|
Computer Hacking
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who achieves goals and solves problems by non-standard means. The term has become associated in popular culture with a security hackersomeone with knowledge of bugs or exploits to break into computer systems and access data which would otherwise be inaccessible to them. In a positive connotation, though, hacking can also be utilized by legitimate figures in legal situations. For example, law enforcement agencies sometimes use hacking techniques to collect evidence on criminals and other malicious actors. This could include using anonymity tools (such as a VPN or the dark web) to mask their identities online and pose as criminals. Hacking can also have a broader sense of any roundabout solution to a problem, or programming and hardware development in general, and hacker culture has spread the term's broader usage to the general public even outside the profession or hobby of electronics (see life hack). Etymology The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coding Da Vinci - Der Kultur-Hackathon (14123515524)
Coding may refer to: Computer science * Computer programming, the process of creating and maintaining the source code of computer programs * Line coding, in data storage * Source coding, compression used in data transmission * Coding theory * Channel coding Other uses * Coding (social sciences), an analytical process in which data are categorized for analysis * Coding strand of DNA in molecular biology * Legal coding, the process of creating summary or keyword data from a document in the legal profession * Medical coding, representation of medical diagnoses and procedures in standard code numbers * Number coding in Metro Manila, a road space rationing policy implemented in Metro Manila, Philippines, commonly referred to as "coding" * Coding (therapy), alternative therapeutic methods used to treat addictions in the post-Soviet countries * Queer coding See also * Code * Entropy encoding In information theory, an entropy coding (or entropy encoding) is any lossless data c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
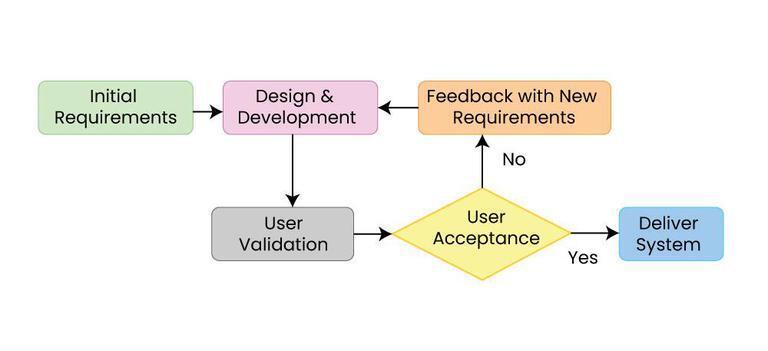
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, writing source code, code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing software requirements, requirements, software design, design, software testing, testing and software release life cycle, release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes management, organizational management, Software project management, project management, configuration management and other aspects. Software development involves many skills and job specializations including software programmer, programming, software test, testing, Technical writing, documentation, graphic design, user support, marketing, and fundraising. Software development involves many software tools, tools including: compiler, integrated develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchist Hackers
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state with stateless societies and voluntary free associations. A historically left-wing movement, anarchism is usually described as the libertarian wing of the socialist movement (libertarian socialism). Although traces of anarchist ideas are found all throughout history, modern anarchism emerged from the Enlightenment. During the latter half of the 19th and the first decades of the 20th century, the anarchist movement flourished in most parts of the world and had a significant role in workers' struggles for emancipation. Various anarchist schools of thought formed during this period. Anarchists have taken part in several revolutions, most notably in the Paris Commune, the Russian Civil War and the Spanish Civil War, whose end marked the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phreaker
Phreaking is a slang term coined to describe the activity of a culture of people who study, experiment with, or explore telecommunication systems, such as equipment and systems connected to public telephone networks. The term ''phreak'' is a sensational spelling of the word ''freak'' with the ''ph-'' from ''Telephone, phone'', and may also refer to the use of various audio Frequency, frequencies to manipulate a phone system. ''Phreak'', ''phreaker'', or ''phone phreak'' are names used for and by individuals who participate in phreaking. The term first referred to groups who had Reverse engineering, reverse engineered the system of tones used to route Long-distance calling, long-distance calls. By re-creating the signaling tones, phreaks could switch calls from the phone handset while avoiding long-distance calling charges which were common then. These fees could be significant, depending on the time, duration and destination of the call. To ease the creation of the routing tones, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Tech (newspaper)
''The Tech'', first published on November 16, 1881, is the student newspaper at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Editions are published biweekly on Thursdays throughout the academic year and about once a month over the summer. ''The Tech'' established an early presence on the World Wide Web, and continues to publish online in tandem with the print edition.Kristina Grifantini"The Tech, Then and Now" ''MIT Technology Review'', June 23, 2008. Organization ''The Tech'' is a completely student-managed, and largely student-written publication, officially recognized as a student activity by the administration of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The newspaper is largely self-supporting financially, deriving most of its income from advertising. The publication has an advisory board composed primarily of ex-staffers who are alumni of MIT. Print edition Printed copies are distributed throughout the MIT campus on the morning of publication. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Shapiro
Fred Richard Shapiro is an American legal scholar and academic working as the editor of '' The Yale Book of Quotations'', ''The Oxford Dictionary of American Legal Quotations'', and several other books. Education Shapiro earned a Bachelor of Science degree from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, a Master of Library Science from the Catholic University of America, and a Juris Doctor from Harvard Law School. Career Shapiro has published numerous articles on language, law, and information science, including "The Politically Correct United States Supreme Court and the Motherfucking Texas Court of Appeals: Using Legal Databases to Trace the Origins of Words and Quotations" and "Who Wrote the Serenity Prayer". He is an associate librarian and lecturer in legal research at Yale Law School Yale Law School (YLS) is the law school of Yale University, a Private university, private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was established in 1824. The 2020–21 acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Stone
''Rolling Stone'' is an American monthly magazine that focuses on music, politics, and popular culture. It was founded in San Francisco, California, in 1967 by Jann Wenner and the music critic Ralph J. Gleason. The magazine was first known for its coverage of rock music and political reporting by Hunter S. Thompson. In the 1990s, the magazine broadened and shifted its focus to a younger readership interested in youth-oriented television shows, film actors, and popular music. It has since returned to its traditional mix of content, including music, entertainment, and politics. The first magazine was released in 1967 and featured John Lennon on the cover, and was then published every two weeks. It is known for provocative photography and its cover photos, featuring musicians, politicians, athletes, and actors. In addition to its print version in the United States, it publishes content through Rollingstone.com and numerous international editions. The magazine experienced a rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart Brand
Stewart Brand (born December 14, 1938) is an American project developer and writer, best known as the co-founder and editor of the ''Whole Earth Catalog''. He has founded a number of organizations, including the WELL, the Global Business Network, and the Long Now Foundation. He is the author of several books, most recently '' Whole Earth Discipline: An Ecopragmatist Manifesto''. Life Brand was born in Rockford, Illinois, and attended Phillips Exeter Academy in New Hampshire. He studied biology at Stanford University under Paul R. Ehrlich, graduating in 1960. As a soldier in the U.S. Army, he was a parachutist and taught infantry skills; he later expressed the view that his experience in the military had fostered his competence in organizing. A civilian again in 1962, he studied design at San Francisco Art Institute, photography at San Francisco State College, and participated in a legitimate scientific study of then-legal LSD with Myron Stolaroff's International Foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Kay
Alan Curtis Kay (born May 17, 1940) published by the Association for Computing Machinery 2012 is an American computer scientist who pioneered work on object-oriented programming and windowing graphical user interface (GUI) design. At Xerox PARC he led the design and development of the first modern windowed computer desktop interface. There he also led the development of the influential object-oriented programming language Smalltalk, both personally designing most of the early versions of the language and coining the term "object-oriented." He has been elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the Royal Society of Arts. He received the Turing Award in 2003. Early life and work In an interview on education in America with the Davis Group Ltd., Kay said: Originally from Springfield, Massachusetts, Kay's family relocated several times due to his father's career in physiology before ultimately settling in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geek
The word ''geek'' is a slang term originally used to describe Eccentricity (behavior), eccentric or non-mainstream people; in current use, the word typically connotes an expert or enthusiast obsessed with a hobby or intellectual pursuit. In the past, it had a generally pejorative meaning of a "peculiar person, especially one who is perceived to be overly intellectual, unfashionable, boring, or socially awkward". In the 21st century, it was reappropriation, reclaimed and used by many people, especially members of some fandoms, as a positive term. Some use the term self-referentially without malice or as a source of pride, often referring simply to "someone who is interested in a subject (usually intellectual or complex) for its own sake". Etymology The word comes from English dialect ''geek'' or ''geck'' (meaning a "fool" or "freak"; from Middle Low German ''Geck''). ''Geck'' is a standard term in modern German and means "fool" or "fop". The root also survives in the Dutch lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jargon File
The Jargon File is a glossary and usage dictionary of slang used by computer programmers. The original Jargon File was a collection of terms from technical cultures such as the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, MIT AI Lab, the Stanford University centers and institutes#Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Stanford AI Lab (SAIL) and others of the old ARPANET Artificial intelligence, AI/Lisp programming language, LISP/PDP-10 communities, including BBN Technologies, Bolt, Beranek and Newman (BBN), Carnegie Mellon University, and Worcester Polytechnic Institute. It was published in paperback form in 1983 as ''The Hacker's Dictionary'' (edited by Guy L. Steele Jr., Guy Steele) and revised in 1991 as ''The New Hacker's Dictionary'' (ed. Eric S. Raymond; third edition published 1996). The concept of the file began with the Tech Model Railroad Club (TMRC) that came out of early TX-0 and PDP-1 hackers in the 1950s, where the term ''hacker'' emerged and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |