|
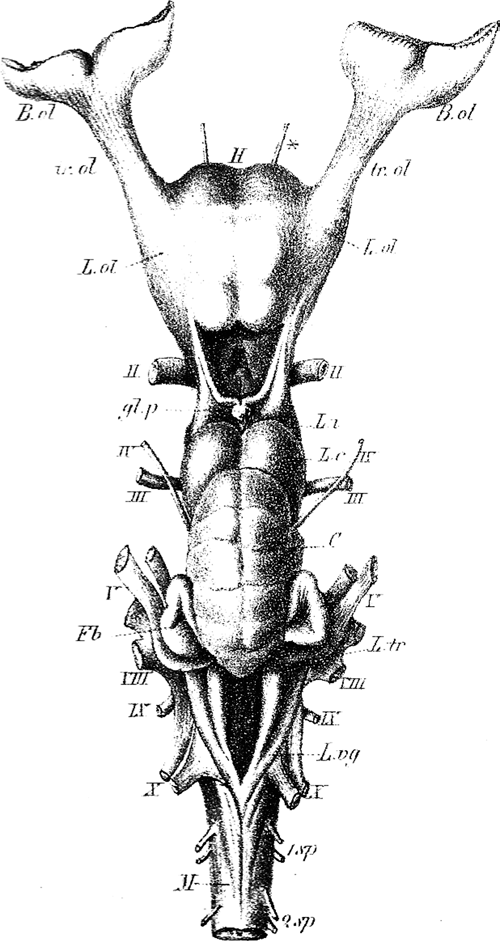
Cranial Nerve Zero
The terminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve zero or simply as CN 0, is a nerve that was not included in the seminal classification of the cranial nerves as CN I through CN XII, but has since been recognized and listed in Terminologia Anatomica, TA2. It was discovered by German scientist Gustav Fritsch in 1878 in the brains of sharks, and was first found in humans in 1913. Studies have confirmed that the terminal nerve is a common finding in the adult human brain. The accepted name of ''terminal nerve'' is due to its entrance in the lamina terminalis regions. The nerve has previously been called cranial nerve XIII, zero nerve, nerve N, and NT. Structure The terminal nerve appears just in front of the other cranial nerves and would, if earlier recognized, have been classified as cranial nerve one. It first appears bilaterally as a microscopic plexus of myelination, unmyelinated peripheral nervous system, peripheral nerve fibers in the subarachnoid space covering the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called Nerve fascicle, fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. The entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are further classified as either Sensory neuron, sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight Gyrus
The portion of the inferior frontal lobe immediately adjacent to the longitudinal fissure (and medial to the medial orbital gyrus and olfactory tract) is named the straight gyrus,(or gyrus rectus) and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface. A specific function for the straight gyrus has not yet been brought to light; however, in males, greater activation of the straight gyrus within the medial orbitofrontal cortex while observing sexually visual pictures has been strongly linked to HSDD (hypoactive sexual desire disorder). Additional images File:Straight gyrus animation small2.gif, Animation. Straight gyrus is depicted as red. File:Straight_gyrus_-_inferior_view.png, Basal surface of cerebrum. Straight gyrus is shown in red. File:Gray743 straight gyrus.png, Coronal section of human brain. Straight gyrus depicted as yellow in center bottom. File:Slide2STE.JPG, Cerebrum. Optic and olfactory nerves.Inferior view. Deep dissection. File:Slide2ZEB.JPG, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odor
An odor (American English) or odour ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive via their olfactory system. While ''smell'' can refer to pleasant and unpleasant odors, the terms ''scent'', ''aroma'', and ''fragrance'' are usually reserved for pleasant-smelling odors and are frequently used in the food and cosmetic industry to describe floral scents or to refer to perfumes. Odor physiology Sense of smell The perception of odors, or sense of smell, is mediated by the olfactory nerve. The olfactory receptor (OR) cells are neurons present in the olfactory epithelium, which is a small patch of tissue at the back of the nasal cavity. There are millions of olfactory receptor neurons that act as sensory signaling cells. Each neuron has cilia in direct contact with the air. Odorous molecules bind to receptor pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Bulb
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and the hippocampus where it plays a role in emotion, memory and learning. The bulb is divided into two distinct structures: the main olfactory bulb and the accessory olfactory bulb. The main olfactory bulb connects to the amygdala via the piriform cortex of the primary olfactory cortex and directly projects from the main olfactory bulb to specific amygdala areas. The accessory olfactory bulb resides on the dorsal-posterior region of the main olfactory bulb and forms a parallel pathway. Destruction of the olfactory bulb results in ipsilateral anosmia, while irritative lesions of the uncus can result in olfactory and gustatory hallucinations. Structure In most vertebrates, the olfactory bulb is the most rostral (forward) part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Nerve
The olfactory nerve, also known as the first cranial nerve, cranial nerve I, or simply CN I, is a cranial nerve that contains sensory nerve fibers relating to the sense of smell. The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory receptor neurons transmit nerve impulses about odors to the central nervous system (olfaction). Derived from the embryonic nasal placode, the olfactory nerve is somewhat unusual among cranial nerves because it is capable of some regeneration if damaged. The olfactory nerve is sensory in nature and originates on the olfactory mucosa in the upper part of the nasal cavity. From the olfactory mucosa, the nerve (actually many small nerve fascicles) travels up through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone to reach the surface of the brain. Here the fascicles enter the olfactory bulb and synapse there; from the bulbs (one on each side) the olfactory information is transmitted into the brain via the olfactory tract. The fascicles of the olfactory nerve are not v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Development
Prenatal development () involves the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth. The term "prenate" is used to describe an unborn offspring at any stage of gestation. In human pregnancy, prenatal development is also called antenatal development. The development of the human embryo follows fertilization, and continues as fetal development. By the end of the tenth week of gestational age, the embryo has acquired its basic form and is referred to as a fetus. The next period is that of fetal development where many organs become fully developed. This fetal period is described both topically (by organ) and chronologically (by time) with major occurrences being listed by gestational age. The very early stages of embryonic development are the same in all mammals, but later stages of development, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomeronasal Organ
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) in various tetrapods. The name is derived from the fact that it lies adjacent to the unpaired vomer bone (from Latin , for its shape) in the nasal septum. It is present and functional in all snakes and lizards, and in many mammals, including cats, dogs, cattle, pigs, and some primates. Humans may have physical remnants of a VNO, but it is vestigial and non-functional. The VNO contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons which have receptors that detect specific non-volatile (liquid) organic compounds which are conveyed to them from the environment. These compounds emanate from prey, predators, and the compounds called sex pheromones from potential mates. Activation of the VNO triggers an appropriate behavioral response to the presence of one of these th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Nerve
The olfactory nerve, also known as the first cranial nerve, cranial nerve I, or simply CN I, is a cranial nerve that contains sensory nerve fibers relating to the sense of smell. The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory receptor neurons transmit nerve impulses about odors to the central nervous system (olfaction). Derived from the embryonic nasal placode, the olfactory nerve is somewhat unusual among cranial nerves because it is capable of some regeneration if damaged. The olfactory nerve is sensory in nature and originates on the olfactory mucosa in the upper part of the nasal cavity. From the olfactory mucosa, the nerve (actually many small nerve fascicles) travels up through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone to reach the surface of the brain. Here the fascicles enter the olfactory bulb and synapse there; from the bulbs (one on each side) the olfactory information is transmitted into the brain via the olfactory tract. The fascicles of the olfactory nerve are not v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory System
The olfactory system, is the sensory nervous system, sensory system used for the sense of smell (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses directly associated with specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system and an accessory olfactory system. The main olfactory system detects airborne substances, while the accessory system senses fluid-phase stimuli. The senses of smell and taste (gustatory system) are often referred to together as the chemosensory system, because they both give the brain information about the chemical composition of objects through a process called transduction (physiology), transduction. Structure Peripheral The peripheral olfactory system consists mainly of the nostrils, ethmoid bone, nasal cavity, and the olfactory epithelium (layers of thin tissue covered in mucus that line the nasal cavity). The primary components of the layers of epithelial tissue are the mucous membranes, olfactory glands, olfactory receptor neurons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Danionidae of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often called a " tropical fish" although it is both tropical and subtropical). The zebrafish is an important and widely used vertebrate model organism in scientific research, particularly developmental biology, but also gene function, oncology, teratology, and drug development, in particular pre-clinical development. It is also notable for its regenerative abilities, and has been modified by researchers to produce many transgenic strains. Taxonomy The zebrafish is a derived member of the genus '' Brachydanio'', of the family Cyprinidae. It has a sister-group relationship with '' Danio aesculapii''. Zebrafish are also closely related to the genus '' Devario'', as demonstrated by a phylogenetic tree of close species. Distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab. Dissection has been used for centuries to explore anatomy. Objections to the use of cadavers have led to the use of alternatives including virtual dissection of computational anatomy, computer models. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |