|
Chromosome 20
Chromosome 20 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 20 spans around 66 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2 and 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 20 was fully sequenced in 2001 and was reported to contain over 59 million base pairs. Since then, due to sequencing improvements and fixes, the length of chromosome 20 has been updated to just over 66 million base pairs. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 20. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
G Banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases (mainly chromosomal abnormalities) through the photographic representation of the entire chromosome complement.Speicher, Michael R. and Nigel P. Carter. "The New Cytogenetics: Blurring the Boundaries with Molecular Biology." ''Nature'' Reviews Genetics, Vol 6. Oct 2005. Method The metaphase chromosomes are treated with trypsin (to partially digest the chromosome) and Staining (biology), stained with Giemsa stain. Heterochromatin, Heterochromatic regions, which tend to be rich with adenine and thymine (AT-rich) DNA and relatively gene-poor, stain more darkly in G-banding. In contrast, less condensed chromatin (Euchromatin)—which tends to be rich with guanine and cytosine (GC-content, GC-rich) and more Transcription (genetics), transcriptionally acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
UniProt
UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature. It is maintained by the UniProt consortium, which consists of several European bioinformatics organisations and a foundation from Washington, DC, USA. The UniProt consortium The UniProt consortium comprises the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB), and the Protein Information Resource (PIR). EBI, located at the Wellcome Trust Genome Campus in Hinxton, UK, hosts a large resource of bioinformatics databases and services. SIB, located in Geneva, Switzerland, maintains the ExPASy (Expert Protein Analysis System) servers that are a central resource for proteomics tools and databases. PIR, hosted by the National Biomedical Research Foundation (NBRF) at the George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BPIFA3
BPI fold containing family A, member 3 (BPIFA3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFA3'' gene. The gene is also known as ''SPLUNC3'' and ''C20orf71'' in humans and the orthologous gene in mice is ''1700058C13Rik''. There are multiple variants of the BPIFA3 projected to be a secreted protein. It is very highly expressed in testis with little or no expression in other tissues. The Human Protein Atlas project and Mouse ENCODE Consortium report RNA-Seq expression at RPKM levels (reads per kilobases of transcript per 1 million mapped reads ) of 29.1 for human testis and 69.4 for mouse, but 0 for all other tissues. Similarly, the Bgee consortium, using multiple techniques in addition to RNA-Seq, reports a relative Expression Score of 95.8 out of 100 for testis and 99.0 for sperm in humans; however low levels of BPIFA3 between 20 and 30 were seen for a variety of tissues such as muscle, glands, prostate, nervous system, and skin. Superfamily BPIFA3 is a member of a BPI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
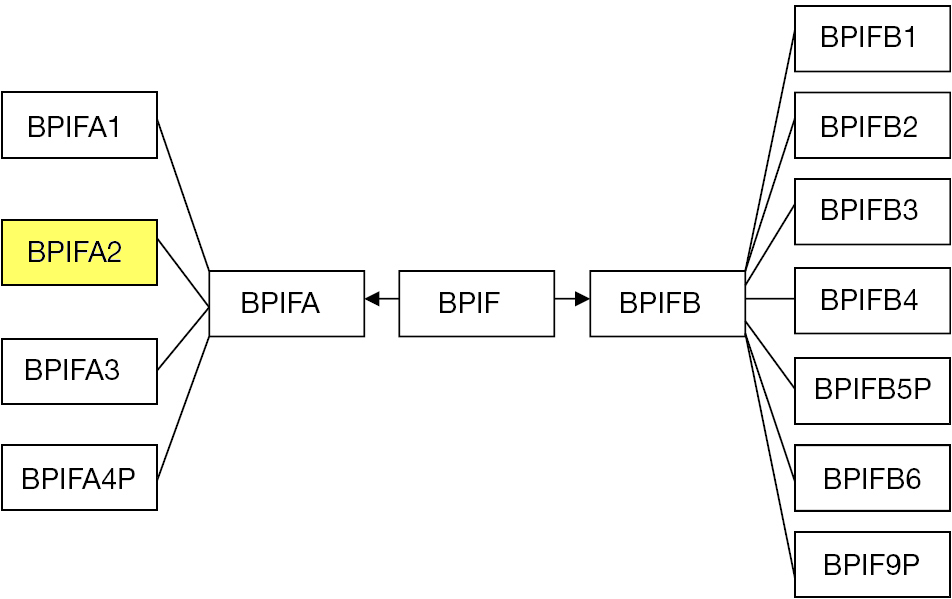
BPIFA2
BPI fold containing family A, member 2 (BPIFA2), also known as Parotid Secretory Protein (PSP), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFA2'' gene. The ''BPIFA2'' gene sequence predicts multiple transcripts ( splice variants); 2 mRNA variants have been well characterized. The resulting BPIFA2 is a secreted protein, expressed at very high levels in the parotid (salivary) gland; at high levels in oropharyngeal mucosa, including tongue; and at moderate levels many other tissue types and glands including mammary gland, testis, lung, bladder, blood, prostate, adrenal gland, kidney, and pancreas. Superfamily BPIFA2 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
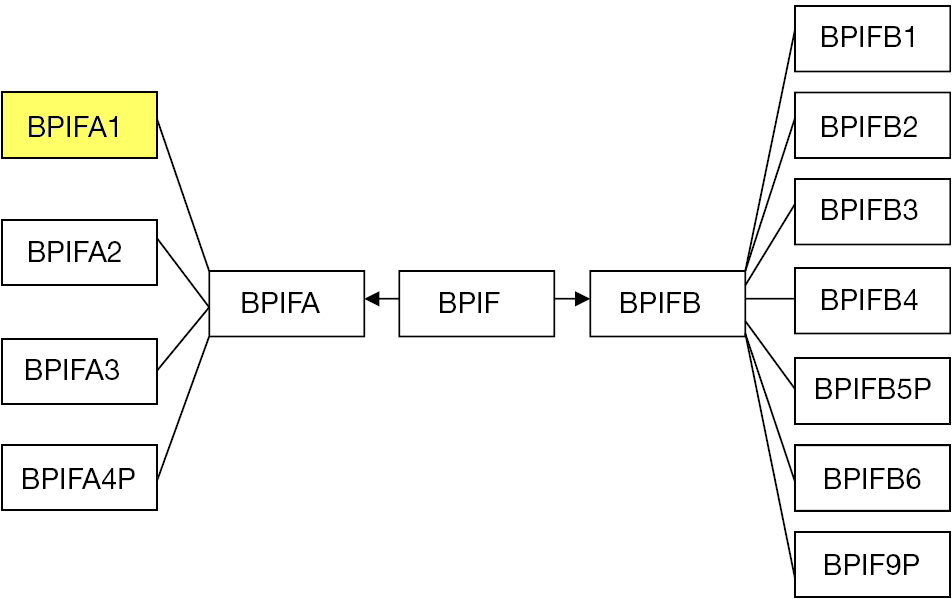
BPIFA1
BPI fold containing family A, member 1 (BPIFA1), also known as Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFA1'' gene. It was also formerly known as "Secretory protein in upper respiratory tracts" (SPURT). The ''BPIFA1'' gene sequence predicts 4 transcripts ( splice variants); 3 mRNA variants have been well characterized. The resulting BPIFA1 is a secreted protein, expressed at very high levels in mucosa of the airways (olfactory and respiratory and epithelium) and salivary glands; at high levels in oropharyneal epithelium, including tongue and tonsils; and at moderate levels many other tissue types and glands including pituitary, testis, lung, bladder, blood, prostate, pancreas, levels in the digestive tract (tongue, stomach, intestinal epithelium) and pancreas. The protein can be detected on the apical side of epithelial cells and in airway surface liquid, nasal mucus, and sputum. Superfamily BPIFA1 is a member of a B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 or BMP-2 belongs to the TGF-β superfamily of proteins. Function BMP-2 like other bone morphogenetic proteins, plays an important role in the development of bone and cartilage. It is involved in the hedgehog pathway, TGF beta signaling pathway, and in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. It is also involved in cardiac cell differentiation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Like many other proteins from the BMP family, BMP-2 has been demonstrated to potently induce osteoblast differentiation in a variety of cell types. BMP-2 may be involved in white adipogenesis and may have metabolic effects. Interactions Bone morphogenetic protein 2 has been shown to interact with BMPR1A. Clinical use and complications Bone morphogenetic protein 2 is shown to stimulate the production of bone. Recombinant human protein (rhBMP-2) is currently available for orthopaedic usage in the United States. Implantation of BMP-2 is performed using a var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BLCAP
Bladder cancer-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BLCAP'' gene. Function BLCAP was identified using a differential display procedure with tumor biopsies obtained from a noninvasive and an invasive bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Although database searches revealed no homology to any human gene at the time of identification, mouse, rat and zebrafish orthologs have since been identified. The protein appears to be down-regulated during bladder cancer progression. The protein also known as BC10 is an 87-amino-acid-long protein, but its biological functions are largely unknown. However it is a widely believed that the protein is involved in tumour suppression by decreasing cell growth through initiating apoptosis. It is widely expressed protein but expression is particularly high in brain and B lymphocytes. Alternative promoters and alternative splicing allow the protein to exist as several different transcript variants. This number is further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BCAS1
Breast carcinoma-amplified sequence 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCAS1'' gene. Breast carcinoma amplified sequence 1 (BCAS1) was isolated from a region at 20q13 which is amplified in a variety of tumor types and associated with more aggressive tumor phenotypes. Among the genes identified from this region, BCAS1 was found to be highly expressed in three amplified breast cancer cell lines and in one breast tumor without amplification at 20q13.2. However, the BCAS1 gene is not in the common region of maximal amplification and its expression was not detected in the breast cancer cell line MCF7, in which this region is highly amplified. Although not consistently expressed, BCAS1 is a candidate oncogene. It is predicted to encode a protein of 584 amino acids Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ARFGEF2
Brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARFGEF2'' gene. Function ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) play an important role in intracellular vesicular trafficking. The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the activation of ARFs by accelerating replacement of bound GDP with GTP and is involved in Golgi transport. It contains a Sec7 domain, which may be responsible for its guanine-nucleotide exchange activity and also brefeldin A inhibition. Interactions ARFGEF2 has been shown to interact with ARFGEF1, PRKAR1A and PRKAR2A cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAR2A'' gene. Function cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by act .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-20-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
APMAP
Adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APMAP'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-20-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adenosylhomocysteinase
Adenosylhomocysteinase (, ''S''-adenosylhomocysteine synthase, ''S''-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, ''S''-adenosylhomocysteinase, SAHase, AdoHcyase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) dependent, reversible hydrolysis of ''S''-adenosylhomocysteine to homocysteine and adenosine. : ''S''-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + H2O L-homocysteine + adenosine AdoHcyase is a highly conserved protein with about 430 to 470 amino acids. The family contains a glycine-rich region in the central part of AdoHcyase; a region thought to be involved in NAD-binding. AdoHcyase binds one NAD+ cofactor per subunit. This protein may use the morpheein model of allosteric regulation. Overall hydrolysis begins with dehydrogenative oxidation of the 3'-OH of the ribose by NAD+ (forming NADH). The resulting ketone is α-deprotonated to the enol before elimination of the homocysteine thiolate. Water then adds to the a,b-unsaturated ketone, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |