|
Cross-cultural Leadership
Cross-cultural psychology attempts to understand how individuals of different cultures interact with each other. Along these lines, cross-cultural leadership has developed as a way to understand leaders who work in the newly globalized market. Today's international organizations require leaders who can adjust to different environments quickly and work with partners and employees of other cultures. It cannot be assumed that a manager who is successful in one country will be successful in another. Related Theories and Research Implicit Leadership Theory The Implicit Leadership Theory (ILT) asserts that people's underlying assumptions, stereotypes, beliefs and schemas influence the extent to which they view someone as a good leader. Since people across cultures tend to hold different implicit beliefs, schemas and stereotypes, it would seem only natural that their underlying beliefs in what makes a good leader differ across cultures. Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions One of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-cultural Psychology
Cross-cultural psychology is the scientific study of human behavior and mental processes, including both their variability and invariance, under diverse cultural conditions. Through expanding research methodologies to recognize cultural variance in behavior, language, and meaning it seeks to extend and develop psychology.Gielen, U. P., & Roopnarine, J. L. (Eds.). (2016). ''Childhood and adolescence: Cross-cultural perspectives and applications'' (2nd ed.). Santa Barbara, CA: Praeger. Since psychology as an academic discipline was developed largely in North America and Europe, some psychologists became concerned that constructs and phenomena accepted as universal were not as invariant as previously assumed, especially since many attempts to replicate notable experiments in other cultures had varying success.Smith, Peter B., Fischer, R., Vignoles, V. L. & Bond, M. H. (Eds.). (2013). ''Understanding Social Psychology Across Cultures: Engaging with others in a changing world'' (2nd ed.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Future Orientation
In psychology and related fields, future orientation is broadly defined as the extent to which an individual thinks about the future, anticipates future consequences, and plans ahead before acting. Across development, future orientation is particularly important during periods of major changes, for example during the transition from adolescence to adulthood, when youth must make choices about social groups, academic paths, as well as risky behaviors like drug and alcohol use, and sexual activity. Several models have been developed to describe the various factors that combine to impact future orientation. Perspectives on future orientation There are several different ways that future orientation has been observed and measured in research. The most prominent constructs include possible selves, optimism, time perspective, delay discounting. While different in definition, all of these constructs are thought to tap into and impact how people think and plan for the future. Despite the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership (or transactional management) is a type of leadership style that focuses on the exchange of skills, knowledge, resources, or effort between leaders and their subordinates. This leadership style prioritizes individual interests and extrinsic motivation as means to obtain a desired outcome. It relies on a system of penalties and rewards to achieve short-term goals. Although James Downton is generally credited with coining the term "transactional leadership", James MacGregor Burns expanded upon the concept in his influential 1978 book ''Leadership''. * Transactional leadership is characterized by two primary factors: contingent rewards and management-by-exception. Contingent reward concerns the rewards that are granted in recognition of effort and good performance. Management-by-exception maintains the status quo, intervening only when subordinates do not meet acceptable performance levels or when corrective action is required to improve performance. Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leader–member Exchange Theory
The leader–member exchange (LMX) theory is a relationship-based approach to leadership that focuses on the two-way ( dyadic) relationship between leaders and followers. The latest version (2016) of leader–member exchange theory of leadership development explains the growth of vertical dyadic workplace influence and team performance in terms of selection and self-selection of informal apprenticeships in leadership. It suggests that leaders select the best and make offers and members of the team accept or not. Apprentices who complete the program develop strong emotional attachments with their mentor-teacher. This is reflected in their descriptions by both of their relationship as one of mutual respect for competence, trust in character and benevolence toward each other. Those who complete the apprenticeship training are more collaborative, helpful to all team members, more deeply engaged in team activities and contribute more to team health and prosperity. This is seen as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
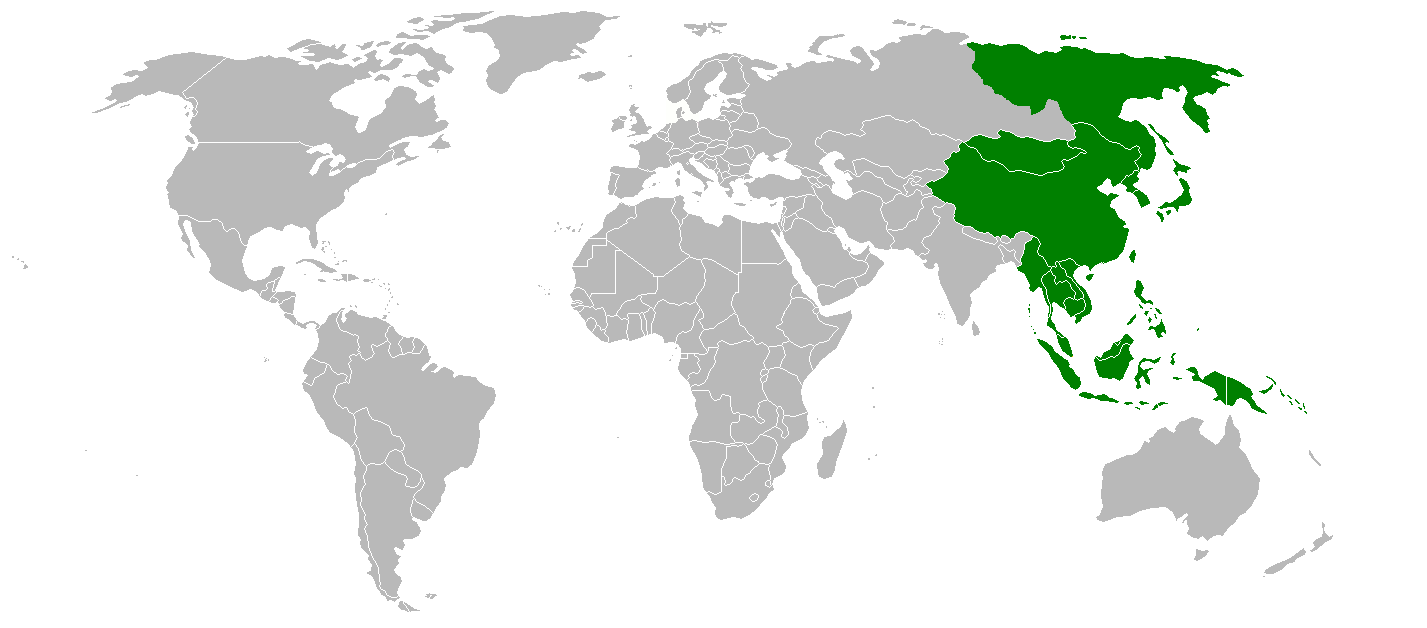
Pacific Asia
Pacific Asia is the region along the east coast of Asia bordering the western Pacific Ocean. It constitutes most of East Asia, Northeast Asia, and Southeast Asia. The region is contested by China, America, and Japan, with India recently engaging as well as part of its Act East policy and overall rise on the world stage. History In ancient times, the central country in much of the region was China, with the Chinese diaspora creating economic integration throughout. Modern era Columbus's 1492 voyage to the Americas marked the beginning of the European expansion which would lead to trans-Pacific contact between Asia and the West. Europeans began colonizing Southeast Asia from the 16th century onwards (though the vast majority was only colonized starting in the mid-19th century), with China also having some of its territory split up between the colonial powers. The Chinese artisans found themselves losing out to Western mass production, with China becoming an insig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geography, and as such it includes countries in both North and South America. Most countries south of the United States tend to be included: Mexico and the countries of Central America, South America and the Caribbean. Commonly, it refers to Hispanic America plus Brazil. Related terms are the narrower Hispanic America, which exclusively refers to Spanish-speaking nations, and the broader Ibero-America, which includes all Iberic countries in the Americas and occasionally European countries like Spain, Portugal and Andorra. Despite being in the same geographical region, English- and Dutch language, Dutch-speaking countries and territories are excluded (Suriname, Guyana, the Falkland Islands, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, Belize, etc.), and French- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social norms, ethical values, Tradition, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, Cultural artifact, artifacts and technology, technologies primarily rooted in History of Europe, European and History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean histories. A broad concept, "Western culture" does not relate to a region with fixed members or geographical confines. It generally refers to the classical era cultures of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome that expanded across the Mediterranean basin and Europe, and later circulated around the world predominantly through colonization and globalization. Historically, scholars have closely associated the idea of Western culture with the classical era of Greco-Roman antiquity. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its Urbanization by country, highly urbanized population is concentrated. The combined Free area of the Republic of China, territories under ROC control consist of list of islands of Taiwan, 168 islands in total covering . The Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area, largest metropolitan area is formed by Taipei (the capital), New Taipei City, and Keelung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries. Tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland China
"Mainland China", also referred to as "the Chinese mainland", is a Geopolitics, geopolitical term defined as the territory under direct administration of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. In addition to the geographical mainland, the geopolitical sense of the term includes islands such as Hainan, Chongming Island, Chongming, and Zhoushan. By convention, territories outside of mainland China include: * Special administrative regions of China, which are regarded as subdivisions of the country, but retain distinct administrative, judicial and economic systems from those on the mainland: ** Hong Kong, formerly a British Hong Kong, British colony ** Macau, formerly a Portuguese Macau, Portuguese colony * Taiwan, along with Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu Islands, Matsu and other minor islands, are collectively known as the Taiwan Area, where has been the major territorial base of the government of the Republic of China (ROC) since 1950. Though the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |