|
Chemical Reactivity
In chemistry, reactivity is the impulse for which a chemical substance undergoes a chemical reaction, either by itself or with other materials, with an overall release of energy. ''Reactivity'' refers to: * the chemical reactions of a single substance, * the chemical reactions of two or more substances that interact with each other, * the systematic study of sets of reactions of these two kinds, * methodology that applies to the study of reactivity of chemicals of all kinds, * experimental methods that are used to observe these processes, and * theories to predict and to account for these processes. The chemical reactivity of a single substance (reactant) covers its behavior in which it: * decomposes, * forms new substances by addition of atoms from another reactant or reactants, and * interacts with two or more other reactants to form two or more products. The chemical reactivity of a substance can refer to the variety of circumstances (conditions that include temperature, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
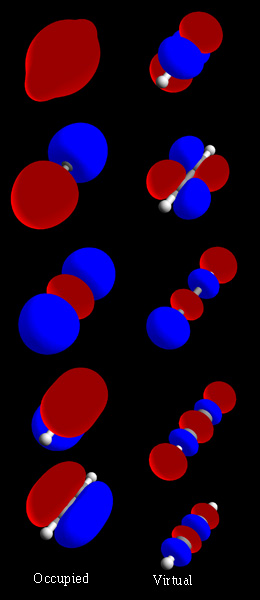
Molecular Orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule by forming a valence chemical bond, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Strain Model
The activation strain model, also referred to as the distortion/interaction model, is a computational tool for modeling and understanding the potential energy curves of a chemical reaction as a function of reaction coordinate (ζ), as portrayed in reaction coordinate diagrams. The activation strain model decomposes these energy curves into 2 terms: the strain of the reactant molecules as they undergo a distortion and the interaction between these reactant molecules. A particularly important aspect of this type of analysis compared others is that it describes the energetics of the reaction in terms of the original reactant molecules and describes their distortion and interaction using intuitive models such as molecular orbital theory that are capable using most quantum chemical programs. Such a model allows for the calculation of transition state energies, and hence the activation energy, of a particular reaction mechanism In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Hybridisation
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds, the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies. History and uses Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals. Pauling pointed out that a carbon atom forms four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e.g. a battery), or sound (e.g. explosion heard when burning hydrogen). The term ''exothermic'' was first coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The opposite of an exothermic process is an endothermic process, one that absorbs energy, usually in the form of heat. The concept is frequently applied in the physical sciences to chemical reactions where chemical bond energy is converted to thermal energy (heat). Two types of chemical reactions Exothermic and endothermic describe two types of chemical reactions or systems found in nature, as follows: Exothermic An exothermic reaction occurs when heat is released to the surroundings. According to the IUPAC, an exothermic reaction is "a reaction for which the overall stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy
In the Arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Activation energy can be thought of as a magnitude of the potential barrier (sometimes called the energy barrier) separating minima of the potential energy surface pertaining to the initial and final thermodynamic state. For a chemical reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate, the temperature of the system should be high enough such that there exists an appreciable number of molecules with translational energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. The term "activation energy" was introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. Other uses Although less commonly used, activation energy also applies to nuclear reactions and various other physical phenomena. Temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemical bonds that each atom of a given chemical element typically forms. Double bonds are considered to be two bonds, triple bonds to be three, quadruple bonds to be four, quintuple bonds to be five and sextuple bonds to be six. In most compounds, the valence of hydrogen is 1, of oxygen is 2, of nitrogen is 3, and of carbon is 4. Valence is not to be confused with the related concepts of the coordination number, the oxidation state, or the number of valence electrons for a given atom. Description The valence is the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; in ammonia, nitrogen has a valence of 3; in water, oxygen has a valence of 2; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds, or some combination of these effects. Chemical bonds are described as having different strengths: there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. Electrons shared between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them. "Constructive quantum mechanical wavefunction interference" stabilizes the paired nuclei (see Theories of chemical bonding). Bonded nuclei maintain an optima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (unit)
The mole (symbol mol) is a unit of measurement, the base unit in the International System of Units (SI) for ''amount of substance'', an SI base quantity proportional to the number of elementary entities of a substance. One mole is an aggregate of exactly elementary entities (approximately 602 sextillion or 602 billion times a trillion), which can be atoms, molecules, ions, ion pairs, or other particles. The number of particles in a mole is the Avogadro number (symbol ) and the numerical value of the '' Avogadro constant'' (symbol ) expressed in mol−1. The relationship between the mole, Avogadro number, and Avogadro constant can be expressed in the following equation:1\text = \frac = \frac The current SI value of the mole is based on the historical definition of the mole as the amount of substance that corresponds to the number of atoms in 12 grams of 12C, which made the molar mass of a compound in grams per mole, numerically equal to the average molecular mass or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces a body through a distance of one metre in the direction of that force. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889). Definition According to the International Bureau of Weights and Measures the joule is defined as "the work done when the point of application of 1 MKS unit of force ewtonmoves a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force." In terms of SI base units and in terms of SI derived units with special names, the joule is defined as One joule is also equivalent to any of the following: * The work required to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilocalorie Per Mole
The kilocalorie per mole is a unit to measure an amount of energy per number of molecules, atoms, or other similar particles. It is defined as one kilocalorie of energy (1000 thermochemical gram calories) per one mole of substance. The unit symbol is written kcal/mol or kcal⋅mol−1. As typically measured, one kcal/mol represents a temperature increase of one degree Celsius in one liter of water (with a mass of 1 kg) resulting from the reaction of one mole of reagents. In SI units, one kilocalorie per mole is equal to 4.184 kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol), which comes to approximately joules per molecule, or about 0.043 eV per molecule. At room temperature (25 °C, 77 °F, or 298.15 K), one kilocalorie per mole is approximately equal to 1.688 kT per molecule. Even though it is not an SI unit, the kilocalorie per mole is still widely used in chemistry and biology for thermodynamical quantities such as thermodynamic free energy, heat of vaporization, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |