|
Color Vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different frequencies independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a complex process between neurons that begins with differential stimulation of different types of photoreceptors by light entering the eye. Those photoreceptors then emit outputs that are propagated through many layers of neurons ultimately leading to higher cognitive functions in the brain. Color vision is found in many animals and is mediated by similar underlying mechanisms with common types of biological molecules and a complex history of the evolution of color vision within different animal taxa. In primates, color vision may have evolved under selective pressure for a variety of visual tasks including the foraging for nutritious young leaves, ripe fruit, and flowers, as well as detecting predator camouflage and emotional states in othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just-noticeable Difference
In the branch of experimental psychology focused on sense, sensation, and perception, which is called psychophysics, a just-noticeable difference or JND is the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable, detectable at least half the time. This limen is also known as the difference limen, difference threshold, or least perceptible difference. Quantification For many sensory modalities, over a wide range of stimulus magnitudes sufficiently far from the upper and lower limits of perception, the 'JND' is a fixed proportion of the reference sensory level, and so the ratio of the JND/reference is roughly constant (that is the JND is a constant proportion/percentage of the reference level). Measured in physical units, we have: \frac = k, where I\! is the original intensity of the particular stimulation, \Delta I\! is the addition to it required for the change to be perceived (the JND), and ''k'' is a constant. This rule was first discovered by Erns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purkinje Effect
The Purkinje effect or Purkinje phenomenon (; sometimes called the Purkinje shift, often pronounced ) is the tendency for the peak luminance sensitivity of the eye to shift toward the blue end of the color spectrum at low illumination (lighting), illumination levels as part of dark adaptation. In consequence, reds will appear darker relative to other colors as light levels decrease. The effect is named after the Czechs, Czech anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkyně. While the effect is often described from the perspective of the human eye, it is well established in a number of animals under the same name to describe the general shifting of spectral sensitivity due to pooling of rod and cone output signals as a part of dark/light adaptation. This effect introduces a difference in color contrast (vision), contrast under different levels of illumination. For instance, in bright sunlight, Pelargonium, geranium flowers appear bright red against the dull green of their leaf, leaves, or adja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Ganglion Cell
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptor cell, photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Bipolar cell of the retina, bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that extends into the brain. These axons form the optic ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopic Vision
Mesopic vision, sometimes also called twilight vision, is a combination of photopic and scotopic vision under low-light (but not necessarily dark) conditions. Mesopic levels range approximately from 0.01 to 3.0 cd/m2 in luminance. Most nighttime outdoor and street lighting conditions are in the mesopic range. Human eyes respond to certain light levels differently. This is because under high light levels typical during daytime (photopic vision), the eye uses cones to process light. Under very low light levels, corresponding to moonless nights without artificial lighting (scotopic vision), the eye uses rods to process light. At many nighttime levels, a combination of both cones and rods supports vision. Photopic vision facilitates excellent color perception, whereas colors are barely perceptible under scotopic vision. Mesopic vision falls between these two extremes. In most nighttime environments, enough ambient light prevents true scotopic vision. In the words of Duco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone Cell
Cone cells or cones are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the vertebrate eye. Cones are active in daylight conditions and enable photopic vision, as opposed to rod cells, which are active in dim light and enable scotopic vision. Most vertebrates (including humans) have several classes of cones, each sensitive to a different part of the visible spectrum of light. The comparison of the responses of different cone cell classes enables color vision. There are about six to seven million cones in a human eye (vs ~92 million rods), with the highest concentration occurring towards the macula and most densely packed in the fovea centralis, a diameter rod-free area with very thin, densely packed cones. Conversely, like rods, they are absent from the optic disc, contributing to the blind spot. Cones are less sensitive to light than the rod cells in the retina (which support vision at low light levels), but allow the perception of color. They are also able to perceive finer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photopic
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions (luminance levels from 10 to 108 cd/m2). In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher visual acuity and temporal resolution than available with scotopic vision. The human eye uses three types of cones to sense light in three bands of color. The biological pigments of the cones have maximum absorption values at wavelengths of about 420 nm (blue), 534 nm (bluish-green), and 564 nm (yellowish-green). The color of the pure signal of the cones could be described as violet, blue-green, and scarlet red, respectively, but, in their wavelengths of maximum absorption other cones are activated as well. The sensitivity ranges of the conecells overlap to provide vision throughout the visible spectrum. The maximum efficacy is 683 lm/W at a wavelength of 555 nm (green). By definition, light at a frequency of hertz has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the photographic film, film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by Chemical synapse, synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rod cell, rods and cone cell, cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Cell
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On average, there are approximately 92 million rod cells (vs ~4.6 million cones) in the human retina. Rod cells are more sensitive than cone cells and are almost entirely responsible for night vision. However, rods have little role in color vision, which is the main reason why colors are much less apparent in dim light. Structure Rods are a little longer and leaner than cones but have the same basic structure. Opsin-containing disks lie at the end of the cell adjacent to the retinal pigment epithelium, which in turn is attached to the inside of the eye. The stacked-disc structure of the detector portion of the cell allows for very high efficiency. Rods are much more common than cones, with about 120 million rod cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotopic
In the study of visual perception, scotopic vision (or scotopia) is the vision of the eye under low-light conditions. The term comes from the Greek ''skotos'', meaning 'darkness', and ''-opia'', meaning 'a condition of sight'. In the human eye, cone cells are nonfunctional in low visible light. Scotopic vision is produced exclusively through rod cells, which are most sensitive to wavelengths of around 498 nm (blue-green) and are insensitive to wavelengths longer than about 640 nm. Under scotopic conditions, light incident on the retina is not encoded in terms of the spectral power distribution. Higher visual perception occurs under scotopic vision as it does under photopic vision. Retinal circuitry Of the two types of photoreceptor cells in the retina, rods dominate scotopic vision. This dominance is due to the increased sensitivity of the photopigment molecule expressed in rods, as opposed to those in cones. Rods signal light increments to rod bipolar cells which, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromaticity
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance. Chromaticity consists of two independent parameters, often specified as '' hue'' (''h'') and ''colorfulness'' (''s''), where the latter is alternatively called ''saturation'', ''chroma'', ''intensity'', or '' excitation purity''. This number of parameters follows from trichromacy of vision of most humans, which is assumed by most models in color science. Quantitative description In color science, the white point of an illuminant or of a display is a neutral reference characterized by a chromaticity; all other chromaticities may be defined in relation to this reference using polar coordinates. The ''hue'' is the angular component, and the ''purity'' is the radial component, normalized by the maximum radius for that hue. ''Purity'' is roughly equivalent to the term '' saturation'' in the HSV color model. The property '' hue'' is as used in general color theory and in specific c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
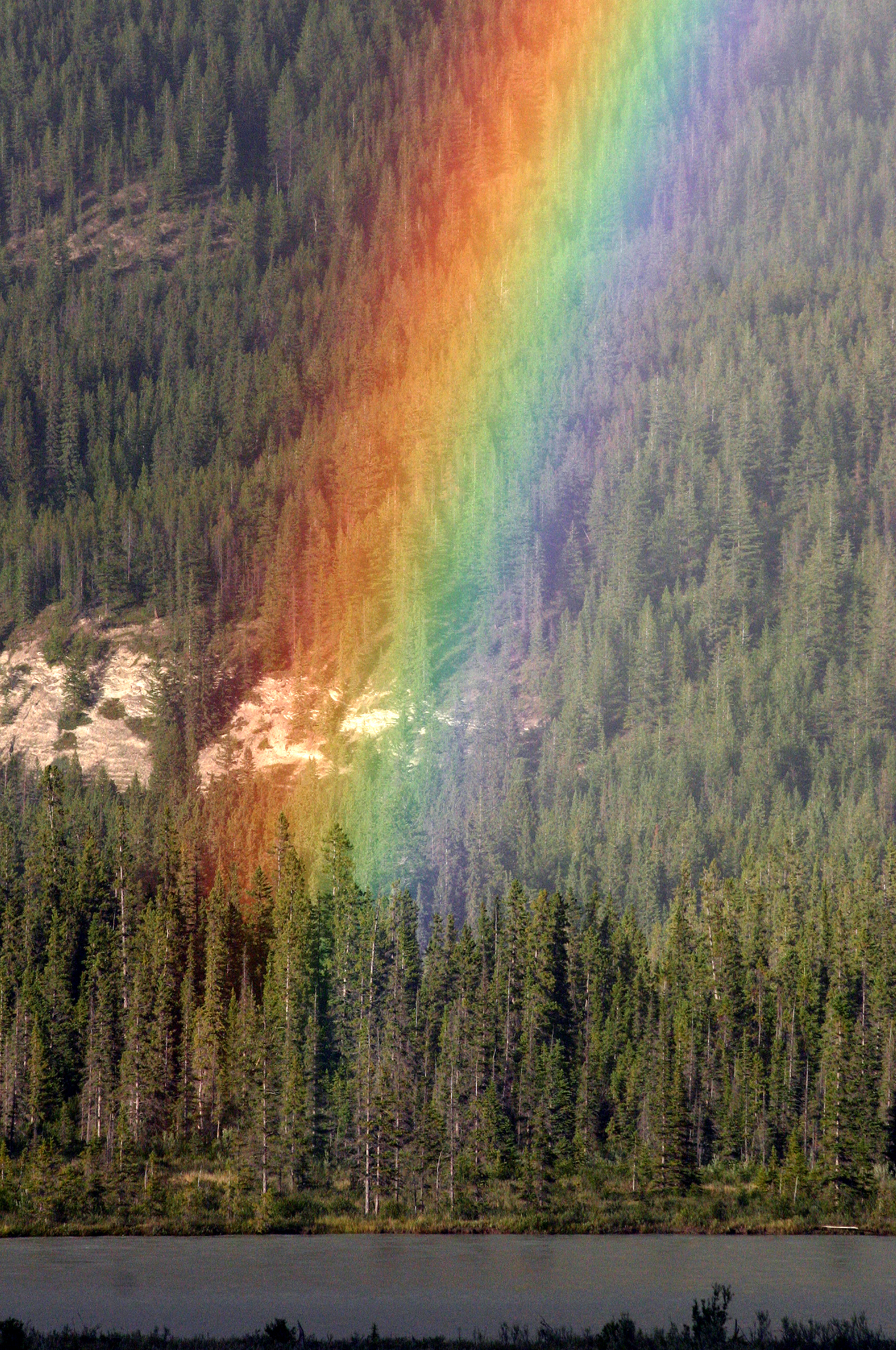
Spectral Color
A spectral color is a color that is evoked by monochromatic light, i.e. either a spectral line with a single wavelength or frequency of light in the visible spectrum, or a relatively narrow spectral band (e.g. lasers). Every wave of visible light is perceived as a spectral color; when viewed as a continuous spectrum, these colors are seen as the familiar rainbow. Non-spectral colors (or extra-spectral colors) are evoked by a combination of spectral colors. In color spaces In color spaces which include all, or most spectral colors, they form a part of boundary of the set of all real colors. When considering a three-dimensional color space (which includes luminance), the spectral colors form a surface. When excluding luminance and considering a two-dimensional color space ( chromaticity diagram), the spectral colors form a curve known as the spectral locus. For example, the spectral locus of the CIE xy chromaticity diagram contains all the spectral colors (to the eye of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |