|
Contactor
A contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching an electrical power circuit. A contactor is typically controlled by a circuit which has a much lower power level than the switched circuit, such as a 24-volt coil electromagnet controlling a 230-volt motor switch. Unlike general-purpose relays, contactors are designed to be directly connected to high-current load devices. Relays tend to be of lower capacity and are usually designed for both ''normally closed'' and ''normally open'' applications. Devices switching more than 15 amperes or in circuits rated more than a few kilowatts are usually called contactors. Apart from optional auxiliary low-current contacts, contactors are almost exclusively fitted with normally open ("form A") contacts. Unlike relays, contactors are designed with features to control and suppress the arc produced when interrupting heavy motor currents. Unlike a circuit breaker, a contactor is not intended to interrupt a short circuit curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relay
A relay Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off A relay is an electrically operated switch. It has a set of input terminals for one or more control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof. Relays are used to control a circuit by an independent low-power signal and to control several circuits by one signal. They were first used in long-distance telegraph circuits as signal repeaters that transmit a refreshed copy of the incoming signal onto another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations. The traditional electromechanical relay uses an electromagnet to close or open the contacts, but relays using other operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
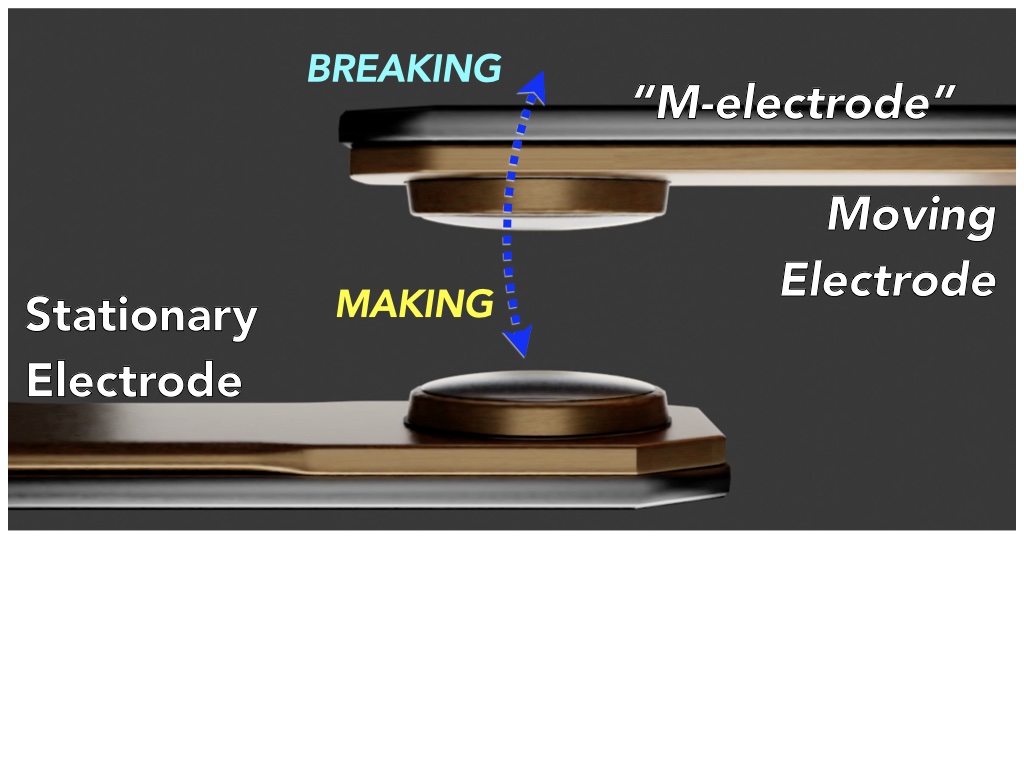
Contact Protection
Contact protection methods are designed to mitigate the wear and degradation occurring during the normal use of contacts within an electromechanical switch, relay or contactor and thus avoid an excessive increase in contact resistance or switch failure. Contact wear A “contact” is a pair of electrodes (typically, one moving; one stationary) designed to control electricity. Electromechanical switches, relays, and contactors “turn power on” when the moving electrode makes contact with the stationary electrode to carry current. Conversely, they “turn power off” when the moving electrode breaks contact and the resulting arc plasma stops burning as the dielectric gap widens sufficiently to prevent current flow. Power relays and contactors have two primary life expectancy ratings: “mechanical life” is based on operating either without current or below the wetting current (i.e., “Dry”) and “electrical life” is based on operating above the wetting current (i.e., “W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utilization Categories
In electrical engineering utilization categories are defined by IEC standards and indicate the type of electrical load and duty cycle of the loads to ease selection of contactors and relays. Definition The utilization categories category for low-voltage switchgear defines the characteristic operating conditions for switchgear such as contactors, circuit-breakers, circuit-breaker-fuse units, contactor relays, etc. These devices are dimensioned for different electrical loads and for different operating conditions. The characteristic of the load to be switched or controlled determines the requirements for the switchgear and its correct selection for the intended application. In particular, the stress on the switching path caused by current and voltage during switching on and off is of enormous importance. For example, the switch-on and switch-off current at resistance load corresponds to the continuous operating current, while, for example, squirrel cage motors consumes multiple of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
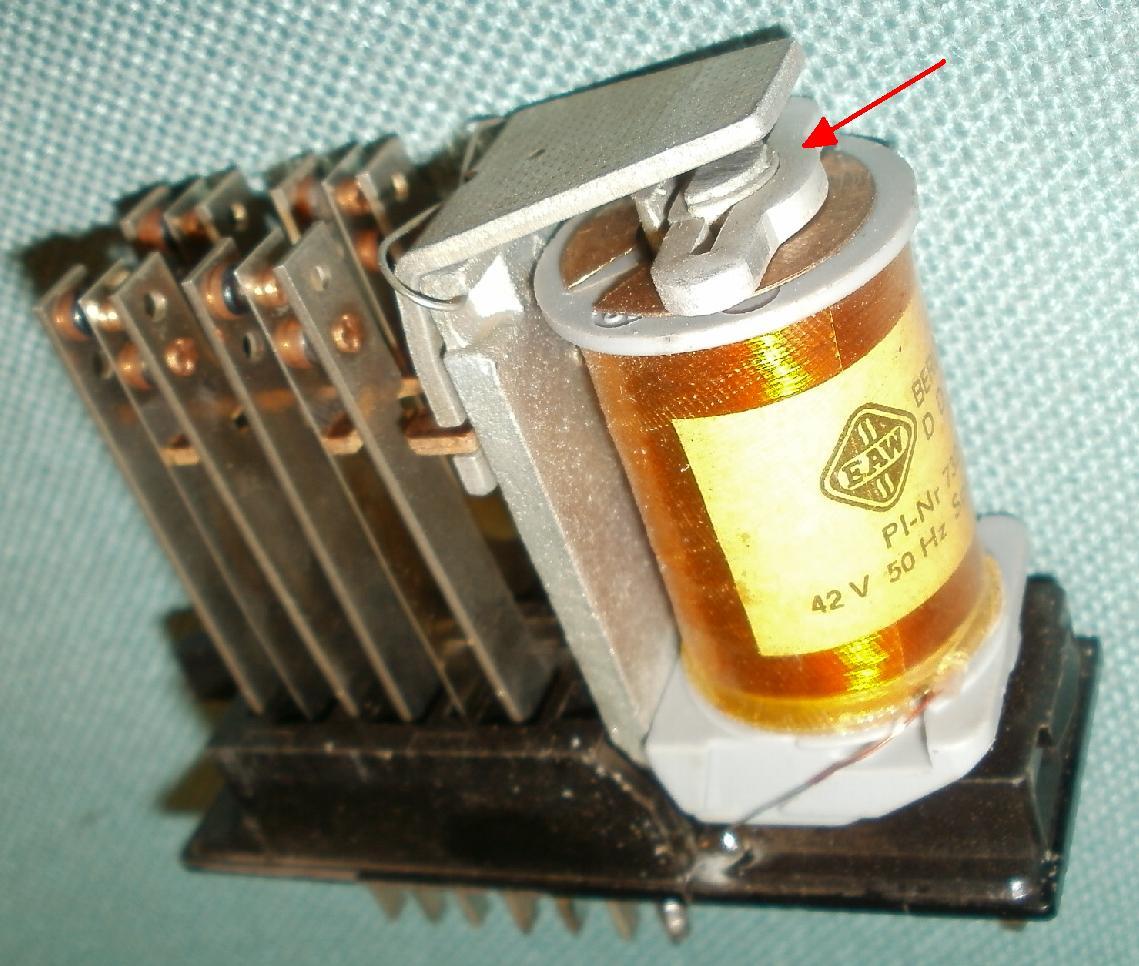
Shading Coil
A shading coil or shading ring (Also called Frager spire or Frager coil) is one or more turns of electrical conductor (usually copper or aluminum) located in the face of the magnet assembly or armature of an alternating current solenoid. The alternating current in the energized primary coil induces an alternating current in the shading coil. This induced current creates an auxiliary magnetic flux which is 90 degrees out of phase from the magnetic flux created by the primary coil. Because of the 90 degree phase difference between the current in the shading coil and the current in the primary coil, the shading coil maintains a magnetic flux and hence a force between the armature and the assembly while the current in the primary coil crosses zero. Without this shading ring, the armature would tend to open each time the main flux goes through zero and create noise, heat and mechanical damages on the magnet faces, so it reduces bouncing or chatter of relay or power contacts. Shad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
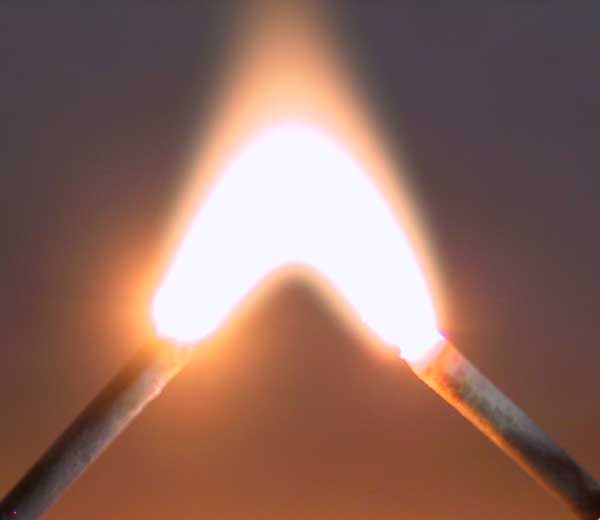
Electric Arc
An electric arc (or arc discharge) is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The electric current, current through a normally Electrical conductance, nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma (physics), plasma, which may produce visible light. An arc discharge is initiated either by thermionic emission or by field emission. After initiation, the arc relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp". Techniques for arc suppression can be used to reduce the duration or likelihood of arc formation. In the late 19th century, Arc lamp, electric arc lighting was in wide use for Street light#Arc lamps, public lighting. Some low-pressure electric arcs are used in many applications. For example, fluorescent lamp, fluorescent tubes, mercury, sodium, and met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Contacts
An electrical contact is an electrical circuit component found in electrical switches, relays, connectors and circuit breakers. Each contact is a piece of electrically conductive material, typically metal. When a pair of contacts touch, they can pass an electrical current with a certain contact resistance, dependent on surface structure, surface chemistry and contact time; when the pair is separated by an insulating gap, then the pair does not pass a current. When the contacts touch, the switch is ''closed''; when the contacts are separated, the switch is ''open''. The gap must be an insulating medium, such as air, vacuum, oil, SF6. Contacts may be operated by humans in push-buttons and switches, by mechanical pressure in sensors or machine cams, and electromechanically in relays. The surfaces where contacts touch are usually composed of metals such as silver or gold alloysMatsushita Electronics, "Relay Techninal Information: Definition of Relay Terminology", § Contact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device Under Test
A device under test (DUT), also known as equipment under test (EUT) and unit under test (UUT), is a manufactured product undergoing testing, either at first manufacture or later during its life cycle as part of ongoing functional testing and calibration checks. This can include a test after repair to establish that the product is performing in accordance with the original product specification. Electronics testing In the electronics industry a DUT is any electronic assembly under test. For example, cell phones coming off of an assembly line may be given a final test in the same way as the individual chips were earlier tested. Each cell phone under test is, briefly, the DUT. For circuit boards, the DUT is often connected to the test equipment using a bed of nails tester of pogo pins. Semiconductor testing In semiconductor testing, the device under test is a die on a wafer or the resulting packaged part. A connection system is used, connecting the part to automatic or manual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
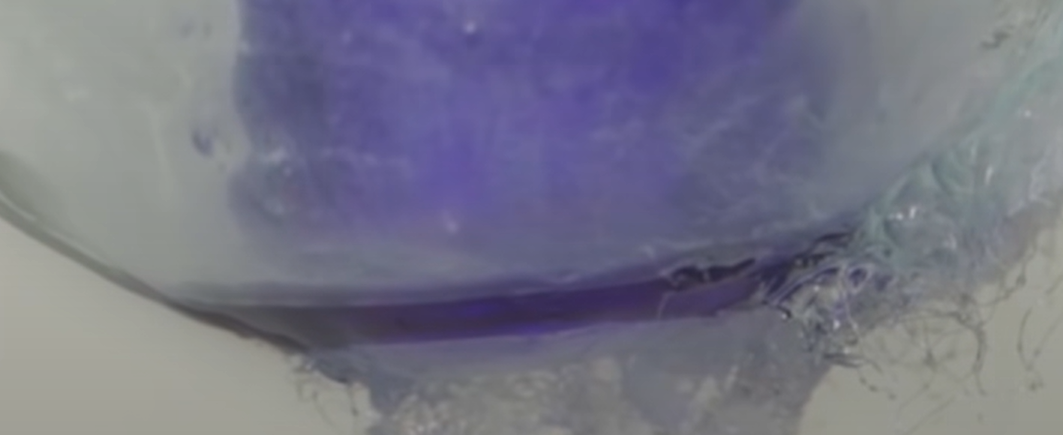
Ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the atmosphere, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odor is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 chemical structure, structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetism, diamagnetic. At standard temperature and pressure, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, Fan (machine), fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', respectively, as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa (the full period is called a ''wave cycle, cycle''). "Alternating current" most commonly refers to power distribution, but a wide range of other appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology, and marine energy, as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards. All electrotechnologies are covered by IEC Standards, including energy production and distribution, electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics, multimedia, telecommunications and medical technology, as well as associated general disciplines such as terminology and symbols, electromagnetic compatibility, measurement and performance, dependa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |