|
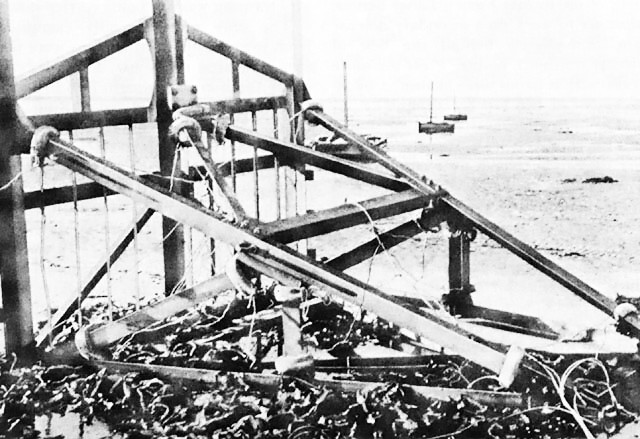
Cointet-element
The Cointet-element, also known as a Belgian Gate or C-element, was a heavy steel fence about wide and high, typically mounted on concrete rollers, used as a mobile Anti-tank obstacles, anti-tank obstacle during World War II. Each individual fence element weighed about and was movable (e.g. with two horses) through the use of two fixed and one rotating roller. Its invention is attributed to a French colonel (later general), Léon-Edmond de Cointet de Fillain who came up with the idea in 1933 to be used in the Maginot Line. Besides their use as barricades to the entrances of forts, bridges and roads, the heavy fences were used in the Belgian "Iron Wall" of the K-W Line, Koningshooikt–Wavre Line (also known as "Dyle Line") and were re-used as beach obstacles on the ''Atlantic Wall'' defending Normandy from Allied invasion. History The Cointet-element formed the main barricade of the Belgian K-W Line, a tank barricade that was built between September 1939 and May 1940. Foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgian Gate
The Cointet-element, also known as a Belgian Gate or C-element, was a heavy steel fence about wide and high, typically mounted on concrete rollers, used as a mobile anti-tank obstacle during World War II. Each individual fence element weighed about and was movable (e.g. with two horses) through the use of two fixed and one rotating roller. Its invention is attributed to a French colonel (later general), Léon-Edmond de Cointet de Fillain who came up with the idea in 1933 to be used in the Maginot Line. Besides their use as barricades to the entrances of forts, bridges and roads, the heavy fences were used in the Belgian "Iron Wall" of the Koningshooikt–Wavre Line (also known as "Dyle Line") and were re-used as beach obstacles on the ''Atlantic Wall'' defending Normandy from Allied invasion. History The Cointet-element formed the main barricade of the Belgian K-W Line, a tank barricade that was built between September 1939 and May 1940. Following tests, the Belgian Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-W Line
The Koningshooikt–Wavre Line, abbreviated to KW Line (; ) and often known as the Dyle Line after the Dijle (Dyle) river, was a -long fortified line of defence prepared by the Belgian Army between Koningshooikt ( Province of Antwerp) and Wavre ( Province of Brabant) which was intended to protect Brussels from a possible German invasion. Construction on the KW Line began in September 1939 after World War II had begun but while Belgium itself remained a neutral state. It was subsequently extended southwards from Wavre towards Namur ( Province of Namur). The line itself consisted of bunkers, anti-tank ditches, and barricades including so-called Cointet-elements and played a key role in Allied strategy during the German invasion of Belgium in May 1940. However, its role in the actual fighting was ultimately minimal. In 2009 an inventory of surviving emplacements was begun. Background In October 1936, Belgium abandoned its previous military alliance with France, fearful that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalities, 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country. It is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, and is separate from the Flemish Region (Flanders), within which it forms an enclave, and the Walloon Region (Wallonia), located less than to the south. Brussels grew from a small rural settlement on the river Senne (river), Senne to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the Second World War, it has been a major centre for international politics and home to numerous international organisations, politicians, Diplomacy, diplomats and civil servants. Brussels is the ''de facto' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Equipment Introduced In The 1930s
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Belgium During World War II
Despite being neutral at the start of World War II, Belgium and its colonial possessions found themselves at war after the country was invaded by German forces on 10 May 1940. After 18 days of fighting, in which Belgian forces were pushed back into a small pocket in the north-west of the country, the Belgian military surrendered to the Germans, beginning an occupation that would endure until 1944. The surrender of 28 May was ordered by King Leopold III without the consultation of his government and sparked a political crisis after the war. Despite the capitulation, many Belgians managed to escape to the United Kingdom where they formed a government and army-in-exile on the Allied side. The Belgian Congo remained loyal to the Belgian government in London and contributed significant material and human resources to the Allied cause. Many Belgians were involved in both armed and passive resistance to German forces, although some chose to collaborate with the German forces. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortification (obstacles)
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a border ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon's Teeth (fortification)
Dragon's teeth are Pyramid (geometry), pyramidal anti-tank obstacles of reinforced concrete first used during the Second World War to impede the movement of tanks and mechanised infantry. The idea was to slow down and channel tanks into Kill zone, killing zones where they could easily be disposed of by anti-tank weapons. They were employed extensively, particularly on the Siegfried Line. World War II Dragon's teeth were used by several armies in the European Theatre of World War II, European theatre. The Wehrmacht, Germans made extensive use of them on the Siegfried Line and the Atlantic Wall. Typically, each tooth was tall. Land mines were often laid between teeth, and further obstacles were constructed along the lines of teeth, such as barbed wire to impede infantry or diagonally-placed steel beams to further hinder tanks. Many were laid in the United Kingdom in 1940–1941, as part of the effort to strengthen the country's British anti-invasion preparations of World War II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Hedgehog
The Czech hedgehog ( or ') is a static anti-tank obstacle defense made of metal angle beams or I-beams (that is, lengths with an L- or 𝐈-shaped cross section). It is similar in shape to metal knucklebones, although on a much larger scale. The hedgehog is very effective in keeping light to medium tanks and vehicles from penetrating a line of defense; it maintains its function even when tipped over by a nearby explosion. Although Czech hedgehogs may provide some scant cover for attacking infantry, infantry forces are generally much less effective against fortified defensive positions than mechanized units. The author of the Czechoslovak invention is Major František Kašík. History Origin The Czech hedgehog's name refers to its origin in Czechoslovakia. The hedgehogs were originally used on the Czech–German border by the Czechoslovak border fortifications—a massive but never-completed fortification system that was turned over to Germany in 1938 after the occupation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheval De Frise
The cheval de frise (, plural chevaux de frise ; , plural , "Frisian horses") was a defensive obstacle, existing in a number of forms, principally as a static anti-cavalry obstacle but also quickly movable to close breaches. The term was also applied to underwater constructions used to prevent the passage of ships or other vessels on rivers. In the anti-cavalry role the cheval de frise typically comprised a portable frame (sometimes just a simple log) with many projecting spikes. Wire obstacles ultimately made this type of device obsolete. The invention of the cheval de frise is attributed to ancient China. The concept of using a defensive obstacle made of wooden or metal stakes predates its use in Europe. Historical records suggest that similar types of defensive barriers, known as ''teng pai'' or ''mó pai'', were used in China as early as the 4th century BC. These early versions of the cheval de frise were employed to protect cities, forts, and other strategic locations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantikwall
The Atlantic Wall () was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticipated Allied invasion of Nazi-occupied Europe from the United Kingdom, during World War II. The manning and operation of the Atlantic Wall was administratively overseen by the German Army, with some support from ''Luftwaffe'' ground forces. The ''Kriegsmarine'' (German Navy) maintained a separate coastal defence network, organised into a number of sea defence zones. Hitler ordered the construction of the fortifications in 1942 through his Führer Directive No. 40. More than half a million French workers were drafted to build it. The wall was frequently mentioned in Nazi propaganda, where its size and strength were usually exaggerated. The fortifications included colossal coastal guns, batteries, mortars, and artillery, and thousands of artillery pieces were sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dender
The Dender () or Dendre () is a long river in Belgium, the right tributary of the river Scheldt. The confluence of the two rivers is in the Belgian town of Dendermonde. The Western or Little Dender is long and begins in Barry near Leuze-en-Hainaut at an elevation of about above sea level. It begins as several canals in the fields merging together to form the Little Dender. As such, it does not have any one specific source. The source of the Eastern Dender, which is long, is near Jurbise at a height of above sea level. The two rivers meet in the town of Ath. From that confluence, the river is called the Dender proper. From Ath, the Dender passes into the Denderstreek through the cities and towns of Geraardsbergen, south of which its tributary, the Mark, flows into it. From this confluence, the river continues to flow through Ninove, Denderleeuw, and Aalst, before ending in Dendermonde. The Dender is navigable up to Aalst for small ships up to 600 tons and further upstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninove
Ninove () is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flanders, Flemish province of East Flanders in Belgium. It is on the river Dender, and is part of the Denderstreek. The municipality comprises the city of Ninove proper and since the 1976 merger of the towns of , , , , Meerbeke, , , , , and . On 1 January 2023 Ninove had a total population of 40.090. The total area is 72.57 km2 which gives a population density of 553 inhabitants per km2. History The oldest version of the name "Ninove", ''Neonifus'' dates from the 9th century. Later versions of the city name were ''Ninive'' and ''Nineve''. The current version of the city name dates from the 14th century. The origin of the city name is not clear. There are two theories about the origin. One states that name is from Roman origin, the other states that it is of Franks, Frankish origin. The meaning of the name, however, is known. Ninove means "nieuw weiland" or in English, "new pasture". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |