single annual season. It was known by different regional names and fell under different forms of tax assessment. England The carucate was named for the carruca heavy plough that began to appear in England in the late 9th century, it may have been introduced during the Viking invasions of England.White Jr., Lynn, The Life of the Silent Majority, pg. 88 of Life and Thought in the Early Middle Ages, ed. Robert S. Hoyt, University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis. 1967 It was also known as a ploughland or plough ( ang, plōgesland, "plough's land") in the Danelaw and usually, but not always, excluded the land's suitability for winter vegetables and desirability to remain fallow in crop rotation. The tax levied on each carucate came to be known as "carucage". Though a carucate might nominally be regarded as an area of 120 acres (49 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Plow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldboard
A plough or plow (Differences between American and British spellings, US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to Decomposition, decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then Harrow (tool), harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Plow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furrow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploughs
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
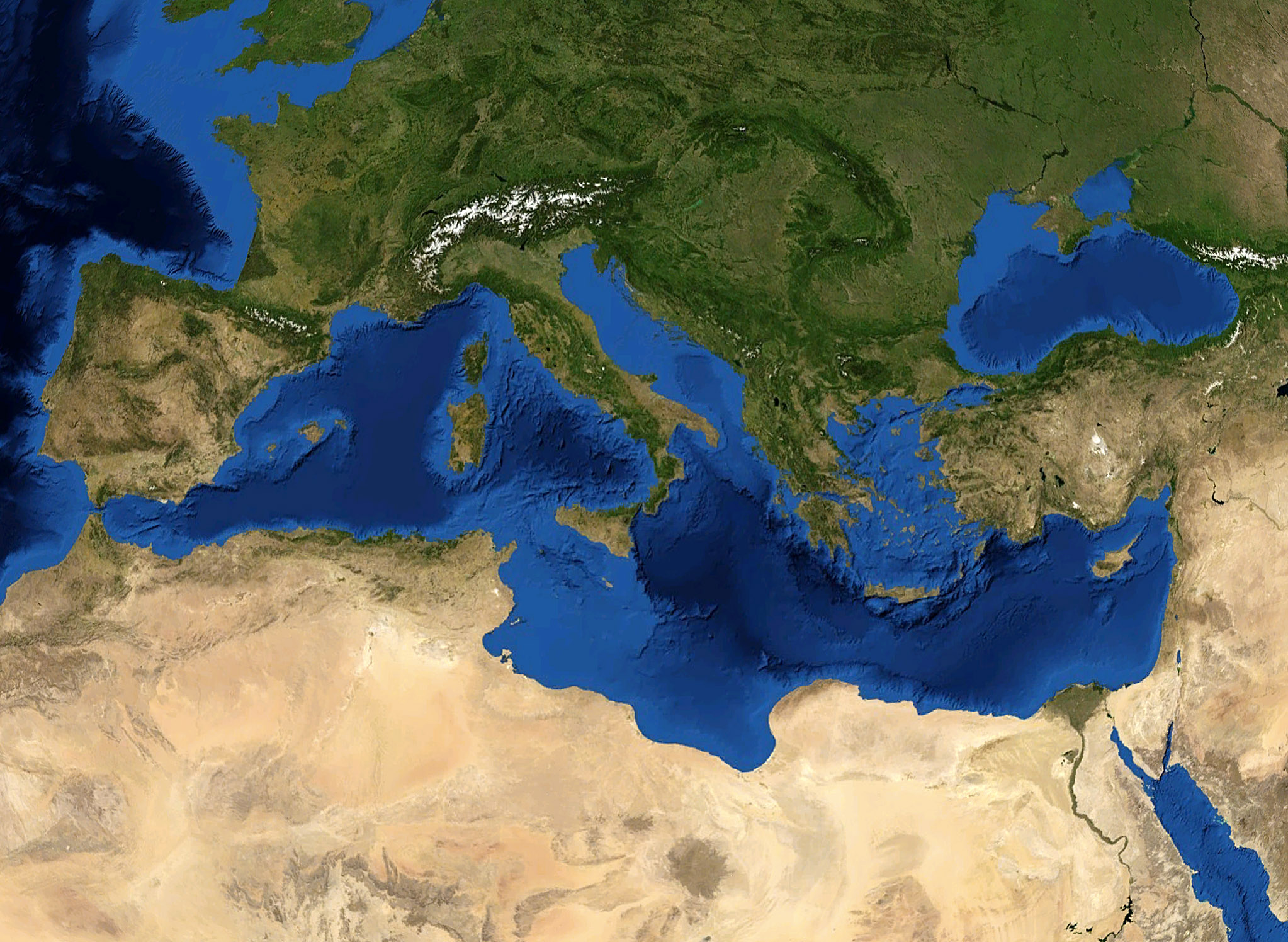
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, East Thrace, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, Southern France, Spain, and Vatican City (the Holy See). Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Apennine Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as their mountainous reliefs, provide them w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackson J
Robert Houghwout Jackson (February 13, 1892 – October 9, 1954) was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court from 1941 until his death in 1954. He had previously served as United States Solicitor General and United States Attorney General, and is the only person to have held all three of those offices. Jackson was also notable for his work as Chief United States Prosecutor at the Nuremberg trials of Nazi war criminals following World War II. Jackson was the last U.S. Supreme Court justice who did not have a law degree. He was Admission to the bar in the United States, admitted to the bar via the older tradition of reading law under an established lawyer, after studying at Albany Law School for just a year. Jackson is well known for his advice that, "Any lawyer worth his salt will tell the suspect, in no uncertain ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology. Climate The climate is mainly Oceanic climate (Cfb), Humid continental climate (Dfb), Subarctic climate (Dfc and Dsc) and Tundra (ET). Geography Northern Europe might be defined roughly to include some or all of the following areas: British Isles, Fennoscandia, the peninsula of Jutland, the Baltic plain that lies to the east and the many islands that lie offshore from mainland Northern Europe and the main European continent. In some cases, Greenland is also included, although it is only politically European, comprising part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and not considered to be geographically in Europe. The area is partly mountainous, including the northern volcanic islands of Iceland and Jan Mayen, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |