|
Continuous Modelling
Continuous modelling is the mathematical practice of applying a model A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided in ... to continuous data (data which has a potentially infinite number, and divisibility, of attributes). They often use differential equations and are converse to discrete modelling. Modelling is generally broken down into several steps: * Making assumptions about the data: The modeller decides what is influencing the data and what can be safely ignored. * Making equations to fit the assumptions. * Solving the equations. * Verifying the results: Various statistical tests are applied to the data and the model and compared. * If the model passes the verification progress, putting it into practice. * If the model fails the verification progress, altering it and subje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical modeling''. Mathematical models are used in applied mathematics and in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). It can also be taught as a subject in its own right. The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
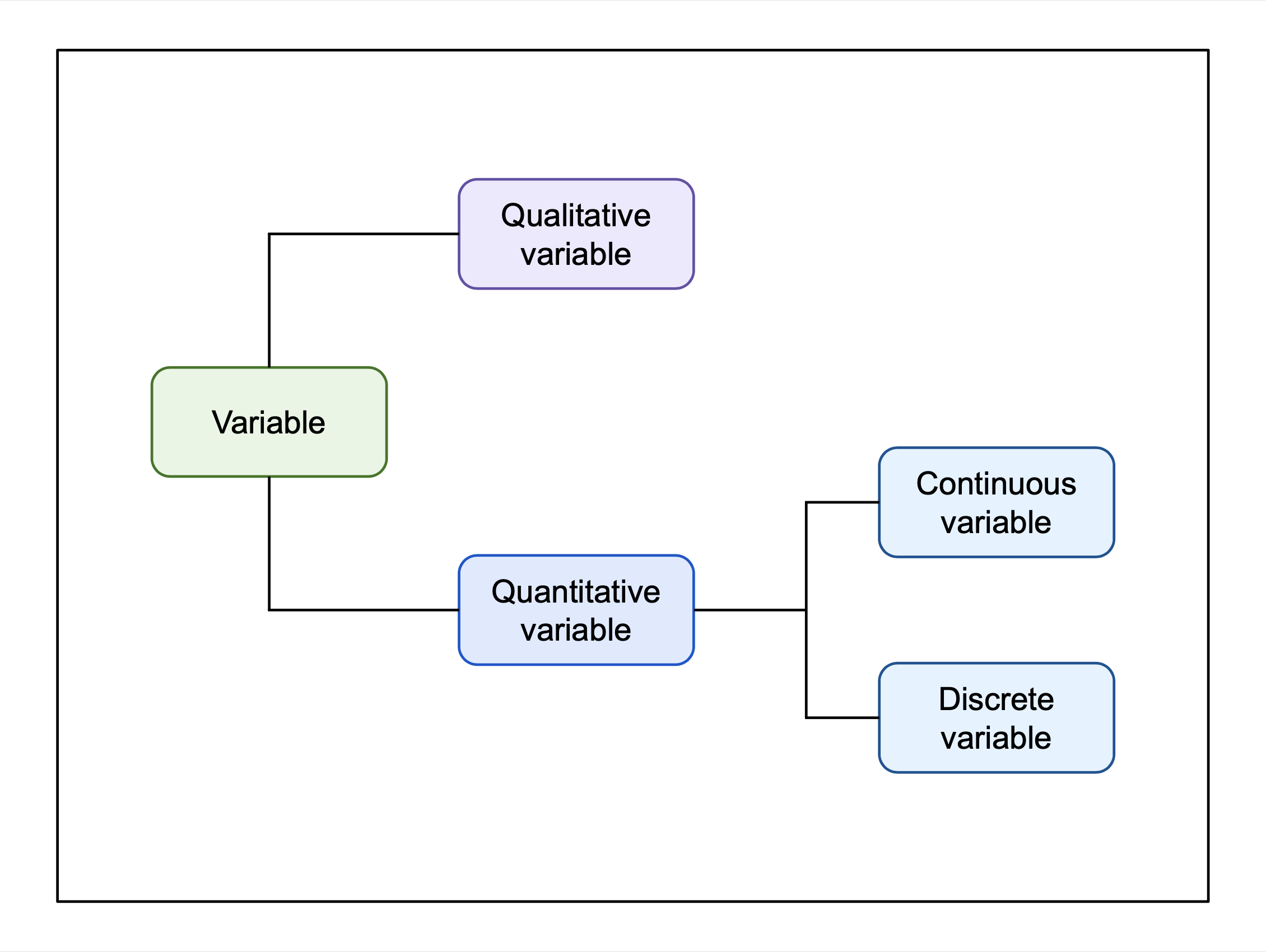
Continuous Variable
In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable (mathematics), variable may be continuous or discrete. If it can take on two real number, real values and all the values between them, the variable is continuous in that Interval (mathematics), interval. If it can take on a value such that there is a non-infinitesimal gap on each side of it containing no values that the variable can take on, then it is discrete around that value. In some contexts, a variable can be discrete in some ranges of the number line and continuous in others. In statistics, continuous and discrete variables are distinct Statistical data type, statistical data types which are described with different probability distributions. Continuous variable A continuous variable is a variable such that there are possible values between any two values. For example, a variable over a non-empty range of the real numbers is continuous if it can take on any value in that range. Methods of calculus are often used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Modelling
Discrete modelling is the discrete analogue of continuous modelling. In discrete modelling, formulae are fit to discrete data—data that could potentially take on only a countable set of values, such as the integers, and which are not infinitely divisible. A common method in this form of modelling is to use recurrence relations. Discrete time In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled. Discrete time Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "poi ... models are well-suited for step-by-step computer simulations and are often appropriate for modelling experimental data, which is typically collected in discrete form. References {{Mathapplied-stub Applied mathematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |