|
Concyclic
In geometry, a set of points are said to be concyclic (or cocyclic) if they lie on a common circle. A polygon whose vertices are concyclic is called a cyclic polygon, and the circle is called its ''circumscribing circle'' or ''circumcircle''. All concyclic points are equidistant from the center of the circle. Three points in the plane that do not all fall on a straight line are concyclic, so every triangle is a cyclic polygon, with a well-defined circumcircle. However, four or more points in the plane are not necessarily concyclic. After triangles, the special case of cyclic quadrilaterals has been most extensively studied. Perpendicular bisectors In general the centre ''O'' of a circle on which points ''P'' and ''Q'' lie must be such that ''OP'' and ''OQ'' are equal distances. Therefore ''O'' must lie on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment ''PQ''. For ''n'' distinct points there are ''n''(''n'' − 1)/2 bisectors, and the concyclic condition is that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermat Point
In Euclidean geometry, the Fermat point of a triangle, also called the Torricelli point or Fermat–Torricelli point, is a point such that the sum of the three distances from each of the three vertices of the triangle to the point is the smallest possible or, equivalently, the geometric median of the three vertices. It is so named because this problem was first raised by Fermat in a private letter to Evangelista Torricelli, who solved it. The Fermat point gives a solution to the geometric median and Steiner tree problems for three points. Construction The Fermat point of a triangle with largest angle at most 120° is simply its first isogonic center or X(13), which is constructed as follows: # Construct an equilateral triangle on each of two arbitrarily chosen sides of the given triangle. # Draw a line from each new vertex to the opposite vertex of the original triangle. # The two lines intersect at the Fermat point. An alternative method is the following: # On each of two ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcircle
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a triangle is a circle that passes through all three vertex (geometry), vertices. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter of the triangle, and its radius is called the circumradius. The circumcenter is the point of intersection (geometry), intersection between the three perpendicular bisectors of the triangle's sides, and is a triangle center. More generally, an -sided polygon with all its vertices on the same circle, also called the circumscribed circle, is called a cyclic polygon, or in the special case , a cyclic quadrilateral. All rectangles, isosceles trapezoids, right kites, and regular polygons are cyclic, but not every polygon is. Straightedge and compass construction The circumcenter of a triangle can be Compass-and-straightedge construction, constructed by drawing any two of the three Bisection#Perpendicular bisectors, perpendicular bisectors. For three non-collinear points, these two lines cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcenter
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a triangle is a circle that passes through all three vertices. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter of the triangle, and its radius is called the circumradius. The circumcenter is the point of intersection between the three perpendicular bisectors of the triangle's sides, and is a triangle center. More generally, an -sided polygon with all its vertices on the same circle, also called the circumscribed circle, is called a cyclic polygon, or in the special case , a cyclic quadrilateral. All rectangles, isosceles trapezoids, right kites, and regular polygons are cyclic, but not every polygon is. Straightedge and compass construction The circumcenter of a triangle can be constructed by drawing any two of the three perpendicular bisectors. For three non-collinear points, these two lines cannot be parallel, and the circumcenter is the point where they cross. Any point on the bisector is equidistant from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumcircle
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a triangle is a circle that passes through all three vertex (geometry), vertices. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter of the triangle, and its radius is called the circumradius. The circumcenter is the point of intersection (geometry), intersection between the three perpendicular bisectors of the triangle's sides, and is a triangle center. More generally, an -sided polygon with all its vertices on the same circle, also called the circumscribed circle, is called a cyclic polygon, or in the special case , a cyclic quadrilateral. All rectangles, isosceles trapezoids, right kites, and regular polygons are cyclic, but not every polygon is. Straightedge and compass construction The circumcenter of a triangle can be Compass-and-straightedge construction, constructed by drawing any two of the three Bisection#Perpendicular bisectors, perpendicular bisectors. For three non-collinear points, these two lines cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Bisector
In geometry, bisection is the division of something into two equal or congruent parts (having the same shape and size). Usually it involves a bisecting line, also called a ''bisector''. The most often considered types of bisectors are the ''segment bisector'', a line that passes through the midpoint of a given segment, and the ''angle bisector'', a line that passes through the apex of an angle (that divides it into two equal angles). In three-dimensional space, bisection is usually done by a bisecting plane, also called the ''bisector''. Perpendicular line segment bisector Definition *The perpendicular bisector of a line segment is a line which meets the segment at its midpoint perpendicularly. *The perpendicular bisector of a line segment AB also has the property that each of its points X is equidistant from segment AB's endpoints: (D)\quad , XA, = , XB, . The proof follows from , MA, =, MB, and Pythagoras' theorem: :, XA, ^2=, XM, ^2+, MA, ^2=, XM, ^2+, MB, ^2=, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Quadrilateral
In geometry, a cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral (four-sided polygon) whose vertex (geometry), vertices all lie on a single circle, making the sides Chord (geometry), chords of the circle. This circle is called the ''circumcircle'' or ''circumscribed circle'', and the vertices are said to be ''concyclic''. The center of the circle and its radius are called the ''circumcenter'' and the ''circumradius'' respectively. Usually the quadrilateral is assumed to be convex polygon, convex, but there are also Crossed quadrilateral, crossed cyclic quadrilaterals. The formulas and properties given below are valid in the convex case. The word cyclic is from the Ancient Greek (''kuklos''), which means "circle" or "wheel". All triangles have a circumcircle, but not all quadrilaterals do. An example of a quadrilateral that cannot be cyclic is a non-square rhombus. The section Cyclic quadrilateral#Characterizations, characterizations below states what necessar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine-point Circle
In geometry, the nine-point circle is a circle that can be constructed for any given triangle. It is so named because it passes through nine significant concyclic points defined from the triangle. These nine points are: * The midpoint of each side of the triangle * The foot of each altitude * The midpoint of the line segment from each vertex of the triangle to the orthocenter (where the three altitudes meet; these line segments lie on their respective altitudes). The nine-point circle is also known as Feuerbach's circle (after Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach), Euler's circle (after Leonhard Euler), Terquem's circle (after Olry Terquem), the six-points circle, the twelve-points circle, the -point circle, the medioscribed circle, the mid circle or the circum-midcircle. Its center is the nine-point center of the triangle. Nine Significant Points of Nine Point Circle The diagram above shows the nine significant points of the nine-point circle. Points are the midpoints of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
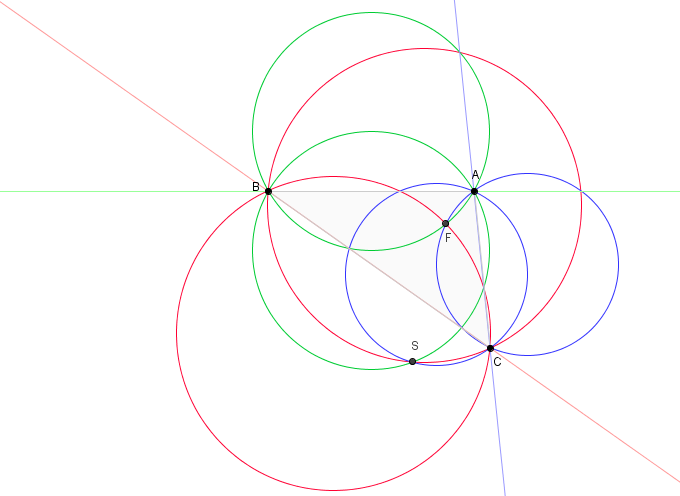
Lester's Theorem
In Euclidean plane geometry, Lester's theorem states that in any scalene triangle, the two Fermat points, the nine-point center, and the circumcenter lie on the same circle. The result is named after June Lester, who published it in 1997, and the circle through these points was called the Lester circle by Clark Kimberling. Lester proved the result by using the properties of complex numbers; subsequent authors have given elementary proofs, proofs using vector arithmetic, and computerized proofs. The center of the Lester circle is also a triangle center. It is the center designated as X(1116) in the Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers. Recently, Peter Moses discovered 21 other triangle A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ... centers lie on the Lester circle. The points ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscribed Polygon
In geometry, a circumscribed circle for a set of points is a circle passing through each of them. Such a circle is said to ''circumscribe'' the points or a polygon formed from them; such a polygon is said to be ''inscribed'' in the circle. * Circumcircle, the circumscribed circle of a triangle, which always exists for a given triangle. * Cyclic polygon, a general polygon that can be circumscribed by a circle. The vertices of this polygon are concyclic points. All triangles are cyclic polygons. * Cyclic quadrilateral, a special case of a cyclic polygon. See also * Smallest-circle problem, the related problem of finding the circle with minimal radius containing an arbitrary set of points, not necessarily passing through them. * Inscribed figure An inscribed triangle of a circle In geometry, an inscribed planar shape or solid is one that is enclosed by and "fits snugly" inside another geometric shape or solid. To say that "figure F is inscribed in figure G" means precisely the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine-point Circle
In geometry, the nine-point circle is a circle that can be constructed for any given triangle. It is so named because it passes through nine significant concyclic points defined from the triangle. These nine points are: * The midpoint of each side of the triangle * The foot of each altitude * The midpoint of the line segment from each vertex of the triangle to the orthocenter (where the three altitudes meet; these line segments lie on their respective altitudes). The nine-point circle is also known as Feuerbach's circle (after Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach), Euler's circle (after Leonhard Euler), Terquem's circle (after Olry Terquem), the six-points circle, the twelve-points circle, the -point circle, the medioscribed circle, the mid circle or the circum-midcircle. Its center is the nine-point center of the triangle. Nine Significant Points of Nine Point Circle The diagram above shows the nine significant points of the nine-point circle. Points are the midpoints of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimensional line segments. A triangle has three internal angles, each one bounded by a pair of adjacent edges; the sum of angles of a triangle always equals a straight angle (180 degrees or π radians). The triangle is a plane figure and its interior is a planar region. Sometimes an arbitrary edge is chosen to be the ''base'', in which case the opposite vertex is called the ''apex''; the shortest segment between the base and apex is the ''height''. The area of a triangle equals one-half the product of height and base length. In Euclidean geometry, any two points determine a unique line segment situated within a unique straight line, and any three points that do not all lie on the same straight line determine a unique triangle situated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |