|
Cardiac Rhythmicity
Cardiac rhythmicity is the spontaneous depolarization and repolarization event that occurs in a repetitive and stable manner within the cardiac muscle. Rhythmicity is often abnormal or lost in cases of cardiac dysfunction or cardiac failure. It is the ability of the heart to maintain a relatively stable relation between its systole and diastole Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventri .... Not increasing one on the expense of the other. However, external factors may lead to the disruption of the heart's rhythmicity. References * PhysioEx 6.0 by Peter Zao, Timothy Stabler, Greta Peterson, Lori Smith Cardiac electrophysiology {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism. Most cells in higher organisms maintain an internal environment that is negatively charged relative to the cell's exterior. This difference in charge is called the cell's membrane potential. In the process of depolarization, the negative internal charge of the cell temporarily becomes more positive (less negative). This shift from a negative to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming positively char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns it to a negative value just after the depolarization phase of an action potential which has changed the membrane potential to a positive value. The repolarization phase usually returns the membrane potential back to the resting membrane potential. The efflux of potassium (K+) ions results in the falling phase of an action potential. The ions pass through the selectivity filter of the K+ channel pore. Repolarization typically results from the movement of positively charged K+ ions out of the cell. The repolarization phase of an action potential initially results in hyperpolarization, attainment of a membrane potential, termed the afterhyperpolarization, that is more negative than the resting potential. Repolarization usually takes several milliseconds. Repolarization is a stage of an action potential in which the cell experiences a decrease of voltage due to the efflux of potassium (K+) ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
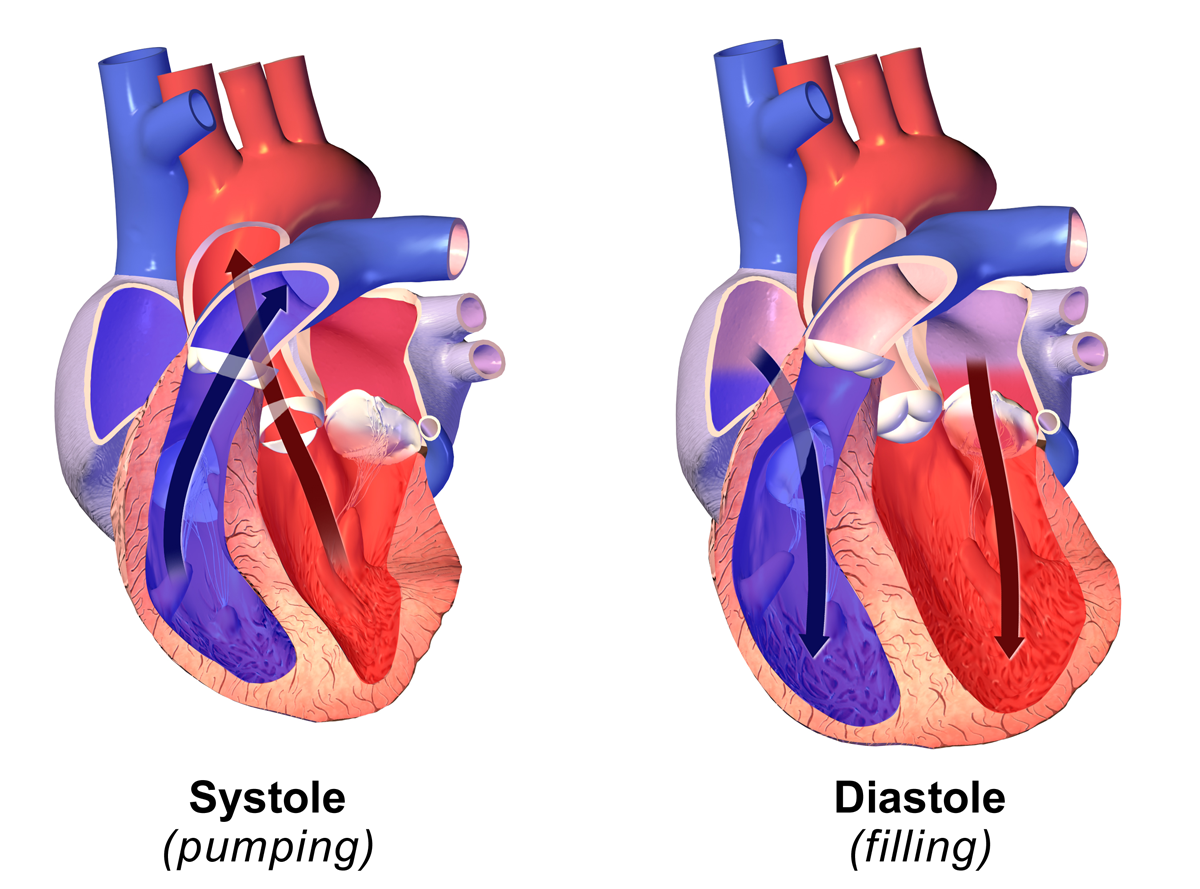
Systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |