 |
Complex Quadratic Polynomial
A complex quadratic polynomial is a quadratic polynomial whose coefficients and variable (mathematics), variable are complex numbers. Properties Quadratic polynomials have the following properties, regardless of the form: *It is a unicritical polynomial, i.e. it has one #Critical_points, finite critical point in the complex plane, Dynamical plane consist of maximally 2 basins: the basin of infinity and basin of the finite critical point (if the finite critical point does not escape) *It can be postcritically finite, i.e. the orbit of the critical point can be finite, because the critical point is periodic or preperiodic. * It is a Unimodality#Unimodal function, unimodal function, * It is a rational function, * It is an entire function. Forms When the quadratic polynomial has only one variable (univariate), one can distinguish its four main forms: * The general form: f(x) = a_2 x^2 + a_1 x + a_0 where a_2 \ne 0 * The factored form used for the logistic map: f_r(x) = r x (1-x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Periodic Points Of Complex Quadratic Mappings
This article describes periodic points of some Complex quadratic polynomial, complex quadratic maps. A map is a formula for computing a value of a variable based on its own previous value or values; a Quadratic equation, quadratic map is one that involves the previous value raised to the power (mathematics), powers one and two; and a complex map is one in which the variable and the parameters are complex numbers. A periodic point of a map is a value of the variable that occurs repeatedly after intervals of a fixed length. These periodic points play a role in the theories of Fatou set, Fatou and Julia sets. Definitions Let :f_c(z) = z^2+c\, be the complex quadratic polynomial, complex quadratic mapping, where z and c are complex numbers. Notationally, f^ _c (z) is the k-fold Function composition, composition of f_c with itself (not to be confused with the kth derivative of f_c)—that is, the value after the ''k''-th Iterated function, iteration of the function f _c. Thus :f^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Quadratic Polynomial
In mathematics, a quadratic function of a single variable is a function of the form :f(x)=ax^2+bx+c,\quad a \ne 0, where is its variable, and , , and are coefficients. The expression , especially when treated as an object in itself rather than as a function, is a quadratic polynomial, a polynomial of degree two. In elementary mathematics a polynomial and its associated polynomial function are rarely distinguished and the terms ''quadratic function'' and ''quadratic polynomial'' are nearly synonymous and often abbreviated as ''quadratic''. The graph of a real single-variable quadratic function is a parabola. If a quadratic function is equated with zero, then the result is a quadratic equation. The solutions of a quadratic equation are the zeros (or ''roots'') of the corresponding quadratic function, of which there can be two, one, or zero. The solutions are described by the quadratic formula. A quadratic polynomial or quadratic function can involve more than one variabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Bodil Branner
Bodil Branner (born 5 February 1943, in Aarhus) is a retired Danish mathematician, one of the founders of European Women in Mathematics and a former chair of the Danish Mathematical Society. Her research concerned holomorphic dynamics and the history of mathematics. Education and career Branner studied mathematics and physics at Aarhus University, where mathematician Svend Bundgaard was one of her mentors, and in 1967 earned a master's degree (the highest degree then available) under the supervision of Leif Kristensen. She had intended to travel to the U.S. for a doctorate, but her husband, a chemist, took an industry job in Copenhagen. Branner could not get a job as a high school teacher because she did not have a teaching qualification, but Bundgaard found her a position as a faculty assistant for Frederik Fabricius-Bjerre at the Technical University of Denmark. Despite this not beginning as an actual faculty position, she eventually earned tenure there in the 1970s. Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
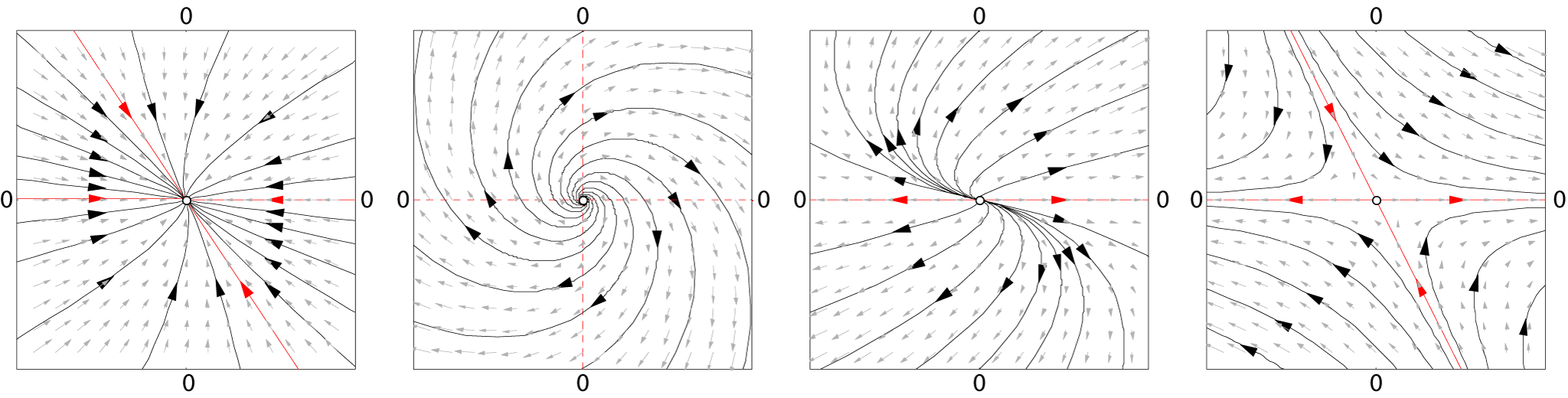
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Dynamical System (definition)
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
External Ray
An external ray is a curve that runs from infinity toward a Julia or Mandelbrot set. Although this curve is only rarely a half-line (ray) it is called a ray because it is an image of a ray. External rays are used in complex analysis, particularly in complex dynamics and geometric function theory. History External rays were introduced in Douady and Hubbard's study of the Mandelbrot set Types Criteria for classification : * plane : parameter or dynamic * map * bifurcation of dynamic rays * Stretching * landing plane External rays of (connected) Julia sets on dynamical plane are often called dynamic rays. External rays of the Mandelbrot set (and similar one-dimensional connectedness loci) on parameter plane are called parameter rays. bifurcation Dynamic ray can be: * bifurcated = branched = broken * smooth = unbranched = unbroken When the filled Julia set is connected, there are no branching external rays. When the Julia set is not connected then some external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Iterated Function
In mathematics, an iterated function is a function that is obtained by composing another function with itself two or several times. The process of repeatedly applying the same function is called iteration. In this process, starting from some initial object, the result of applying a given function is fed again into the function as input, and this process is repeated. For example, on the image on the right: : Iterated functions are studied in computer science, fractals, dynamical systems, mathematics and renormalization group physics. Definition The formal definition of an iterated function on a set ''X'' follows. Let be a set and be a function. Defining as the ''n''-th iterate of , where ''n'' is a non-negative integer, by: f^0 ~ \stackrel ~ \operatorname_X and f^ ~ \stackrel ~ f \circ f^, where is the identity function on and denotes function composition. This notation has been traced to and John Frederick William Herschel in 1813. Herschel credited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dyadic Transformation
The dyadic transformation (also known as the dyadic map, bit shift map, 2''x'' mod 1 map, Bernoulli map, doubling map or sawtooth map) is the mapping (i.e., recurrence relation) : T: , 1) \to [0, 1)^\infty : x \mapsto (x_0, x_1, x_2, \ldots) (where [0, 1)^\infty is the set of sequences from [0, 1)) produced by the rule : x_0 = x : \text n \ge 0,\ x_ = (2 x_n) \bmod 1. Equivalently, the dyadic transformation can also be defined as the iterated function map of the piecewise linear function : T(x)=\begin2x & 0 \le x < \frac \\2x-1 & \frac \le x < 1. \end The name ''bit shift map'' arises because, if the value of an iterate is written in binary notation, the next iterate is obtained by shifting the binary point one bit to the right, and if the bit to the left of the new binary point is a "one", replacing it with a zero. The dyadic transformation provides an example of ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Fatou Set
In complex dynamics, the Julia set and the Fatou set are two complementary sets (Julia "laces" and Fatou "dusts") defined from a function. Informally, the Fatou set of the function consists of values with the property that all nearby values behave similarly under repeated iteration of the function, and the Julia set consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Thus the behavior of the function on the Fatou set is "regular", while on the Julia set its behavior is " chaotic". The Julia set of a function is commonly denoted \operatorname(f), and the Fatou set is denoted \operatorname(f). These sets are named after the French mathematicians Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou whose work began the study of complex dynamics during the early 20th century. Formal definition Let f(z) be a non-constant meromorphic function from the Riemann sphere onto itself. Such functions f(z) are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Julia Set
In complex dynamics, the Julia set and the Classification of Fatou components, Fatou set are two complement set, complementary sets (Julia "laces" and Fatou "dusts") defined from a function (mathematics), function. Informally, the Fatou set of the function consists of values with the property that all nearby values behave similarly under iterated function, repeated iteration of the function, and the Julia set consists of values such that an arbitrarily small Perturbation theory, perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Thus the behavior of the function on the Fatou set is "regular", while on the Julia set its behavior is "chaos theory, chaotic". The Julia set of a function is commonly denoted \operatorname(f), and the Fatou set is denoted \operatorname(f). These sets are named after the French mathematicians Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou whose work began the study of complex dynamics during the early 20th century. Form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Mandelbrot Set
The Mandelbrot set () is a two-dimensional set (mathematics), set that is defined in the complex plane as the complex numbers c for which the function f_c(z)=z^2+c does not Stability theory, diverge to infinity when Iteration, iterated starting at z=0, i.e., for which the sequence f_c(0), f_c(f_c(0)), etc., remains bounded in absolute value. This set was first defined and drawn by Robert W. Brooks and Peter Matelski in 1978, as part of a study of Kleinian groups. Afterwards, in 1980, Benoit Mandelbrot obtained high-quality visualizations of the set while working at IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York. Images of the Mandelbrot set exhibit an infinitely complicated Boundary (topology), boundary that reveals progressively ever-finer Recursion, recursive detail at increasing magnifications; mathematically, the boundary of the Mandelbrot set is a ''fractal curve''. The "style" of this recursive detail depends on the region of the set boundary being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Complex Dynamics
Complex dynamics, or holomorphic dynamics, is the study of dynamical systems obtained by Iterated function, iterating a complex analytic mapping. This article focuses on the case of algebraic dynamics, where a polynomial or rational function is iterated. In geometric terms, that amounts to iterating a mapping from some algebraic variety to itself. The related theory of arithmetic dynamics studies iteration over the rational numbers or the p-adic numbers instead of the complex numbers. Dynamics in complex dimension 1 A simple example that shows some of the main issues in complex dynamics is the mapping f(z)=z^2 from the complex numbers C to itself. It is helpful to view this as a map from the complex projective line \mathbf^1 to itself, by adding a point \infty to the complex numbers. (\mathbf^1 has the advantage of being compact space, compact.) The basic question is: given a point z in \mathbf^1, how does its ''orbit'' (or ''forward orbit'') :z,\; f(z)=z^2,\; f(f(z))=z^4, f(f(f(z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |