|
Critical Transition
Critical transitions are abrupt shifts in the state of ecosystems, the climate, financial and economic systems or other complex system, complex dynamical systems that may occur when changing conditions pass a critical or bifurcation theory, bifurcation point. As such, they are a particular type of regime shift. Recovery from such shifts may require more than a simple return to the conditions at which a transition occurred, a phenomenon called hysteresis. In addition to natural systems, critical transitions are also studied in psychology, medicine, economics, sociology, military, and several other disciplines. Early-warning signals Critical slow down Significant efforts have been made to identify early-warning signals of critical transitions.Scheffer, M., et al. (2009) Early-warning signals for critical transitions. ''Nature'' 461, 53–59Dakos, V., et al. (2008) Slowing down as an early warning signal for abrupt climate change. ''P Natl Acad Sci Usa'' 105, 14308–14312van Nes, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal Environmental factor, factors. External factors—including climate—control the ecosystem's structure, but are not influenced by it. By contrast, internal factors control and are controlled by ecosystem processes; these include decomposition, the types of species present, root competition, shading, disturbance, and succession. While external factors generally determine which Resource (biology), resource inputs an ecosystem has, their availability within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors. Ecosystems are wikt:dynamic, dynamic, subject to periodic disturbances and always in the process of recovering from past disturbances. The tendency of an ecosystem to remain clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deforestation Of The Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, spanning an area of 3,000,000 km2 (1,200,000 sq mi), is the world's largest rainforest. It encompasses the largest and most biodiverse tropical rainforest on the planet, representing over half of all rainforests. The Amazon region includes the territories of nine nations, with Brazil containing the majority (60%), followed by Peru (13%), Colombia (10%), and smaller portions in Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia (6%), Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. Over one-third of the Amazon rainforest is designated as formally acknowledged indigenous territory, amounting to more than 3,344 territories. Historically, indigenous Amazonian peoples have relied on the forest for various needs such as food, shelter, water, fiber, fuel, and medicines. The forest holds significant cultural and cosmological importance for them. Despite external pressures, deforestation rates are comparatively lower in indigenous territories due to legal land titling initiatives that have red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percolation Theory
In statistical physics and mathematics, percolation theory describes the behavior of a network when nodes or links are added. This is a geometric type of phase transition, since at a critical fraction of addition the network of small, disconnected clusters merge into significantly larger Glossary of graph theory, connected, so-called spanning clusters. The applications of percolation theory to materials science and in many other disciplines are discussed here and in the articles Network theory and Percolation (cognitive psychology). Introduction A representative question (and the etymology, source of the name) is as follows. Assume that some liquid is poured on top of some porosity, porous material. Will the liquid be able to make its way from hole to hole and reach the bottom? This physical question is mathematical model, modelled mathematically as a Grid graph, three-dimensional network of graph (discrete mathematics), vertices, usually called "sites", in which the graph (dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascade Effect (ecology)
An ecological cascade effect is a series of secondary extinctions that are triggered by the primary extinction of a key species in an ecosystem. Secondary extinctions are likely to occur when the threatened species are: dependent on a few specific food sources, mutualistic (dependent on the key species in some way), or forced to coexist with an invasive species that is introduced to the ecosystem. Species introductions to a foreign ecosystem can often devastate entire communities, and even entire ecosystems. These exotic species monopolize the ecosystem's resources, and since they have no natural predators to decrease their growth, they are able to increase indefinitely. Olsen et al. showed that exotic species have caused lake and estuary ecosystems to go through cascade effects due to loss of algae, crayfish, mollusks, fish, amphibians, and birds. However, the principal cause of cascade effects is the loss of top predators as the key species. As a result of this loss, a dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem Collapse
An ecosystem, short for ecological system, is defined as a collection of interacting organisms within a biophysical environment. Ecosystems are never static, and are continually subject to both stabilizing and destabilizing processes. Stabilizing processes allow ecosystems to adequately respond to destabilizing changes, or perturbations, in ecological conditions, or to recover from degradation induced by them: yet, if destabilizing processes become strong enough or fast enough to cross a critical threshold within that ecosystem, often described as an ecological 'tipping point', then an ecosystem collapse (sometimes also termed ecological collapse) occurs. Ecosystem collapse does not mean total disappearance of life from the area, but it does result in the loss of the original ecosystem's defining characteristics, typically including the ecosystem services it may have provided. Collapse of an ecosystem is effectively irreversible more often than not, and even if the reversal is po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Threshold
Ecological threshold is the point at which a relatively small change or disturbance in external conditions causes a rapid change in an ecosystem. When an ecological threshold has been passed, the ecosystem may no longer be able to return to its state by means of its inherent Ecological resilience, resilience. Crossing an ecological threshold often leads to rapid change of ecosystem health. Ecological threshold represent a non-linearity of the responses in ecological or biological systems to environmental impact, pressures caused by human activities or natural processes. Critical load, regime shift, critical transition and tipping point (climatology), tipping point are examples of other closely related terms. Characteristics Thresholds can be characterized as points or as zones. Zone-type thresholds imply a gradual shift or transition from one state to another rather than an abrupt change at a specific point. Ecological thresholds have caught attention because many cases of catast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Resilience
In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or Disturbance (ecology), disturbance by resisting damage and subsequently recovering. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the Introduced species, introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a Ecological threshold, threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. When such thresholds are associated with a critical or bifurcation theory, bifurcation point, these regime shifts may also be referred to as critical transitions. Human activities that adversely affect ecological resilience such as loss of biodiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deforestation And Climate Change
Deforestation is a primary Causes of global warming, contributor to climate change, and climate change affects the health of forests. Land use change, especially in the form of deforestation, is the second largest source of carbon dioxide emissions from human activities, after the burning of fossil fuels. Greenhouse gases are emitted from deforestation during the burning of forest Biomass (ecology), biomass and decomposition of remaining plant material and soil carbon. Global models and national greenhouse gas inventories give similar results for deforestation emissions. , deforestation is responsible for about 11% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon emissions from tropical deforestation are accelerating. When forests grow they are a carbon sink and therefore have potential to Climate change mitigation, mitigate the effects of climate change. Some of the effects of climate change, such as more wildfires, invasive species, and more extreme weather events can lead to more fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipping Points In The Climate System
In Climatology, climate science, a tipping point is a critical threshold that, when crossed, leads to large, accelerating and often irreversible changes in the climate system. If tipping points are crossed, they are likely to have severe impacts on human society and may accelerate global warming. Tipping behavior is found across the climate system, for example in ice sheets, mountain glaciers, Ocean circulation, circulation patterns in the ocean, in ecosystems, and the atmosphere. Examples of tipping points include Permafrost carbon cycle, thawing permafrost, which will release methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, or melting ice sheets and glaciers reducing Earth's albedo, which would warm the planet faster. Thawing permafrost is a threat multiplier because it holds roughly twice as much carbon as the amount currently circulating in the atmosphere. Tipping points are often, but not necessarily, Abrupt climate change, abrupt. For example, with average global warming somewhere bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
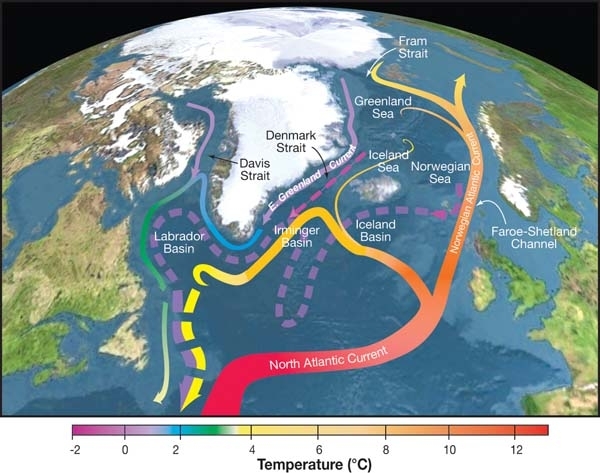
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is the main ocean current system in the Atlantic Ocean.IPCC, 2021Annex VII: Glossary [Matthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.)]. IClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2215–2256, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.022. It is a component of Earth's ocean circulation system and plays an important role in the climate system. The AMOC includes Atlantic currents at the surface and at great depths that are driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrupt Climate Change
An abrupt climate change occurs when the climate system is forced to transition at a rate that is determined by the climate system energy-balance. The transition rate is more rapid than the rate of change of the external forcing, though it may include sudden forcing events such as meteorite impacts. Abrupt climate change therefore is a variation beyond the variability of a climate. Past events include the end of the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse, Younger Dryas, Dansgaard–Oeschger events, Heinrich events and possibly also the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum. The term is also used within the context of climate change to describe sudden climate change that is detectable over the time-scale of a human lifetime. Such a sudden climate change can be the result of feedback loops within the climate system or tipping points in the climate system. Scientists may use different timescales when speaking of ''abrupt events''. For example, the duration of the onset of the Paleoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |