|
Chartoularios Tou Kanikleiou
The (), more formally or () was one of the most senior Byzantine aristocracy and bureaucracy, offices in the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine imperial chancery.. Its holder was the keeper of the imperial inkstand, the ''kanikleion'', which was shaped as a little dog () and contained the scarlet ink with which the Byzantine emperor signed state documents. The office first appears in the 9th century, and was usually held in tandem with other government offices. In the ''Kletorologion'' of 899 it is ranked among the "special dignities" (, ), following the ''synkellos'' and preceding the ''protostrator''. In the overall order of precedence, he ranked behind the ''chartoularios tou vestiariou'' and before the ''protostrator'', and is recorded as usually holding the rank of ''protospatharios''. His proximity to the imperial person and the nature of his task made the very influential, especially in formulating imperial chrysobulls. The office was often given to trusted aides by the emperors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Aristocracy And Bureaucracy
Throughout the fifth century, Diadochi, Hellenistic-Eastern political systems, Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophies, and Theocracy, theocratic Christian concepts had gained power in the Greek-speaking Eastern Mediterranean due to the intervention of important religious figures there such as Eusebius, Eusebius of Caesarea () and Origen, Origen of Alexandria () who had been key to developing the constant Christianized worldview of late antiquity. By the 6th century, such ideas had already influenced the definitive power of the monarch as the Vicar of Christ, representative of God on earth and of his kingdom as an imitation of Kingdom of God (Christianity), God's holy realm. The Byzantine Empire was a multi-ethnic monarchy, monarchic theocracy adopting, following, and applying the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox-Hellenistic kingdoms, Hellenistic political systems and Hellenistic philosophy, philosophies. The monarch was the incarnation of the law''nomos empsychos''and his power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus (; 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar Slayer (, ), was the senior Byzantine emperor from 976 to 1025. He and his brother Constantine VIII were crowned before their father Romanos II died in 963, but they were too young to rule. The throne thus went to two generals, Nikephoros Phokas (963–969) and John Tzimiskes (r. 969–976) before Basil became senior emperor, though his influential great-uncle Basil Lekapenos remained as the '' de facto'' ruler until 985. His reign of 49 years and 11 months was the longest of any Roman emperor. The early years of Basil's reign were dominated by civil wars against two powerful generals from the Byzantine Anatolian aristocracy: first Bardas Skleros and later Bardas Phokas, which ended shortly after Phokas' death and Skleros' submission in 989. Basil then oversaw the stabilization and expansion of the eastern frontier of the Byzantine Empire and the complete subjugation of the First Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
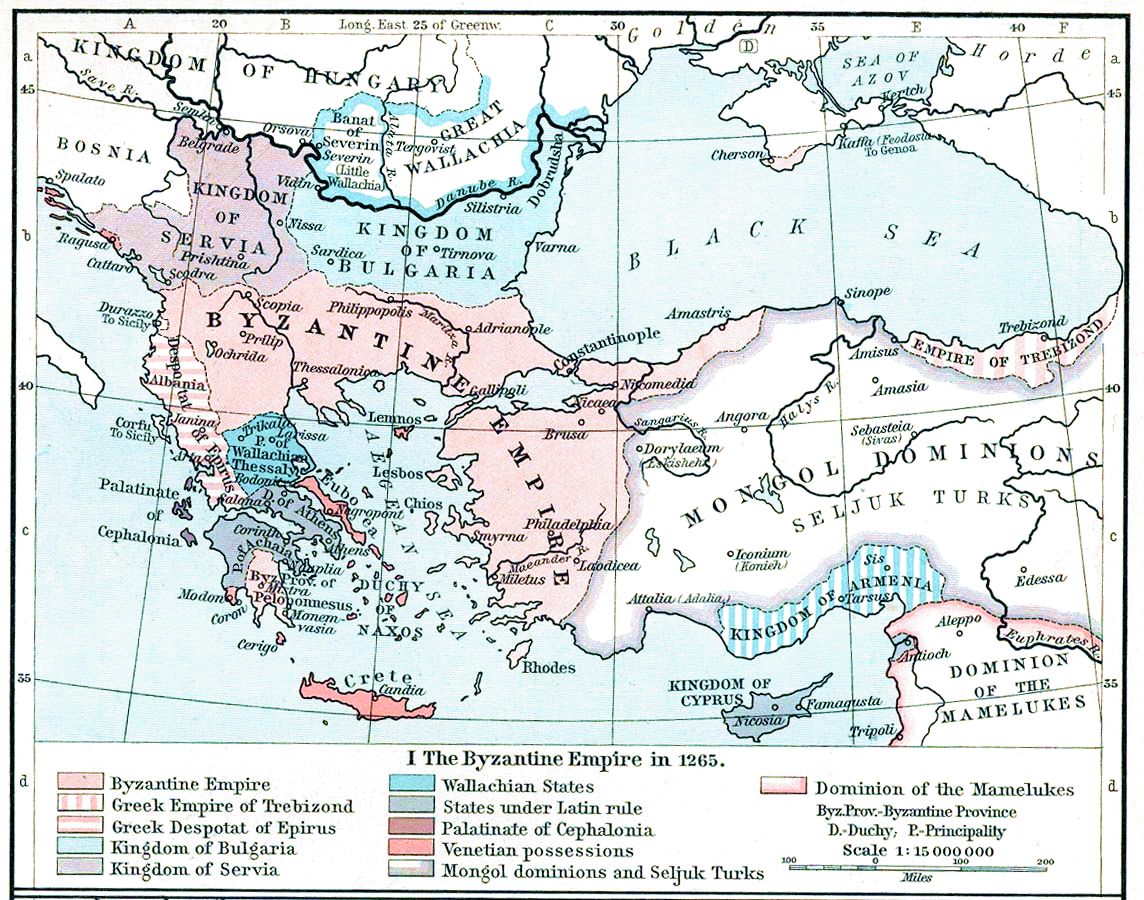
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Palaiologos
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinization of names, Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored empire's final decline. The Turks conquered most of Byzantium's remaining Anatolian territories, and Andronikos spent the last years of his reign fighting his Andronikos III Palaiologos, own grandson in the First Palaiologan Civil War. The war ended in Andronikos' forced abdication in 1328, after which he retired to a monastery for the remainder of his life. Life Early life Andronikos was born on 25 March 1259, at Nicaea. He was the eldest surviving son of Michael VIII Palaiologos and Theodora Palaiologina (Byzantine empress), Theodora Palaiologina, grandniece of John III Doukas Vatatzes. Andronikos was acclaimed co-emperor in 1261, after his father Michael VIII recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire, but he was not crowned unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesazon
The () was a high dignitary and official during the last centuries of the Byzantine Empire, who acted as the chief minister and principal aide of the Byzantine emperor. In the West, the dignity was understood as being that of the imperial chancellor (). History and functions The term's origins lie in the 10th century, when senior ministers were sometimes referred to as the (), i.e. 'mediators' between the emperor and his subjects (cf. ). The title first became official in the mid-11th century, when it was conferred on Constantine Leichoudes, the future ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople.. In the Komnenian period, it was awarded to senior government officials who functioned as ''de facto'' prime ministers, such as the and the , but had not yet acquired a permanent and specific function, nor the power that would characterize it in later years. Rather, it was a title bestowed on the principal imperial secretary of the moment, who acted precisely as an "intermediary" between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Choumnos
Nikephoros Choumnos (, 1253 – 16 January 1327) was a Byzantine scholar and official of the early Palaiologan period, one of the most important figures in the flowering of arts and letters of the so-called "Palaiologan Renaissance". He is notable for his eleven-year tenure as chief minister of emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos, his intense intellectual rivalry with fellow scholar and official Theodore Metochites, and for building the monastery of the Theotokos Gorgoepēkoos (Θεοτόκος Γοργοεπήκοος) in Constantinople. Life Choumnos was born between 1250 and 1255. He came from an already distinguished family, which since the 11th century had provided several high-ranking officials.Kazhdan (1991), p. 433 Nikephoros studied rhetoric and philosophy under the future Patriarch of Constantinople Gregory of Cyprus, and upon conclusion of his studies entered the imperial bureaucracy. He makes his first appearance in history , with the lowly rank of ''quaestor'', as he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the focus of the Byzantine military shifted to the Balkans, against the Bulgarians, leaving the Anatolian fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes (; 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known as Theodore II Doukas Laskaris. Life John Doukas Vatatzes, born in about 1192 in Didymoteicho, was probably the son of the general Basil Vatatzes, who was killed in battle in 1194, and his wife, a cousin of the Emperors Isaac II Angelos and Alexios III Angelos. John Doukas Vatatzes had two older brothers. The eldest was Isaac Doukas Vatatzes (1188-1261), while his younger brother died young. Through his marriage to Eudokia Angelina he fathered Theodora Doukaina Vatatzaina, who later married Michael VIII Palaiologos. The middle brother's name is unknown, but his daughter married the ''protovestiarios'' Alexios Raoul. A successful soldier from a military family, John had risen to the position of protovestiarites when he was chosen in about 1216 by Emperor Theodore I Komnenos Laskaris as the second husband for his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Alyates
Nikephoros (), Nikiforos or Nicephorus is a Greek male name, meaning "Bringer of Victory", which was commonly used among the Byzantine Empire's aristocracy. It may refer to: Rulers * Nikephoros I Logothetes, Byzantine emperor 802–811 * Nikephoros II Phokas, Byzantine emperor 963–969 * Nikephoros III Botaneiates, Byzantine emperor 1078–1081 * Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, despot of Epirus 1267–1297 * Nikephoros II Orsini, ruler of Epirus 1335–1338 and 1356–1359 Ecclesiastical leaders * Nicephorus I of Constantinople, Byzantine writer and patriarch, 758–828, author of the ''Stichometry'' and other works * Nicephorus II of Constantinople, patriarch in exile at Nicaea * Nicephorus of Antioch, Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch, 1084–1090 * Nicephorus II of Kiev, Metropolitan of Kyiv and all Ruthenia, 1183–1198 * Patriarch Nicephorus of Alexandria, Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria between 1639 and 1645 * Nikiforos of Didymoteicho, Metropolitan of Didymoteicho in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos (; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Latinized as Comnenus, also called Porphyrogenitus (; " born in the purple"), was a Byzantine emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history of Byzantium and the Mediterranean. His reign saw the last flowering of the Komnenian restoration, during which the Byzantine Empire experienced a resurgence of military and economic power and enjoyed a cultural revival. Eager to restore his empire to its past glories as the great power of the Mediterranean world, Manuel pursued an energetic and ambitious foreign policy. In the process he made alliances with Pope Adrian IV and the resurgent West. He invaded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily, although unsuccessfully, being the last Eastern Roman emperor to attempt reconquests in the western Mediterranean. The passage of the potentially dangerous Second Crusade through his empire was adroitly managed. Manuel established a Byzantine protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Styppeiotes
Theodore Styppeiotes or Stypeiotes () was a high-ranking bureaucrat of the Byzantine Empire and a member of the court of Emperor Manuel I Komnenos (). A well-educated and capable man, he advanced rapidly in the imperial hierarchy from imperial secretary (''grammatikos'') to the influential post of ''kanikleios'', keeper of the imperial inkstand. In he engineered the downfall of John Hagiotheodorites, and succeeded him as ''mesazon'', the ''de facto'' chief minister of the Empire. He long enjoyed the favour and trust of Manuel, who even wed him with his niece Eudokia. However, in 1158/59, Styppeiotes abruptly fell from power and was imprisoned and political mutilation in Byzantine culture, blinded. The sources provide different reasons, from Styppeiotes conspiring to deprive the Emperor of power to the machinations of his rival, John Kamateros (logothetes tou dromou), John Kamateros, and scholars still dispute the true background of this event. Life The origin and early life of Theod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Ouranos
Nikephoros Ouranos (; fl. c. 980 – c. 1010), Latinized as Nicephorus Uranus, was a high-ranking Byzantine official and general during the reign of Emperor Basil II (r. 976–1025). One of the emperor's closest associates, he was active in Europe in the wars against the Bulgarians, scoring a major victory at Spercheios, and against the Arabs in Syria, where he held command during the first decade of the 11th century as Basil's virtual viceroy. A well-educated man, he wrote a military manual (''Taktika'') and composed several surviving poems and hagiographies. Biography Very little is known of Ouranos's origin, his early years, or his family, and the chronicles represent him very much as a " new man". A '' prōtospatharios'' and '' asēkrētis'' Basil Ouranos, possibly an elder relative, is attested, and we know from Nikephoros's letters that he had a brother named Michael. Nikephoros Ouranos himself first enters history in the early 980s, during negotiations between Byzantium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |