|
Copy-editing
Copy editing (also known as copyediting and manuscript editing) is the process of revising written material (" copy") to improve quality and readability, as well as ensuring that a text is free of errors in grammar, style, and accuracy. ''The Chicago Manual of Style'' states that manuscript editing encompasses "simple mechanical corrections (mechanical editing) through sentence-level interventions (linear editing) to substantial remedial work on literary style and clarity, disorganized passages, baggy prose, muddled tables and figures, and the like (substantive editing)". In the context of print publication, copy editing is done before typesetting and again before proofreading. Outside traditional book and journal publishing, the term "copy editing" is used more broadly, and is sometimes referred to as proofreading; the term sometimes encompasses additional tasks. Although copy editors are generally expected to make simple revisions to smooth awkward passages, they do not have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Style Guides
A style guide, or style manual, is a set of standards for the writing and design of documents, either for general use or for a specific publication, organization or field. The implementation of a style guide provides uniformity in style and formatting within a document and across multiple documents. A set of standards for a specific organization is often known as an "in-house style". Style guides are common for general and specialized use, for the general reading and writing audience, and for students and scholars of medicine, journalism, law, and various academic disciplines. International Several basic style guides for technical and scientific communication have been defined by international standards organizations. These are often used as elements of and refined in more specialized style guides that are specific to a subject, region, or organization. Some examples are: * EN 15038, Annex DEuropean Standard for Translation Services (withdrawn) * ISO 8Presentation of periodic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
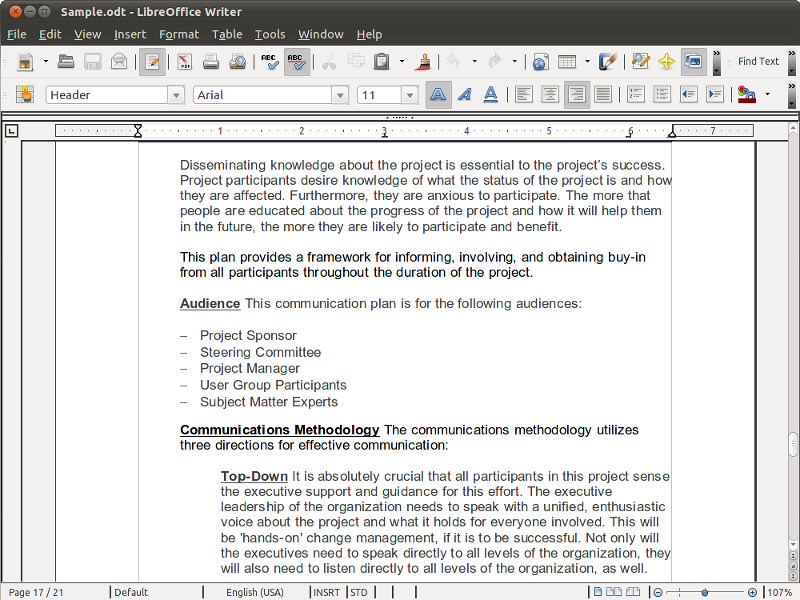
Example Of Copyedited Manuscript
Example may refer to: * ''exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, and example.edu: second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS Example (P165), HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * The Example (comics), ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * Example (album), ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample, a district of Barcelona with di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, mostly of writing and images. Modern books are typically composed of many pages bound together and protected by a cover, what is known as the '' codex'' format; older formats include the scroll and the tablet. As a conceptual object, a ''book'' often refers to a written work of substantial length by one or more authors, which may also be distributed digitally as an electronic book ( ebook). These kinds of works can be broadly classified into fiction (containing invented content, often narratives) and non-fiction (containing content intended as factual truth). But a physical book may not contain a written work: for example, it may contain ''only'' drawings, engravings, photographs, sheet music, puzzles, or removable content like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galley Proof
In printing and publishing, proofs are the preliminary versions of publications meant for review by authors, editors, and proofreaders, often with extra-wide margins. Galley proofs may be uncut and unbound, or in some cases electronically transmitted. They are created for proofreading and copyediting purposes, but may also be used for promotional and review purposes. Historical galley proofs Proof, in the typographical sense, is a term that dates to around 1600. The primary goal of proofing is to create a tool for verification that the job is accurate separate from the pages produced on the press. All needed or suggested changes are physically marked on paper proofs or electronically marked on electronic proofs by the author, editor, and proofreaders. The compositor, typesetter, or printer receives the edited copies, corrects and re-arranges the type or the pagination, and arranges for the press workers to print the final or published copies. Galley proofs or galleys ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading
In typography, leading ( ) is the space between adjacent lines of type; the exact definition varies. In hand typesetting, leading is the thin strips of lead (or aluminium) that were inserted between lines of type in the composing stick to increase the vertical distance between them. The thickness of the strip is called leading and is equal to the difference between the size of the type and the distance from one baseline (typography), baseline to the next. For instance, given a type size of 10 Point (typography), points and a distance between baselines of 12 points, the leading would be 2 points. The term is still used in modern page layout, page-layout software such as QuarkXPress, the Affinity Suite, and Adobe InDesign. Consumer-oriented word-processing software often talks of line spacing or, more accurately, interline spacing. Origins The word comes from lead strips that were put between set lines of lead type, hence the pronunciation "ledding" and not "lee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Processor
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features. Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and desktop computers. The functions of a word processor program are typically between those of a simple text editor and a desktop publishing program; Many word processing programs have gained advanced features over time providing similar functionality to desktop publishing programs. Common word processor programs include LibreOffice Writer, Google Docs and Microsoft Word. Background Word processors developed from mechanical machines, later merging with computer technology. The history of word processing is the story of the gradual automation of the physical aspects of writing and editing, and then to the refinement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spell Checker
In software, a spell checker (or spelling checker or spell check) is a software feature that checks for misspellings in a text. Spell-checking features are often embedded in software or services, such as a word processor, email client, electronic dictionary, or search engine. Design A basic spell checker carries out the following processes: * It scans the text and extracts the words contained in it. * It then compares each word with a known list of correctly spelled words (i.e. a dictionary). This might contain just a list of words, or it might also contain additional information, such as hyphenation points or lexical and grammatical attributes. * An additional step is a language-dependent algorithm for handling morphology. Even for a lightly inflected language like English, the spell checker will need to consider different forms of the same word, such as plurals, verbal forms, contractions, and possessives. For many other languages, such as those featuring agglutination and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Question
A question is an utterance which serves as a request for information. Questions are sometimes distinguished from interrogatives, which are the grammar, grammatical forms, typically used to express them. Rhetorical questions, for instance, are interrogative in form but may not be considered wiktionary:bona fide, bona fide questions, as they are not expected to be answered. Questions come in a number of varieties. For instance; ''Polar questions'' are those such as the English language, English example "Is this a polar question?", which can be answered with yes and no, "yes" or "no". ''Alternative questions'' such as "Is this a polar question, or an alternative question?" present a list of possibilities to choose from. ''Open-ended question, Open questions'' such as "What kind of question is this?" allow many possible resolutions. Questions are widely studied in linguistics and philosophy of language. In the subfield of pragmatics, questions are regarded as illocutionary acts whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reprint
A reprint is a re-publication of material that has already been previously published. The term ''reprint'' is used with slightly different meanings in several fields. Academic publishing In academic publishing, offprints, sometimes also known as reprints, are bulk reproductions of individual articles previously published in academic journals.Carter, John, and Nicolas Barker. (2004) ''ABC for Book Collectors''. 8th edition. New Castle, DE: Oak Knoll. p. 153. Offprints from scientific, technical, and medical (STM) journals are used by researchers in some fields to generate awareness among audiences who don't subscribe to the journal e.g. physicians, consumers, investors etc. They are usually ordered directly from the publisher of the journal. However, some third-party service providers also exist, serving as an intermediary that provides a single source of offprints from multiple publishers. Book publishing In book publishing, if a reprint has been revised from an earlier versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States and fair dealings doctrine in the United Kingdom. Some jurisdictions require "fixing" copyrighted works in a tangible form. It is often shared among multiple authors, each of whom holds a set of rights to use or license the work, and who are commonly referred to as rights holders. These rights normally include reproduction, control over derivative works, distribution, public performance, and moral rights such as attribution. Copyrights can be granted by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliography
Bibliography (from and ), as a discipline, is traditionally the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects; in this sense, it is also known as bibliology (from ). English author and bibliographer John Carter describes ''bibliography'' as a word having two senses: one, a list of books for further study or of works consulted by an author (or enumerative bibliography); the other one, applicable for collectors, is "the study of books as physical objects" and "the systematic description of books as objects" (or descriptive bibliography). Etymology The word was used by Greek writers in the first three centuries CE to mean the copying of books by hand. In the 12th century, the word started being used for "the intellectual activity of composing books." The 17th century then saw the emergence of the modern meaning, that of description of books. Currently, the field of bibliography has expanded to include studies that consider the book as a material object. Bibliography, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Contents
A table of contents (or simply contents, abbreviated as TOC), is a list usually part of the Book design#Front matter, front matter preceding the main text of a book or other written work containing the titles of the text's sections, sometimes with descriptions. History Pliny the Elder credits Quintus Valerius Soranus (d. 82 BC) as the first author to provide a table of contents to help readers navigate a lengthy work. Classical Origins The Roman writer Quintus Valerius Soranus (d. 82 BCE) is credited as the first to attach a list of contents to a written work, according to the Roman historian Pliny the Elder. In his ''Natural History'', Pliny writes: "Soranus was the first to include a list of his book’s chapters to help the reader understand its content."Pliny's own table of contents for his encyclopedic Natural History (Pliny), ''Historia naturalis'' ("Natural History") may be viewed onlinin Latinanin English(following dedication). In Indian and Chinese Civilizations In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |