|
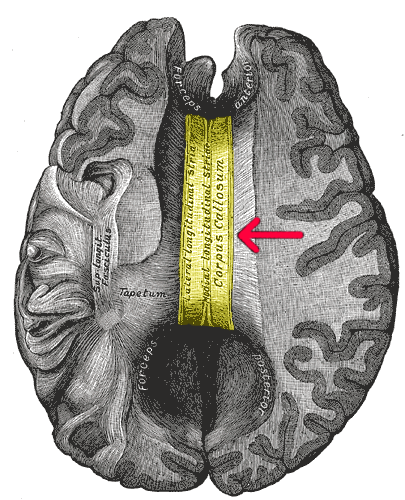
Corpus Callosotomy
A corpus callosotomy () is a palliative surgical procedure for the treatment of medically refractory epilepsy. The procedure was first performed in 1940 by William P. van Wagenen. In this procedure, the corpus callosum is cut through, in an effort to limit the spread of epileptic activity between the two halves of the brain. Although the corpus callosum is the largest white matter tract connecting the hemispheres, some limited interhemispheric communication is still possible via the anterior and posterior commissures. After the operation, however, the brain often struggles to send messages between hemispheres, which can lead to side effects such as speech irregularities, disconnection syndrome, and alien hand syndrome. History The first instances of corpus callosotomy were performed in the 1940s by William P. van Wagenen, who co-founded and served as president of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Attempting to treat epilepsy, van Wagenen studied and publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gray 733-emphasizing-corpus-callosum
Grey (more frequent in British English) or gray (more frequent in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning that it has no chroma. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash, and of lead. The first recorded use of ''grey'' as a color name in the English language was in 700 CE.Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 196 ''Grey'' is the dominant spelling in European and Commonwealth English, while ''gray'' is more common in American English; however, both spellings are valid in both varieties of English. In Europe and North America, surveys show that gray is the color most commonly associated with neutrality, conformity, boredom, uncertainty, old age, indifference, and modesty. Only one percent of respondents chose it as their favorite color. Etymology ''Grey'' comes from the Middle English or , from the Old English , and is related to the Dutch and Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Attention Deficit Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and Developmental psychology, developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction. Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as time management, Cognitive inhibition, inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks, collectively predisposing to a diminished Quality of life (healthcare), quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy. As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other mental disorders as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment. While ADHD involves a lack of su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neurolinguistics
Neurolinguistics is the study of Nervous system, neural mechanisms in the human brain that control the comprehension, production, and acquisition of language. As an interdisciplinary field, neurolinguistics draws methods and theories from fields such as neuroscience, linguistics, cognitive science, communication disorders and neuropsychology. Researchers are drawn to the field from a variety of backgrounds, bringing along a variety of experimental techniques as well as widely varying theoretical perspectives. Much work in neurolinguistics is informed by models in psycholinguistics and theoretical linguistics, and is focused on investigating how the brain can implement the processes that theoretical and psycholinguistics propose are necessary in producing and comprehending language. Neurolinguists study the physiological mechanisms by which the brain processes information related to language, and evaluate linguistic and psycholinguistic theories, using aphasiology, brain imagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Volition (psychology)
Volition, also known as will or conation, is the cognitive process by which an individual decides on and commits to a particular course of action. It is defined as purposive striving and is one of the primary human psychological functions. Others include affect (feeling or emotion), motivation (goals and expectations), and cognition (thinking). Volitional processes can be applied consciously or they can be automatized as habits over time. Most modern conceptions of volition address it as a process of conscious action control which becomes automatized (e.g. see Heckhausen and Kuhl; Gollwitzer; Boekaerts and Corno). Overview Many researchers treat ''volition'' and '' willpower'' as scientific and colloquial terms (respectively) for the same process. When a person ''makes up their mind'' to do a thing, that state is termed 'immanent volition'. When we put forth any particular act of choice, that act is called an emanant, executive, or imperative volition. When an immanent or sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multisensory Integration
Multisensory integration, also known as multimodal integration, is the study of how information from the different sensory modality, sensory modalities (such as sight, sound, touch, smell, self-motion, and taste) may be integrated by the nervous system. A coherent representation of objects combining modalities enables animals to have meaningful perceptual experiences. Indeed, multisensory integration is central to adaptive behavior because it allows animals to perceive a world of coherent perceptual entities. Multisensory integration also deals with how different sensory modalities interact with one another and alter each other's processing. General introduction Multimodal perception is how animals form coherent, valid, and robust perception by sensory processing, processing sensory stimuli from various modalities. Surrounded by multiple objects and receiving multiple sensory stimulations, the brain is faced with the decision of how to categorize the stimuli resulting from different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cerebral Hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of axon, nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix (neuroanatomy), fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions. There are three known poles of the cerebral hemispheres: the ''occipital lobe, occipital pole'', the ''frontal lobe, frontal pole'', and the ''temporal lobe, temporal pole''. The central sulcus is a prominent fissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called Nerve fascicle, fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. The entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are further classified as either Sensory neuron, sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intellectual Disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability (in the United Kingdom), and formerly mental retardation (in the United States), Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010).Archive is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant impairment in intellectual and adaptive functioning that is first apparent during childhood. Children with intellectual disabilities typically have an intelligence quotient (IQ) below 70 and deficits in at least two adaptive behaviors that affect everyday living. According to the DSM-5, intellectual functions include reasoning, problem solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning from experience. Deficits in these functions must be confirmed by clinical evaluation and individualized standard IQ testing. On the other hand, adaptive behaviors include the social, developmental, and practical skills people learn to perform tasks in their everyday lives. Deficits in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition (a situation or factor) that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain treatment. Absolute contraindications are contraindications for which there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action (that is, overriding the prohibition). For example: * Children and teenagers with viral infections should not be given aspirin because of the risk of Reye syndrome. * A person with an anaphylactic food allergy should never eat the food to which they are allergic. * A person with hemochromatosis should not be administered iron preparations. * Some medications are so teratogenic that they are absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy; examples include thalidomide and isotretinoin. Relative contraindications are contraindications for circumstances in which the patient is at hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neurological Disease
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique diagnosis, treatment, and patient care challenges. At their core, they represent disruptions to the intricate communication systems within the nervous system, stemming from genetic predispositions, environmental factors, infections, structural abnormalities, or degenerative processes. The impact of neurological disorders is profound and far-reaching. Conditions like epilepsy create recurring seizures through abnormal electrical brain activity, while multiple sclerosis damages the protective myelin covering of nerve fibers, interrupting communication between the brain and body. Parkinson's disease progressively affects movement through the loss of dopamine-producing nerve cells, and strokes can cause immediate and potentially permanent neurological damage by interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Human Cranium
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate. In the human, the skull comprises two prominent parts: the neurocranium and the facial skeleton, which evolved from the first pharyngeal arch. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and, in fish, specialized tactile organs such as barbels near the mouth. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones and ossicles, which is made up of a number of fused flat and irregular bones. The cranial bones are joined at firm fibrous junctions called sutures and contains many foramina, fossae, processes, and sinuses. In zoology, the openings in the skull are called fenestrae, the most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |