|
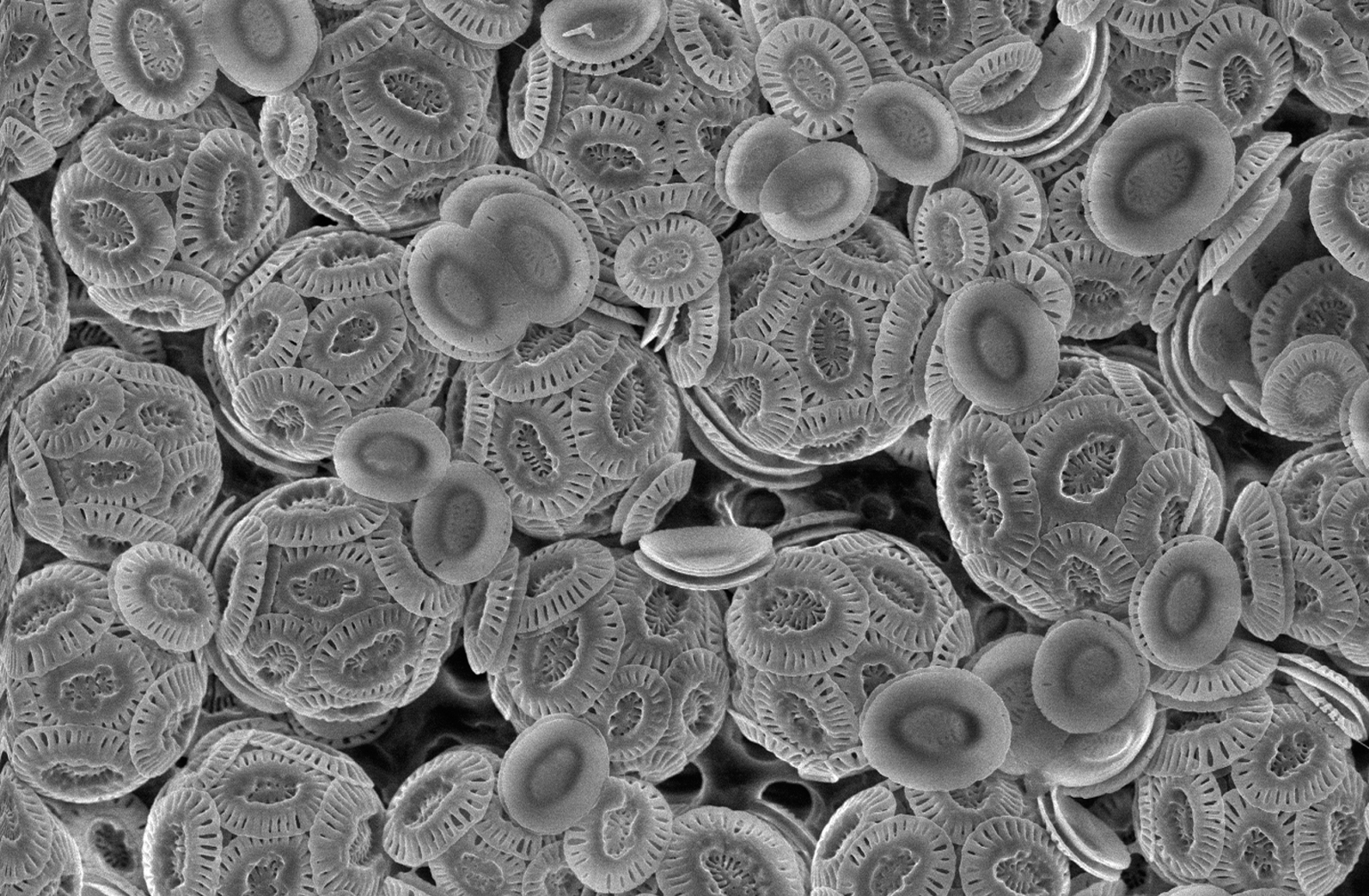
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker (ecologist), Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division (botany), division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively Marine (ocean), marine, are photosynthesis, photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the Photic zone, sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coccosphere
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a '' coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coccolithophores
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a '' coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calcifying Organism
Marine biogenic calcification is the production of calcium carbonate by organisms in the global ocean. Marine biogenic calcification is the biologically mediated process by which marine organisms produce and deposit calcium carbonate minerals to form skeletal structures or hard tissues. This process is a fundamental aspect of the life cycle of some marine organisms, including corals, mollusks, foraminifera, certain types of plankton, and other calcifying marine invertebrates. The resulting structures, such as Seashell, shells, skeletons, and coral reefs, function as protection, support, and shelter and create some of the most biodiverse habitats in the world. Marine biogenic calcifiers also play a key role in the biological carbon pump and the biogeochemical cycling of nutrients, alkalinity, and organic matter. Processes of Marine Biogenic Calcification Biochemical mechanisms Cellular and molecular processes of biogenic calcification Calcium carbonate plays a fundamental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
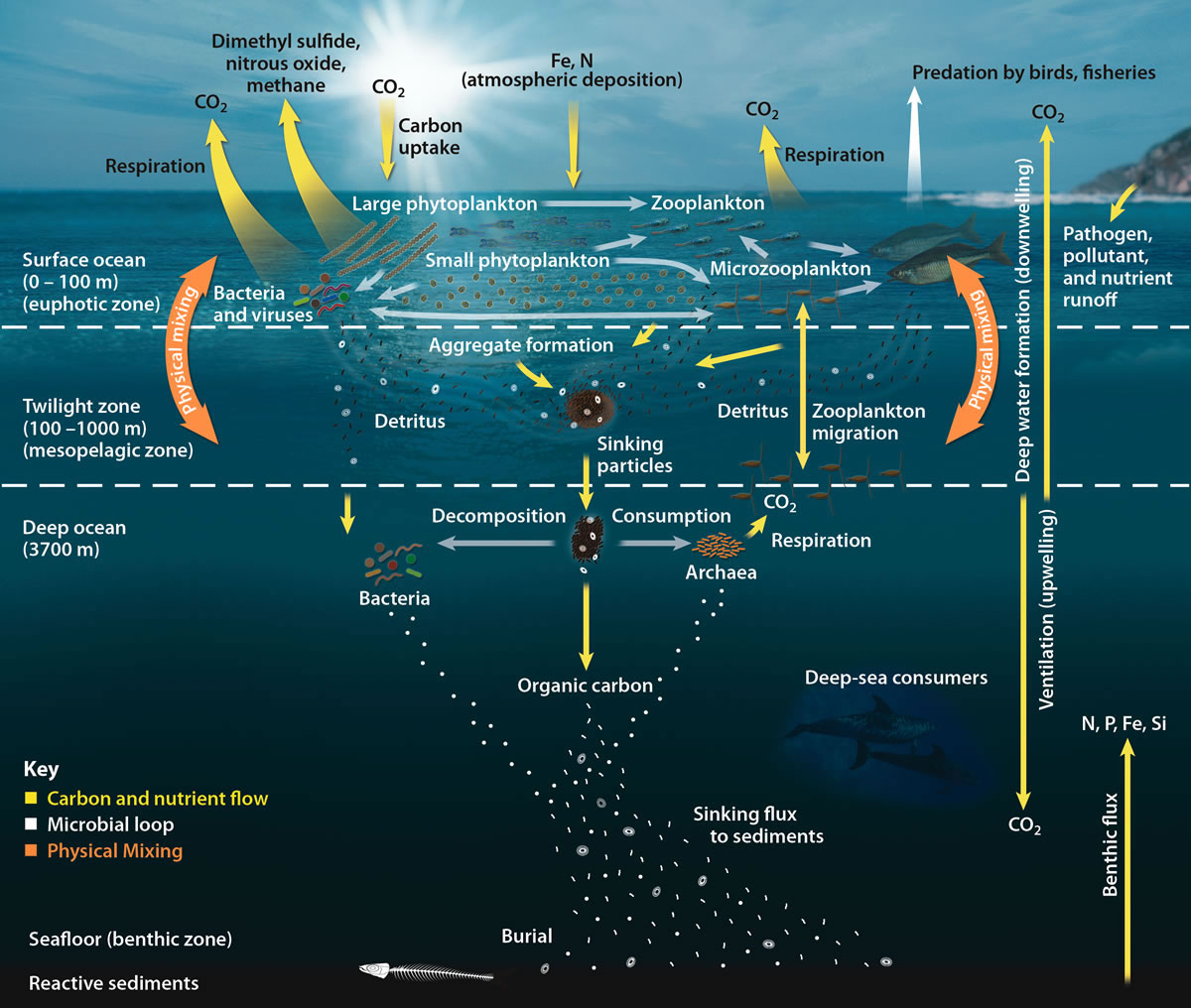
Biological Pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated process which results in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protista
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic rank, taxonomic kingdom (biology), kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroup (biology), supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR supergroup, SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic diversity, genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
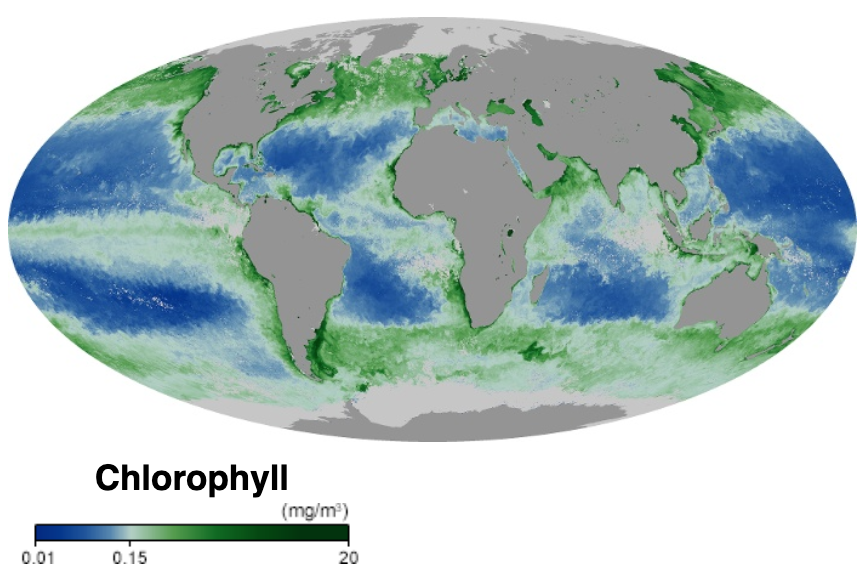
Marine Primary Production
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotrophs. Most marine primary production is generated by a diverse collection of marine microorganisms called algae and cyanobacteria. Together these form the principal primary producers at the base of the ocean food chain and produce half of the world's oxygen. Marine primary producers underpin almost all marine animal life by generating nearly all of the oxygen and food marine animals need to exist. Some marine primary producers are also ecosystem eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
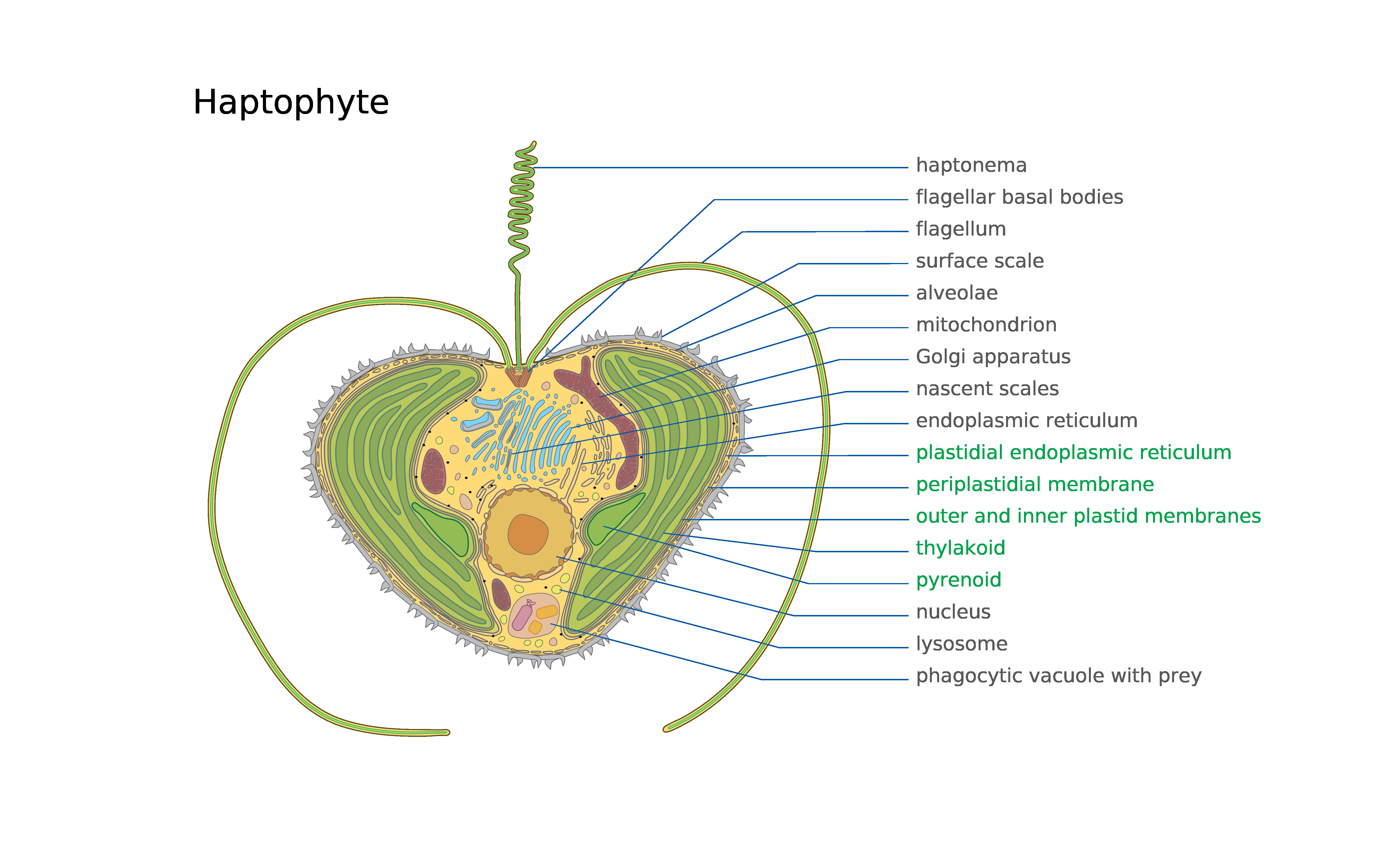
Haptophyta
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for '' Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at the class rank rather than as a division. Although the phylogenetics of this group has become much better understood in recent years, there remains some dispute over which rank is most appropriate. Characteristics The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algal endosymbionts. Haptophyte chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a, c1, and c2 but lack chlorophyll b. For carotenoids, they have beta-, alpha-, and gamma- carotenes. Like diatoms and brown algae, they have also fucoxanthin, an oxidized isoprenoid derivative that is likely the most important driver of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, microscopic fungi, and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. fresh water, Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in lakes and rivers. Mostly, plankton just drift where currents take them, though some, like jellyfish, swim slowly but not fast enough to generally overcome the influence of currents. Although plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, there are also airborne versions that live part of their lives drifting in the at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
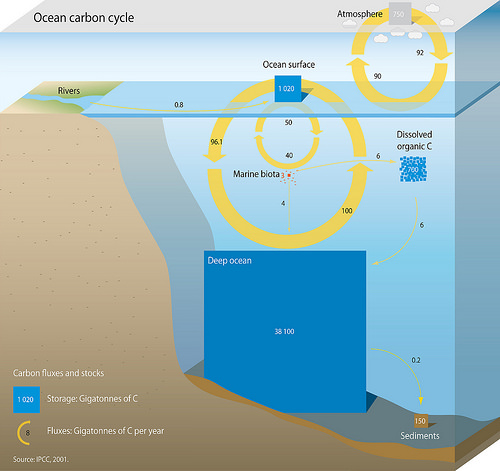
Oceanic Carbon Cycle
The oceanic carbon cycle (or marine carbon cycle) is composed of processes that exchange carbon between various pools within the ocean as well as between the atmosphere, Earth interior, and the seafloor. The carbon cycle is a result of many interacting forces across multiple time and space scales that circulates carbon around the planet, ensuring that carbon is available globally. The Oceanic carbon cycle is a central process to the global carbon cycle and contains both inorganic carbon (carbon not associated with a living thing, such as carbon dioxide) and organic carbon (carbon that is, or has been, incorporated into a living thing). Part of the marine carbon cycle transforms carbon between non-living and living matter. Three main processes (or pumps) that make up the marine carbon cycle bring atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into the ocean interior and distribute it through the oceans. These three pumps are: (1) the solubility pump, (2) the carbonate pump, and (3) the biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hacrobia
The cryptomonads-haptophytes assemblage is a proposed but disputed monophyletic grouping of unicellular eukaryotes that are not included in the SAR supergroup. Several alternative names have been used for the group, including Hacrobia (derived from "ha-" referring to Haptophyta, "-cr-" referring to cryptomonads, and "-bia" as a general suffix referring to life); CCTH (standing for Cryptophyta, Centrohelida, Telonemia and Haptophyta); and "Eukaryomonadae". , it is unclear whether this group is monophyletic or not; results of phylogenetic studies are "often dependent on the selection of taxa and gene data set". Two 2012 studies produced opposite results. Members In the past, heterokonts, haptophytes, and cryptomonads have sometimes been grouped together in a group known as chromists. Though the heterokonts are now split out, Cryptophyta and Haptophyta are considered in some studies to be closely related (and are sometimes simply referred to as the "Cryptophyta+Haptophyta" g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photic Zone
The photic zone (or euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone) is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of Aquatic ecosystem, aquatic life due to the activity (Marine primary production, primary production) of the phytoplankton. The thicknesses of the photic and euphotic zones vary with the intensity of sunlight as a function of season and latitude and with the degree of water turbidity. The bottommost, or aphotic, zone is the region of perpetual darkness that lies beneath the photic zone and includes most of the ocean waters. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |