|
Comparator Applications
A comparator is an electronic component that compares two input voltages. Comparators are closely related to operational amplifiers, but a comparator is designed to operate with positive feedback and with its output saturated at one power rail or the other. If necessary, an op-amp can be pressed into service as a poorly performing comparator, but its slew rate will be impaired. Comparator : Bistable output that indicates which of the two inputs has a higher voltage. That is, : V_ = \begin V_ & \text V_1 > V_2, \\ V_ & \text V_1 < V_2, \\ 0 & \text V_1 = V_2, \end where and are nominally the positive and negative supply voltages (which are not shown in the diagram). Threshold detector Circuit diagram for threshold detector with hysteresis The threshold detector with |
|
|
Comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It has two analog input terminals V_+ and V_- and one binary digital output V_\text. The output is ideally : V_\text = \begin 1, & \textV_+ > V_-, \\ 0, & \textV_+ < V_-. \end A comparator consists of a specialized high- gain . They are commonly used in devices that measure and digitize analog signals, such as s (ADCs), as well as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Bistable Multivibrator
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state devices such as relaxation oscillators, timers, latches and flip-flops. The first multivibrator circuit, the astable multivibrator oscillator, was invented by Henri Abraham and Eugene Bloch during World War I. It consisted of two vacuum tube amplifiers cross-coupled by a resistor-capacitor network. They called their circuit a "multivibrator" because its output waveform was rich in harmonics. A variety of active devices can be used to implement multivibrators that produce similar harmonic-rich wave forms; these include transistors, neon lamps, tunnel diodes and others. Although cross-coupled devices are a common form, single-element multivibrator oscillators are also common. The three types of multivibrator circuits are: # Astable multivibrator, in which the circuit is not stable in either state —it continually switches from one state to the other. It functions as a relaxation oscillator. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Square Wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions between minimum and maximum are instantaneous. The square wave is a special case of a pulse wave which allows arbitrary durations at minimum and maximum amplitudes. The ratio of the high period to the total period of a pulse wave is called the duty cycle. A true square wave has a 50% duty cycle (equal high and low periods). Square waves are often encountered in electronics and signal processing, particularly digital electronics and digital signal processing. Its stochastic counterpart is a two-state trajectory. Origin and uses Square waves are universally encountered in digital switching circuits and are naturally generated by binary (two-level) logic devices. They are used as timing references or "clock signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Oscillate
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term '' vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Relaxation Oscillator
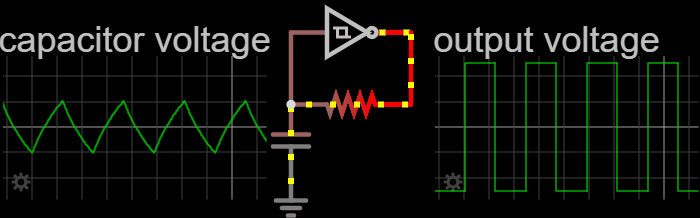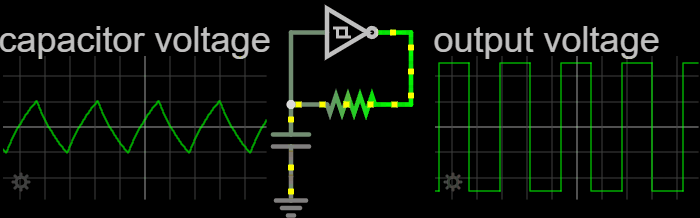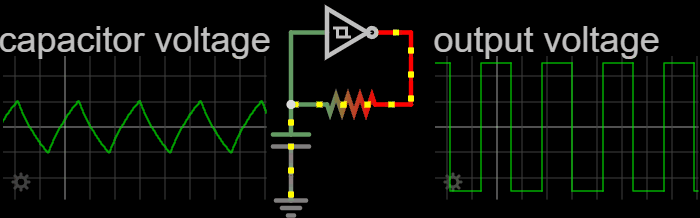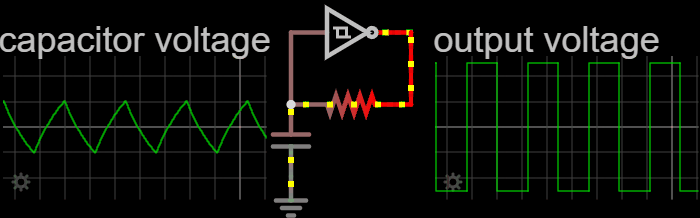
In electronics, a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Schmitt Trigger
In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an passivity (engineering), active circuit which converts an analog signal, analog input signal to a digital signal, digital output signal. The circuit is named a ''trigger'' because the output retains its value until the input changes sufficiently to trigger a change. In the non-inverting configuration, when the input is higher than a chosen threshold, the output is high. When the input is below a different (lower) chosen threshold the output is low, and when the input is between the two levels the output retains its value. This dual threshold action is called ''hysteresis'' and implies that the Schmitt trigger possesses memory and can act as a bistable multivibrator (latch or Flip-flop (electronics), flip-flop). There is a close relation between the two kinds of circuits: a Schmitt trigger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances. Whereas positive feedback tends to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaos theory, chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing, can be very stable, accurate, and responsive. Negative feedback is widely used in Mechanical engineering, mechanical and electronic engineering, and it is observed in many other fields including biology, chemistry and economics. General negative feedback systems are studied in Control engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
RC Network
A resistor–capacitor circuit (RC circuit), or RC filter or RC network, is an electric circuit composed of resistors and capacitors. It may be driven by a voltage or current source and these will produce different responses. A first order RC circuit is composed of one resistor and one capacitor and is the simplest type of RC circuit. RC circuits can be used to filter a signal by blocking certain frequencies and passing others. The two most common RC filters are the high-pass filters and low-pass filters; band-pass filters and band-stop filters usually require RLC filters, though crude ones can be made with RC filters. Natural response The simplest RC circuit consists of a resistor with resistance and a charged capacitor with capacitance connected to one another in a single loop, without an external voltage source. The capacitor will discharge its stored energy through the resistor. If is taken to be the voltage of the capacitor's top plate relative to its bottom plate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Op-Amp Relaxation Oscillator
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) single-ended output, and an extremely high gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathematical operations in analog computers. By using negative feedback, an op amp circuit's characteristics (e.g. its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth, and functionality) can be determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. This flexibility has made the op amp a popular building block in analog circuits. Today, op amps are used widely in consumer, industrial, and scientific electronics. Many standard integrated circuit op amps cost only a few cents; however, some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over . Op amps may be packaged as components or used as elements of more complex integrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Relaxation Oscillator
In electronics, a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Electrical Ground
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Electrical circuits may be connected to ground for several reasons. Exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment are connected to ground to protect users from electrical shock hazards. If internal insulation fails, dangerous voltages may appear on the exposed conductive parts. Connecting exposed conductive parts to a "ground" wire which provides a low-impedance path for current to flow back to the incoming neutral (which is also connected to ground, close to the point of entry) will allow circuit breakers (or RCDs) to interrupt power supply in the event of a fault. In electric power distribution systems, a protective earth (PE) conductor is an essential part of the safety provided by the earthing system. Connection to ground also limits the build-up of static el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |