|
Closed-cell PVC Foamboard
Closed-cell PVC foamboard is a lightweight rigid material used primarily in the manufacture of signs and displays. It is considered robust for outdoor use, being immune to rain and resistant to wind and sunlight. History In 1912, the first patents for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) were filed in Britain and Germany. It was not until the early 1930s that PVC was able to be produced cheaply, limiting its marketable applications for the time. World War II helped make the substance popular, as manufacturers used it to make an assortment of items for soldiers. It was here that PVC's water resistance was shown to be an important property, and tools made from PVC were used in many marine applications. After the war, PVC was not a popular choice of materials in the marine industry due to its density. In the 1970s, the need for a strong, moisture-resistant material led to plastic manufactures working with PVC to make it lighter. This led to the creation of PVC foamboard, by combining PVC with po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force. The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is. Calculations The stiffness, k, of a body is a measure of the resistance offered by an elastic body to deformation. For an elastic body with a single degree of freedom (DOF) (for example, stretching or compression of a rod), the stiffness is defined as k = \frac where, * F is the force on the body * \delta is the displacement produced by the force along the same degree of freedom (for instance, the change in length of a stretched spring) Stiffness is usually defined under quasi-static conditions, but sometimes under dynamic loading. In the International System of Units, stiffness is typically measured in newtons per meter (N/m). In Imperial units, stiffness is typically measured in pounds (lbs) per inch. Generally speaking, deflections (or motions) of an infinitesima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
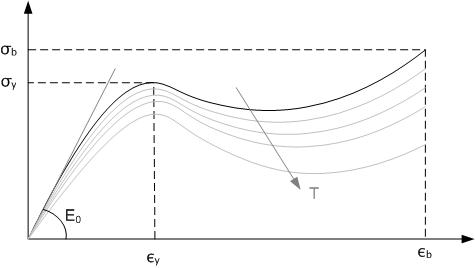
Heat Gun
A heat gun is a device used to emit a stream of hot air, usually at temperatures between , with some hotter models running around , which can be held by hand. Heat guns usually have the form of an elongated body pointing at what is to be heated, with a handle fixed to it at right angles and a pistol grip trigger in the same pistol form factor as many other power tools. Though it shares similarities to a hair dryer, it is not meant as a substitute for the latter, which safely spreads the heat out across its nozzle to prevent scalp burning and has a limited temperature range, while heat guns have a concentrated element and nozzle, along with higher temperatures, which can easily scald the scalp or catch the hair on fire. Construction A heat gun comprises a source of heat, usually an electrically heated element or a propane/liquified petroleum gas, a mechanism to move the hot air such as an electric fan, unless gas pressure is sufficient; a nozzle to direct the air, which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. While typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser most commonly through optics. The laser optics and CNC (computer numerical control) are used to direct the laser beam to the material. A commercial laser for cutting materials uses a motion control system to follow a CNC or G-code of the pattern to be cut onto the material. The focused laser beam is directed at the material, which then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish. History In 1965, the first production laser cutting machine was used to drilling, drill holes in diamond Die (manufacturing), dies. This machine was made by the Western Electric Engineering Research Center. In 1967, the British pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dioxins And Dioxin-like Compounds
Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds (DLCs) are a group of chemical compounds that are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environmental pollutant, environment. They are mostly by-products of burning or various industrial processes or, in the case of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl, PCBs and polybrominated biphenyl, PBBs, unwanted minor components of intentionally produced mixtures. Some of them are highly toxic, but the toxicity among them varies 30,000-fold. They are grouped together because their mechanism of action is the same. They activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AH receptor), albeit with very different binding affinities, leading to high differences in toxicity and other effects. They include: * Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, Polychlorinated dibenzo''-p-''dioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins. PCDDs are derivatives of dibenzodioxin, dibenzo''-p-''dioxin. There are 75 PCDD congener (chemistry), congeners, differing in the number and location of chlorine atoms, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. Etymology Because it was produced from halite, rock salt according to the methods of Johann Rudolph Glauber, hydrochloric acid was historically called by European alchemists ''spirits of salt'' or ''acidum salis'' (salt acid). Both names are still used, especially in other languages, such as , , , , , , , , , , (''ensan''), zh, 盐酸 (''yánsuān''), and (''yeomsan''). Gaseous HCl was called ''marine acid air''. The name ''muriatic acid'' has the same origin (''muriatic'' means "pertaining to brine or salt", hence ''muriate'' means hydrochloride), and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Theatrical Property
A prop, formally known as a (theatrical) property, is an object actors use on stage or screen during a performance or screen production. In practical terms, a prop is considered to be anything movable or portable on a stage or a set, distinct from the actors, scenery, costumes, and electrical equipment. This includes handheld items such as books, cups, weapons, and tools that actors interact with during a performance. Props help to create a realistic setting, convey information, or add to the storytelling by showing details about the characters or the environment. Term The earliest known use of the term "properties" in English to refer to stage accessories is in the 1425 CE morality play, '' The Castle of Perseverance''. During the Renaissance in Europe, small acting troupes functioned as cooperatives, pooling resources and dividing any income. Many performers provided their own costumes and small objects needed for performance, hence the term "property" suggesting these ite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scale Model
A scale model is a physical model that is geometrically similar to an object (known as the ''prototype''). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small prototypes such as anatomical structures or subatomic particles. Models built to the same scale as the prototype are called '' mockups''. Scale models are used as tools in engineering design and testing, promotion and sales, filmmaking special effects, military strategy, and hobbies such as rail transport modeling, wargaming and racing; and as toys. Model building is also pursued as a hobby for the sake of artisanship. Scale models are constructed of plastic, wood, or metal. They are usually painted with enamel, lacquer, or acrylics. Model prototypes include all types of vehicles (railroad trains, cars, trucks, military vehicles, aircraft, and spacecraft), buildings, people, and science fiction themes (spaceships and robots). Methods M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paints
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based, and each has distinct characteristics. Primitive forms of paint were used tens of thousands of years ago in cave paintings. Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted (such as a house). History Paint was used in some of the earliest known human artworks. Some cave paintings drawn with red or yellow ochre, hematite, manganese oxide, and charcoal may have been made by early ''Homo sapiens'' as long as 40,000 years ago. Paint may be even older. In 2003 and 2004, South African archeologists reported finds in Blombos Cave of a 100,000-year-ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Signage
Signage is the design or use of signs and symbols to communicate a message. Signage also means signs ''collectively'' or being considered as a group. The term ''signage'' is documented to have been popularized in 1975 to 1980. Signs are any kind of visual graphics created to display information to a particular audience. This is typically manifested in the form of wayfinding information in places such as streets or on the inside and outside buildings. Signs vary in form and size based on location and intent, from more expansive banners, billboards, and murals, to smaller street signs, street name signs, sandwich boards and lawn signs. Newer signs may also use digital signage, digital or electronic sign, electronic displays. The main purpose of signs is to communicate, to convey information designed to assist the receiver with decision-making based on the information provided. Alternatively, promotional signage may be designed to persuade receivers of the merits of a given produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped, and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |