|
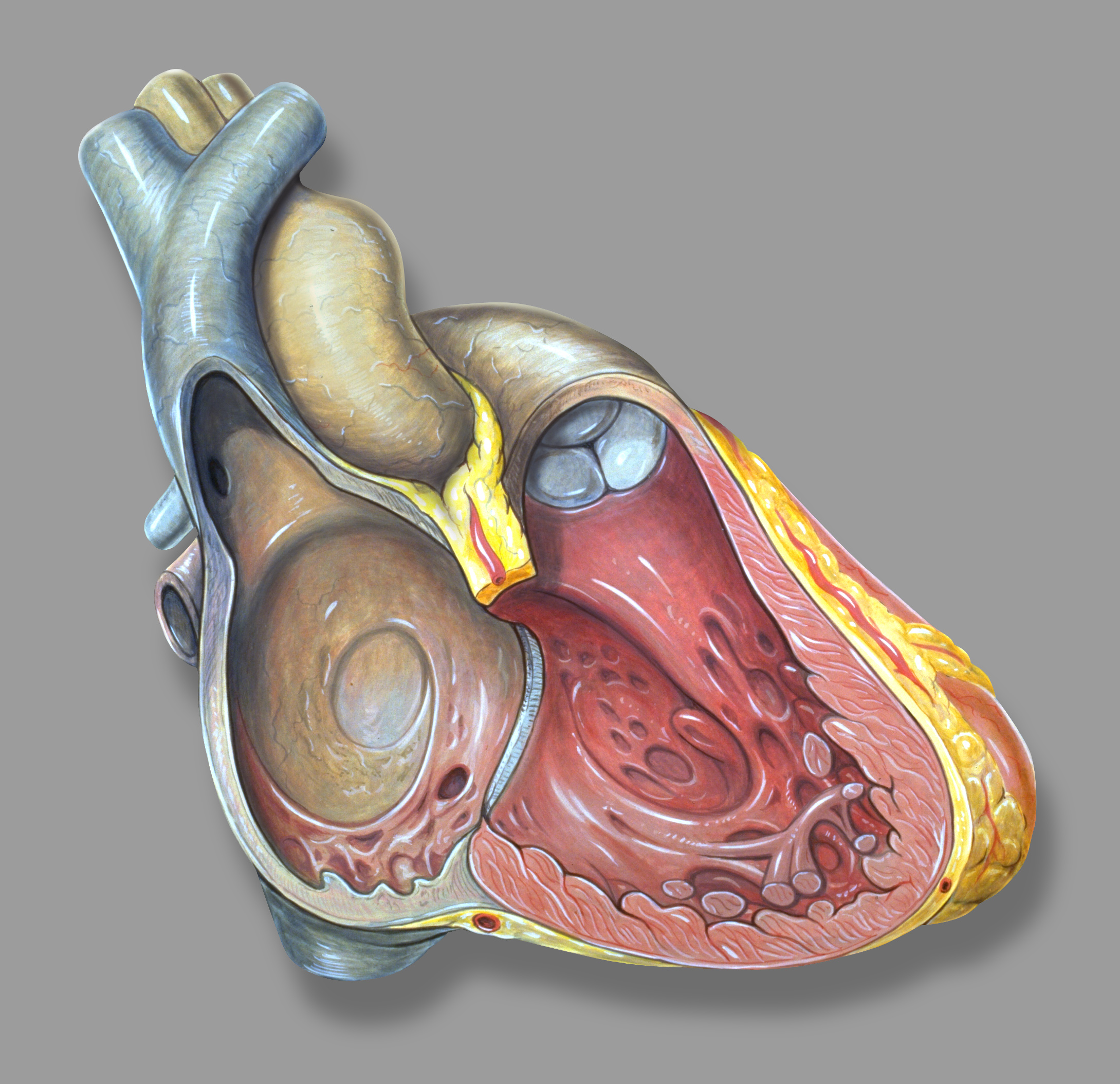
Crista Terminalis
The crista terminalis (also known as the terminal crest, or crista terminalis of His) is a vertical ridge on the posterolateral inner surface of the adult right atrium extending between the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava. The crista terminalis denotes where the junction of the embryologic sinus venosus and the right atrium occurred during embryonic development. It forms a boundary between the rough trabecular portion and the smooth, sinus venosus-derived portion (sinus venarum) of the internal surface of the right atrium. The sinoatrial node is located within the crista terminalis. Anatomy The crista terminalis generally takes the form of a smooth-surfaced, crescent-shaped thickened portion of heart muscle at the opening into the right atrial appendage. It consists of fibromuscular tissue. Features On the external aspect of the right atrium, corresponding to the crista terminalis, is a groove - the terminal sulcus. The crista terminalis provides the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm His Jr
Wilhelm His Jr. (29 December 1863 – 10 November 1934) was a Swiss cardiologist and anatomist, son of Wilhelm His Sr. In 1893, His discovered the bundle of His, the collection of specialized cardiac muscle cells in the heart The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ... that transmits electrical impulses and helps synchronize contraction of the cardiac muscles. Later in life, as a professor of medicine at the University of Berlin, he was one of the first to recognize that "the heartbeat has its origin in the individual cells of heart muscle." Werner–His disease (or trench fever) was also named after him. Angle of His (or incisura cardiaca) was posthumously named after him by Daniel John Cunningham in 1906. Works * ''Die Front der Ärzte'' . Velhagen & Klasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Atrium
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle, the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, previously known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. Auricles in this modern terminology are distinguished by having thicker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vena Cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm. Venous return from the lower half, below the diaphragm, flows through the inferior vena cava. The SVC is located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. It is the typical site of central venous access via a central venous catheter or a peripherally inserted central catheter. Mentions of "the cava" without further specification usually refer to the SVC. Structure The superior vena cava is formed by the left and right brachiocephalic veins, which receive blood from the upper limbs, head and neck, behind the lower border of the first right costal cartilage. It passes vertically downwards behind the first intercostal space and receives the azygos vei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth Lumbar vertebrae, lumbar vertebra. The inferior vena cava is the lower ("anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which carries blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta. It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies Posterior (anatomy), posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Venosus
The sinus venosus is a large quadrangular cavity which precedes the atrium on the venous side of the chordate heart. In mammals, the sinus venosus exists distinctly only in the embryonic heart where it is found between the two venae cavae; in the adult, the sinus venosus becomes incorporated into the wall of the right atrium to form a smooth part called the sinus venarum which is separated from the rest of the atrium by a ridge called the crista terminalis. In most mammals, the sinus venosus also forms the sinoatrial node and the coronary sinus. Development In the embryo, the thin walls of the sinus venosus are connected below with the right ventricle, and medially with the left atrium, but are free in the rest of their extent. It receives blood from the vitelline vein, umbilical vein and common cardinal vein The common cardinal veins, also known as the ducts of Cuvier, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermatozoon). Once fertilized, the ovum becomes a single diploid cell known as a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitosis, mitotic cell division, divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage (embryo), cleavage) and cellular differentiation, leading to development of a multicellular embryo after passing through an organizational checkpoint during mid-embryogenesis. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to the early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages. The main stages of animal embryonic development are as follows: * The zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions (called cleavage) to form a structure called a morula. * The morula develops into a structure called a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Venarum
The sinus venarum (also known as the sinus of the vena cava, or sinus venarum cavarum) is the portion of the right atrium in the adult human heart where the inner surface of the right atrium is smooth, whereas the rest of the inner surface is rough (trabeculated) due to the presence of pectinate muscles. The sinus venarum represents the portion of the adult heart that develops from the right sinus horn of the foetal sinus venosus. The sinus venarum is demarcated from the rest of the right atrium by the crista terminalis The crista terminalis (also known as the terminal crest, or crista terminalis of His) is a vertical ridge on the posterolateral inner surface of the adult right atrium extending between the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava. The cris ... (internally) and the sulcus terminalis (externally). References {{Portal bar, Anatomy Cardiac anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinoatrial Node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an ellipse, oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of Cell (biology), cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approximately 15 millimetre, mm long, 3 mm wide, and 1 mm thick, located directly below and to the side of the superior vena cava. These cells produce an Action potential, electrical impulse known as a cardiac action potential that travels through the electrical conduction system of the heart, causing it to muscle contraction, contract. In a healthy heart, the SA node continuously produces action potentials, setting the rhythm of the heart (sinus rhythm), and so is known as the heart's cardiac pacemaker, natural pacemaker. The rate of action potentials produced (and therefore the heart rate) is influenced by the nerves that supply it. Structure The sinoatrial node is an Ellipse, oval-shaped structure that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Sulcus (heart)
The terminal sulcus is a groove on the outer surface of the right atrium of the heart marking the transition between the sinus venarum cavarum (which has a distinct embryological origin) and the rest of the right atrium (which features pectinate muscles on its inner surface). The terminal sulcus corresponds to the position of the terminal crest on the inner surface of the right atrium. The terminal sulcus (and crest) indicate the position of the sinoatrial node. Anatomy The terminal sulcus extends from the front of the superior vena cava to the front of the inferior vena cava, and represents the line of union of the sinus venosus of the embryo An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ... with the primitive atrium. The superior border of the terminal sulcus designates t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectinate Muscles
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart. Structure Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the part of the wall in front of this, the right atrial appendage. In the left atrium, the pectinate muscles are confined to the inner surface of its atrial appendage. They tend to be fewer and smaller than in the right atrium The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves. .... This is due to the embryological origin of the auricles, which are the true atria. Some sources cite that the pectinate muscles are useful in increasing the power of contraction without increasing heart mass substantially. Pectinate muscles of the atria are different f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Venarum
The sinus venarum (also known as the sinus of the vena cava, or sinus venarum cavarum) is the portion of the right atrium in the adult human heart where the inner surface of the right atrium is smooth, whereas the rest of the inner surface is rough (trabeculated) due to the presence of pectinate muscles. The sinus venarum represents the portion of the adult heart that develops from the right sinus horn of the foetal sinus venosus. The sinus venarum is demarcated from the rest of the right atrium by the crista terminalis The crista terminalis (also known as the terminal crest, or crista terminalis of His) is a vertical ridge on the posterolateral inner surface of the adult right atrium extending between the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava. The cris ... (internally) and the sulcus terminalis (externally). References {{Portal bar, Anatomy Cardiac anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echocardiogram, a cardiac echo, or simply an echo. Echocardiography is routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnorma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |