|
Coelophysidae
Coelophysoidea is an extinct clade of theropod dinosaurs common during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the coelurosaurs, with which they were formerly classified, and some species had delicate cranial crests. Sizes range from about 1 to 6 m in length. It is unknown what kind of external covering coelophysoids had, and various artists have portrayed them as either scaly or feathered. Some species may have lived in packs, as inferred from sites where numerous individuals have been found together. Examples of coelophysoids include ''Coelophysis'', ''Procompsognathus'' and '' Liliensternus''. Most dinosaurs formerly referred to as being in the dubious taxon "Podokesauridae" are now classified as coelophysoids. The family Coelophysidae, which is contained within Coelophysoidea, flourished in the Late Triassic and Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podokesaurus
''Podokesaurus'' is a genus of coelophysoid dinosaur that lived in what is now the eastern United States during the Early Jurassic Period. The first fossil was discovered by the geologist Mignon Talbot near Mount Holyoke, Massachusetts, in 1910. The specimen was fragmentary, preserving much of the body, limbs, and tail. In 1911, Talbot described and named the new genus and species ''Podokesaurus holyokensis'' based on it. The full name can be translated as "swift-footed lizard of Holyoke". This discovery made Talbot the first woman to find and describe a non-bird dinosaur. The holotype fossil was recognized as significant and was studied by other researchers, but was lost when the building it was kept in burned down in 1917; no unequivocal ''Podokesaurus'' specimens have since been discovered. It was made state dinosaur of Massachusetts in 2022. Estimated to have been about in length and in weight, ''Podokesaurus'' was lightly constructed with hollow bones, and would have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panguraptor
''Panguraptor'' ("Pangu Chinese godplunderer") is a genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur known from fossils discovered in Lower Jurassic rocks of southern China. The type and only known species is ''Panguraptor lufengensis''. The generic name refers to the deity Pangu but also to the supercontinent Pangaea for which in a geological context the same characters are used: 盘古. ''Raptor'' means "seizer", "robber" in Latin. The specific name is a reference to the Lufeng Formation. It was described in 2014 by You Hai-Lu and colleagues. History and naming The specimen that would be named ''Panguraptor'' was discovered by a survey team of the Bureau of Land and Resources of Lufeng County, China, on the hillside behind Xiaolishu Village, Lufeng Dinosaur Mountain Town. The team found the partially articulated skeleton exposed on the slope on . Due to weathering, there was not time to slowly clean the skeleton, so it was glued and plastered on location over the course of two days befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
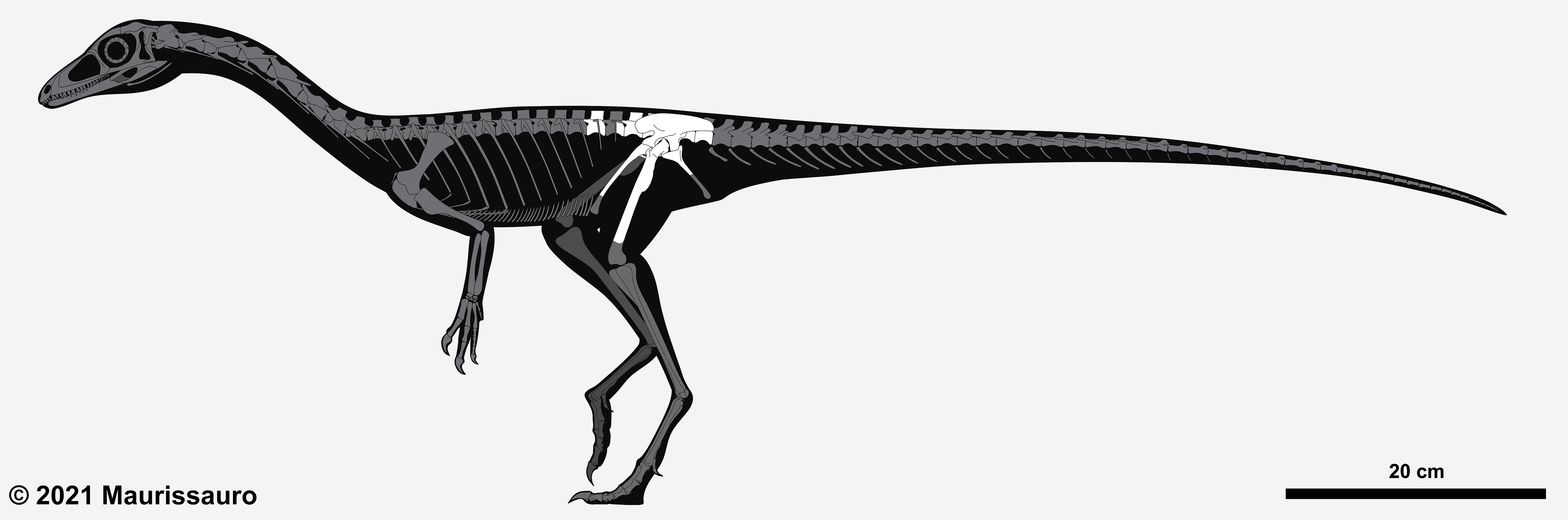
Procompsognathus
''Procompsognathus'' is an extinct genus of Coelophysidae, coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 210 million years ago during the later part of the Triassic Period (geology), Period, in what is now Germany. ''Procompsognathus'' was a small-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to long. Discovery and naming The fragmentary and poorly preserved skeleton of ''Procompsognathus'' was found in the Middle Stubensandstein member of the Löwenstein Formation at the ''Weiße Steinbruch'', the quarry of Albert Burrer on the northern slopes of the Baden-Württemberg, Stromberg region near Pfaffenhofen, Baden-Württemberg, Pfaffenhofen in Württemberg, Germany. The discovery was made by Albert Burrer in the spring of 1909 in white sandstone and gray/blue marl sediments that were deposited during the Norian Stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Triassic period. The holotype SMNS 12591, consisted of three blocks of sandstone: on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( Traditional English pronunciation of Latin, traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is a genus of coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived Approximation, approximately 215 to 201.4 million years ago during the Late Triassic Period (geology), period from the middle Norian to Rhaetian age in what is now the southwestern United States. ''Megapnosaurus'' was once considered to be a species within this genus, but this interpretation has been challenged and the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' is now considered valid. ''Coelophysis'' was a small, slenderly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore that could grow up to long. It is one of the earliest known dinosaur genera. Scattered material representing similar animals has been found worldwide in some Late Triassic and Early Jurassic formations. The type species ''C. bauri'', originally given to the genus ''Coelurus'' by Edward Drinker Cope in 1887, was described by the latter in 1889. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapnosaurus
''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μέγα = "big", ἄπνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαῦρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Africa. The species was a small to medium-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to long and weigh up to . It was originally given the genus name ''Syntarsus'', but that name was later determined to be preoccupied by a beetle. The species was subsequently given a new genus name, ''Megapnosaurus'', by Ivie, Ślipiński & Węgrzynowicz in 2001. Some studies have classified it as a species within the genus ''Coelophysis,'' but this interpretation has been challenged by more subsequent studies and the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' is now considered valid. Discovery and history The first fossils of ''Megapnosaurus'' were found in 1963 by a group of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis Bauri
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is a genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 215 to 201.4 million years ago during the Late Triassic period from the middle Norian to Rhaetian age in what is now the southwestern United States. ''Megapnosaurus'' was once considered to be a species within this genus, but this interpretation has been challenged and the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' is now considered valid. ''Coelophysis'' was a small, slenderly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore that could grow up to long. It is one of the earliest known dinosaur genera. Scattered material representing similar animals has been found worldwide in some Late Triassic and Early Jurassic formations. The type species ''C. bauri'', originally given to the genus '' Coelurus'' by Edward Drinker Cope in 1887, was described by the latter in 1889. The names ''Longosaurus'' and ''Rioarribasaurus'' are synonymous with ''Coelophysis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendraig
''Pendraig'' (meaning "chief dragon" in Middle Welsh) is a genus of coelophysoid theropod dinosaur from South Wales. It contains one species, ''Pendraig milnerae'', named after Angela Milner. The specimen was discovered in the Pant-y-Ffynnon Quarry, Pant-y-Ffynnon quarry. In life it would have measured in length. History The holotype of ''Pendraig'' were found in the Pant-y-Ffynnon Quarry, Pant-y-ffynnon Quarry in Wales in 1952 by Kenneth Kermack, Kenneth Alexander Kermack and Pamela Lamplugh Robinson along with the holotypes of ''Pantydraco'' and ''Terrestrisuchus'', and were subsequently lost in the collections of the Natural History Museum, London. The fossils were originally thought to belong to a "coelurosaur" (in the outdated sense of the word) and even subsequently classified as a species of "''Syntarsus''" (now ''Megapnosaurus'' or ''Coelophysis''). Recently Angela Milner and Susannah Maidment rediscovered the fossils stored with some crocodile bones (likely ''Terrestris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gojirasaurus
''Gojirasaurus'' (meaning "Godzilla lizard") is a genus of " coelophysoid" theropod dinosaur from the Late Triassic of New Mexico. It is named after the giant monster movie character , and contains a single species, ''Gojirasaurus quayi''. Discovery ''Gojirasaurus quayi'' was described and named by Kenneth Carpenter in 1997 based on a partial skeleton, the holotype specimen UCM 47221, from Quay County, New Mexico. The holotype is an assortment of various postcranial bones, including a right scapula, right pubis, left tibia, left metatarsal V, four vertebral centra, a neural arch, and fragments of ribs and gastralia. In addition, a single large serrated tooth is associated with the postcranial material. The holotype is housed in the collections of the University of Colorado Museum of Natural History, in Boulder, Colorado. The specimen hails from purplish-grey mudstones of the Bull Canyon Formation (sometimes called the Cooper Canyon Formation), a major fossiliferou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucianovenator
''Lucianovenator'' is an extinct genus of coelophysidae, coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur which lived in Argentina during the Triassic. The genus name ''Lucianovenator'' translates to "Luciano's hunter", in reference to Don Luciano Leyes, who first reported the remains. The species name ''bonoi'' refers to Tulio del Bono, a local scientific authority who collaborated on the describers' research. It is one of the few Neotheropoda, neotheropods known from South America. Discovery The holotype (PVSJ 906) of ''Lucianovenator bonoi'' was found in the "Quebrada del puma" locality of the Quebrada del Barro Formation in Argentina, which is estimated to be from the late Norian to Rhaetian in age, approximately 210 to 202 million years ago. PVSJ 906 represents an articulated vertebral sequence from the third Cervical vertebrae, cervical to fourth dorsal vertebra, as well as a sacrum and a partial pelvis. In addition, three more specimens were referred to ''Lucianovenator''. These in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis? Kayentakatae
''Coelophysis''? ''kayentakatae'' is an extinct species of neotheropod dinosaur that lived approximately 200–196 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now the southwestern United States. It was originally named ''Syntarsus kayentakatae'', but the genus ''Syntarsus'' was found to be preoccupied by a Colydiine beetle, so it was moved to the genus ''Megapnosaurus'', and then to ''Coelophysis''. A 2022 reassessment suggests that this species may require a new genus name. Discovery The holotype of "S." ''kayentakatae'' (MNA V2623) was recovered in the Silty Facies Member of the Kayenta Formation in Arizona. This material was collected in 1977 from carbonaceous sandstone deposited during the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages of the Jurassic period.Padian, K (1997) Glen Canyon Group In: Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs, edited by Currie, P. J., and Padian, K., Academic Press. Specimen UCMP 128659 was discovered in 1982 and referred to ''Megapnosaurus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camposaurus
''Camposaurus'' ( ) is a coelophysid dinosaur genus from the Norian stage of the Late Triassic period of North America. The pertinent fossil remains date back to the early to middle Norian stage, and is widely regarded as the oldest known neotheropod. Description ''Camposaurus'' is a small, carnivorous, theropod dinosaur. Its approximate length and weight cannot be reliably estimated because of the sparse material that is known from this genus. ''Camposaurus'' is known from partial lower leg bones, holotype UCMP 34498 (which includes distal tibiae, distal fibulae, and astragalocalcanea), and other fragmentary material. Like other Coelophysidae, coelophysids, it has fused tibio-tarsals and fibulo-tarsals. Unlike its relatives, the area of the tibia that fits with the fibula has a distinct ridge at the back. Another unique feature is the lack of a large medial Condyle (anatomy), condyle on the Talus bone, astragalus. The type species, ''C. arizonensis'', was formally named and des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furcula
The (Latin for "little fork"; : furculae) or wishbone is a forked bone found in most birds and some species of non-avian dinosaurs, and is either an interclavicle or formed by the fusion of the two clavicles. In birds, its primary function is in the strengthening of the thoracic skeleton to withstand the rigors of flight. In birds The furcula works as a strut between a bird's shoulders, and articulates to each of the bird's scapulae. In conjunction with the coracoid and the scapula, it forms a unique structure called the triosseal canal, which houses a strong tendon that connects the supracoracoideus muscles to the humerus. This system is responsible for lifting the wings during the recovery stroke. As the thorax is compressed by the flight muscles during downstroke, the upper ends of the furcula spread apart, expanding by as much as 50% of its resting width, and then contracts. X-ray films of starlings in flight have shown that in addition to strengthening the thorax, the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |