|
Capite
In old English law, a capite (from Latin ''caput'', head) was a tenure, abolished by Act 12 Chas. II, xxiv. (Tenures Abolition Act 1660), by which either person or land was held immediately of the king, or of his crown, either by knight-service or socage. A holder of a capite is termed a tenant-in-chief In medieval and early modern Europe, the term ''tenant-in-chief'' (or ''vassal-in-chief'') denoted a person who held his lands under various forms of feudal land tenure directly from the king or territorial prince to whom he did homage, as opp .... References * Common law English laws {{England-law-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenures Abolition Act 1660
The Tenures Abolition Act 1660 (12 Car 2 c 24), sometimes known as the Statute of Tenures, was an Act of the Parliament of England which changed the nature of several types of feudal land tenure in England. The long title of the Act was ''An act for taking away the Court of Wards and liveries, and tenures in capite, and by knights-service, and purveyance, and for settling a revenue upon his Majesty in lieu thereof''. This Act was partly in force in Great Britain at the end of 2010, though only section 4: Passed by the Convention Parliament in 1660, shortly after the English Restoration, the Act replaced various types of military and religious service that tenants owed to the Crown with socage, and compensated the monarch with an annual fixed payment of £100,000 to be raised by means of a new tax on alcohol. ( Frankalmoin, copyhold, and certain aspects of grand serjeanty were excluded.) It completed a process that had begun in 1610 during the reign of James I with the propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures. Principal elements of English law Although the common law has, historically, been the foundation and prime source of English law, the most authoritative law is statutory legislation, which comprises Acts of Parliament, regulations and by-laws. In the absence of any statutory law, the common law with its principle of ''stare decisis'' forms the residual source of law, based on judicial decisions, custom, and usage. Common law is made by sitting judges who apply both statutory law and established principles which are derived from the reasoning from earlier decisions. Equity is the other historic source of judge-made law. Common law can be amended or repealed by Parliament. Not being a civil law system, it has no comprehensive codification. However, most of its criminal law has been codified from its common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
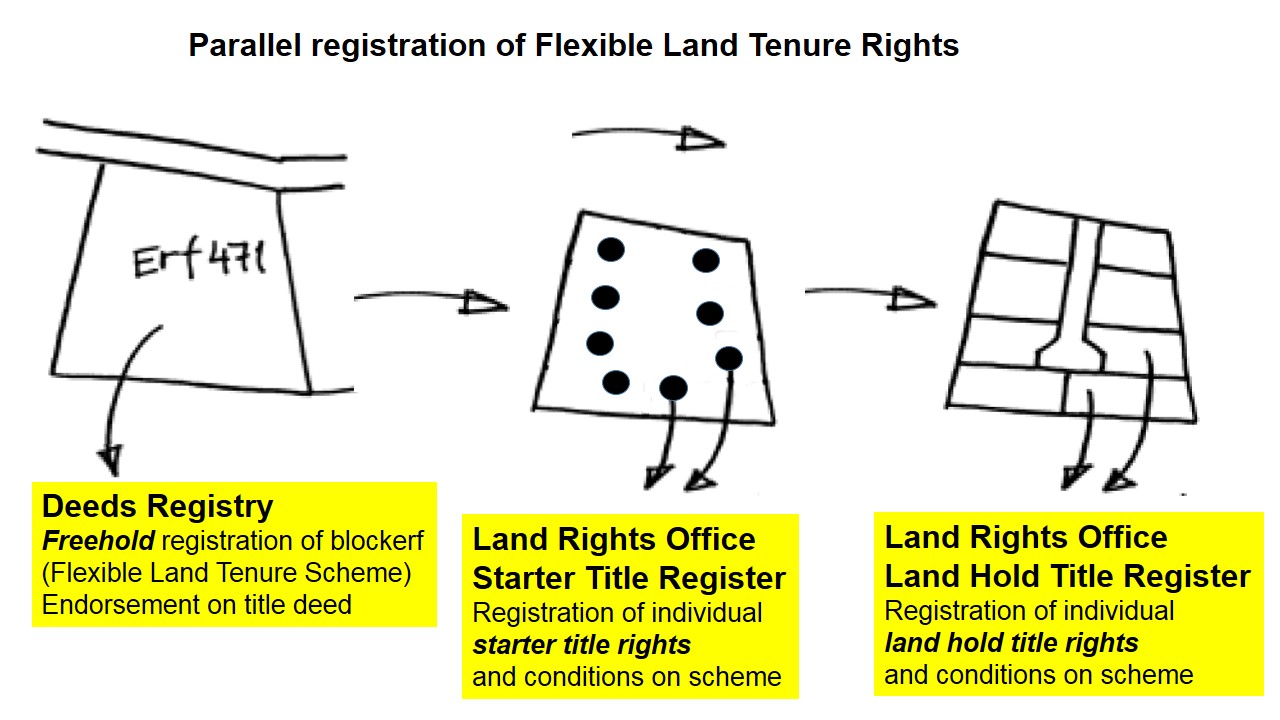
Land Tenure
In common law systems, land tenure, from the French verb "tenir" means "to hold", is the legal regime in which land owned by an individual is possessed by someone else who is said to "hold" the land, based on an agreement between both individuals. It determines who can use land, for how long and under what conditions. Tenure may be based both on official laws and policies, and on informal local customs (insofar higher law does allow that). In other words, land tenure implies a system according to which land is held by an individual or the actual tiller of the land but this person does not have legal ownership. It determines the holder's rights and responsibilities in connection with their holding. The sovereign monarch, known in England as The Crown, held land in its own right. All land holders are either its tenants or sub-tenants. ''Tenure'' signifies a legal relationship between tenant and lord, arranging the duties and rights of tenant and lord in relationship to the land. Ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Tenure
In common law systems, land tenure, from the French verb "tenir" means "to hold", is the legal regime in which land owned by an individual is possessed by someone else who is said to "hold" the land, based on an agreement between both individuals. It determines who can use land, for how long and under what conditions. Tenure may be based both on official laws and policies, and on informal local customs (insofar higher law does allow that). In other words, land tenure implies a system according to which land is held by an individual or the actual tiller of the land but this person does not have legal ownership. It determines the holder's rights and responsibilities in connection with their holding. The sovereign monarch, known in England as The Crown, held land in its own right. All land holders are either its tenants or sub-tenants. ''Tenure'' signifies a legal relationship between tenant and lord, arranging the duties and rights of tenant and lord in relationship to the land. Ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight-service
Knight-service was a form of feudal land tenure under which a knight held a fief or estate of land termed a knight's fee (''fee'' being synonymous with ''fief'') from an overlord conditional on him as tenant performing military service for his overlord. History It is associated in its origin with that development in warfare which made the mailed horseman, armed with lance and sword, the most important factor in battle. It was long believed that knight-service was developed out of the liability, under the English system, of every five hides of land to provide one soldier in war. It is now held that, on the contrary, it was a novel system in England when it was introduced after the Conquest by the Normans, who relied essentially on their mounted knights, while the English fought on foot. It existed in Normandy where a knight held a fief termed a ''fief de haubert'', from the hauberk or coat of mail (Latin: ''lorica'') worn by knights. Allusion is made to this in the coronation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socage
Socage () was one of the feudal duties and land tenure forms in the English feudal system. It eventually evolved into the freehold tenure called "free and common socage", which did not involve feudal duties. Farmers held land in exchange for clearly defined, fixed payments made at specified intervals to feudal lords. The lord was therefore obligated to provide certain services, such as protection, to the farmer and other duties to the Crown. Payments usually took the form of cash, but occasionally could be made with goods. Socage contrasted with other forms of tenure, including serjeanty, frankalmoin and knight-service. The English statute ''Quia Emptores'' of Edward I (1290) established that socage tenure passed from one generation or nominee to the next would be subject to inquisitions post mortem, which would usually involve a feudal relief tax. This contrasts with the treatment of leases, which could be lifelong or readily subject to forfeiture and rent increase. As fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenant-in-chief
In medieval and early modern Europe, the term ''tenant-in-chief'' (or ''vassal-in-chief'') denoted a person who held his lands under various forms of feudal land tenure directly from the king or territorial prince to whom he did homage, as opposed to holding them from another nobleman or senior member of the clergy.Bloch ''Feudal Society Volume 2'' p. 333Coredon ''Dictionary of Medieval Terms & Phrases'' p. 272 The tenure was one which denoted great honour, but also carried heavy responsibilities. The tenants-in-chief were originally responsible for providing knights and soldiers for the king's feudal army.Bracton, who indiscriminately called tenants-in-chief "barons" stated: "sunt et alii potentes sub rege qui barones dicuntur, hoc est robur belli" ("there are other magnates under the king, who are called barons, that is the hardwood of war"), quoted in Sanders, I.J., ''Feudal Military Service in England'', Oxford, 1956, p.3; "Bracton's definition of the ''baro''" (plur ''baron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresence in the sky, but the articulate voice of some sovereign or quasi sovereign that can be identified," ''Southern Pacific Company v. Jensen'', 244 U.S. 205, 222 (1917) (Oliver Wendell Holmes, dissenting). By the early 20th century, legal professionals had come to reject any idea of a higher or natural law, or a law above the law. The law arises through the act of a sovereign, whether that sovereign speaks through a legislature, executive, or judicial officer. The defining characteristic of common law is that it arises as precedent. Common law courts look to the past decisions of courts to synthesize the legal principles of past cases. ''Stare decisis'', the principle that cases should be decided according to consistent principled rules s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)