|
Cervical Vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. The bone is named for Atlas of Greek mythology, just as Atlas bore the weight of the heavens, the first cervical vertebra supports the head. However, the term atlas was first used by the ancient Romans for the seventh cervical vertebra (C7) due to its suitability for supporting burdens. In Greek mythology, Atlas was condemned to bear the weight of the heavens as punishment for rebelling against Zeus. Ancient depictions of Atlas show the globe of the heavens resting at the base of his neck, on C7. Sometime around 1522, anatomists decided to call the first cervical vertebra the atlas. Scholars believe that by switching the designation atlas from the seventh to the first cervical vertebra Renaissance anatomists were commenting that the point of man's burden had shifted from his shoulders to his head—that man's true burden was not a physical load, but rather, his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-toed Sloth
The three-toed or three-fingered sloths are arboreal neotropical mammals. They are the only members of the genus ''Bradypus'' (meaning "slow-footed") and the family Bradypodidae. The five living species of three-toed sloths are the brown-throated sloth, the maned sloth, the pale-throated sloth, the southern maned sloth, and the pygmy three-toed sloth. In complete contrast to past morphological studies, which tended to place ''Bradypus'' as the sister group to all other folivorans, molecular studies place them nested within the sloth superfamily Megatherioidea, making them the only surviving members of that radiation. Extant species Evolution A study of mitochondrial cytochrome b and 16S rRNA sequences suggests that '' B. torquatus'' diverged from '' B. variegatus'' and '' B. tridactylus'' about 12 million years ago, while the latter two split 5 to 6 million years ago. The diversification of ''B. variegatus'' lineages was estimated to have started 4 to 5 million years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuchal Ligament
The nuchal ligament is a ligament at the back of the neck that is continuous with the supraspinous ligament. Structure The nuchal ligament extends from the external occipital protuberance on the skull and median nuchal line to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra in the lower part of the neck. From the anterior border of the nuchal ligament, a fibrous lamina is given off. This is attached to the posterior tubercle of the atlas, and to the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae, and forms a septum between the muscles on either side of the neck. The trapezius and splenius capitis muscle attach to the nuchal ligament. Function It is a tendon-like structure that has developed independently in humans and other animals well adapted for running. In some four-legged animals, particularly ungulates and canids, the nuchal ligament serves to sustain the weight of the head. Clinical significance In Chiari malformation treatment, decompression and duraplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenius Capitis Muscle
The splenius capitis () () is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae in the neck and upper thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking the head. Structure It arises from the lower half of the nuchal ligament, from the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra, and from the spinous processes of the upper three or four thoracic vertebrae. The fibers of the muscle are directed upward and laterally and are inserted, under cover of the sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and into the rough surface on the occipital bone The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ... just below the lateral third of the superior nuchal line. The splenius capitis is deep to ster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
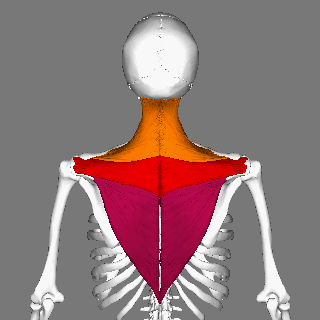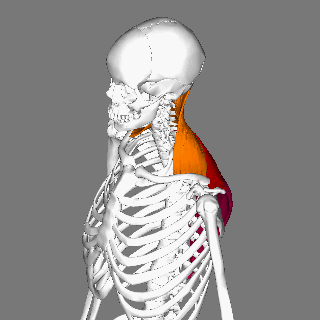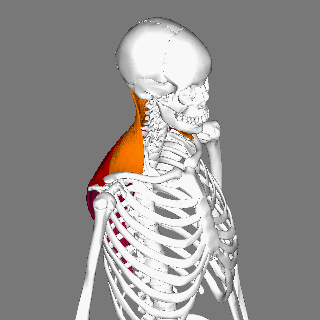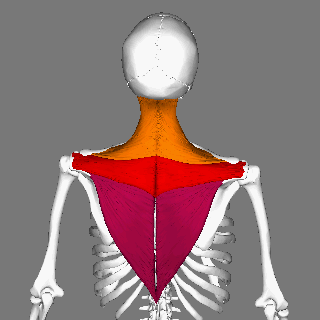
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: * an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; * a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and * a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezoid, trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the spinous process of C7, the external occipital protuberance, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Foramen
In a typical vertebra, the vertebral foramen is the foramen (opening) of a vertebra bounded ventrally/anteriorly by the body of the vertebra, and the dorsally/posteriorly by the vertebral arch. In the articulated spine, the successive vertebral foramina of the stacked vertebrae (together with adjacent structures) collectively form the spinal canal (vertebral canal) which lodges the spinal cord and its meninges In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ... as well as spinal nerve roots and blood vessels. See also * Atlas (anatomy)#Vertebral foramen References External links * - "Superior and lateral views of typical vertebrae"Vertebral foramen- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School * - "Typical Lumbar Vertebra, Superior View; Lumbar Vertebral Column, O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
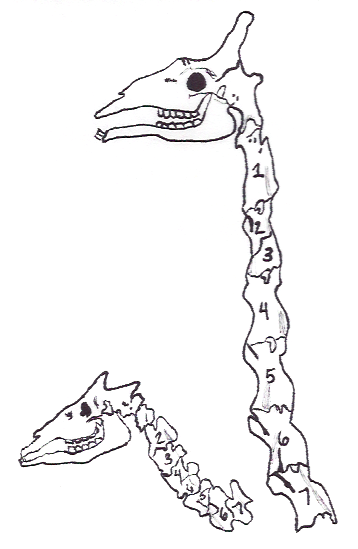
Okapi Giraffe Neck
The okapi (; ''Okapia johnstoni''), also known as the forest giraffe, Congolese giraffe and zebra giraffe, is an artiodactyl mammal that is endemic to the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo in central Africa. However, non-invasive genetic identification has suggested that a population has occurred south-west of the Congo River as well. It is the only species in the genus ''Okapia''. Although the okapi has striped markings reminiscent of zebras, it is most closely related to the giraffe. The okapi and the giraffe are the only living members of the family Giraffidae. The okapi stands about tall at the shoulder and has a typical body length around . Its weight ranges from . It has a long neck, and large, flexible ears. Its coat is a chocolate to reddish brown, much in contrast with the white horizontal stripes and rings on the legs, and white ankles. Male okapis have short, distinct horn-like protuberances on their heads called ossicones, less than in length. Females p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anatomy
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy (also called macroscopic anatomy, topographical anatomy, regional anatomy, or anthropotomy) is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye. Microscopic anatomy is the study of minute anatomical structures assisted with microscopes, which includes histology (the study of the organization of tissues), and cytology (the study of cells). Anatomy, human physiology (the study of function), and biochemistry (the study of the chemistry of living structures) are complementary basic medical sciences that are generally together (or in tandem) to students studying medical sciences. In some of its facets human anatomy is closely related to embryology, comparative anatomy and comparative embryology, through common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Cervical Ganglion
The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia (i.e. of the cervical portion of the sympathetic trunk). It is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery. It is often united with the first (and sometimes the second) thoracic ganglion to form the cervicothoracic ganglion (stellate ganglion). Anatomy The inferior cervical ganglion is irregularly shaped. It is substantially larger than the middle cervical ganglion (but smaller than the superior cervical ganglion). As the sympathetic trunk curves posteriorly between the neck and thorax, this ganglion is oriented in a nearly anteroposterior axis. The ganglion is presumed to represent the union of the cervical segmental sympathetic ganglia C7-C8 and the thoracic segmental sympathetic ganglia T1, but sometimes up to T4 as well - the T1 ganglion may or may not be separate to leave a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Veins
The vertebral vein is formed in the suboccipital triangle, from numerous small tributaries which spring from the internal vertebral venous plexuses and issue from the vertebral canal above the posterior arch of the atlas. They unite with small veins from the deep muscles at the upper part of the back of the neck, and form a vessel which enters the foramen in the transverse process of the atlas, and descends, forming a dense plexus around the vertebral artery, in the canal formed by the transverse foramina of the upper six cervical vertebrae. This plexus ends in a single trunk, which emerges from the transverse foramina of the sixth cervical vertebra, and opens at the root of the neck into the back part of the innominate vein near its origin, its mouth being guarded by a pair of valves. On the right side, it crosses the first part of the subclavian artery In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |