|
Celsius Scale
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius temperature scale "Celsius temperature scale, also called centigrade temperature scale, scale based on 0 ° for the melting point of water and 100 ° for the boiling point of water at 1 atm pressure." (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the closely related Kelvin scale. The degree Celsius (symbol: °C) can refer to a specific point on the Celsius temperature scale or to a difference or range between two temperatures. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701–1744), who proposed the first version of it in 1742. The unit was called ''centigrade'' in several languages (from the Latin ''centum'', which means 100, and ''gradus'', which means steps) for many years. In 1948, the International Committee for Weights and Measures renamed it to honor Celsius and also to remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermometer
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature (the hotness or coldness of an object) or temperature gradient (the rates of change of temperature in space). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the pyrometric sensor in an infrared thermometer) in which some change occurs with a change in temperature; and (2) some means of converting this change into a numerical value (e.g. the visible scale that is marked on a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the digital readout on an infrared model). Thermometers are widely used in technology and industry to monitor processes, in meteorology, in medicine (''medical thermometer''), and in scientific research. A standard scale While an individual thermometer is able to measure degrees of hotness, the readings on two thermometers cannot be compared unless they conform to an agreed scale. Today there is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SI Base Unit
The SI base units are the standard units of measurement defined by the International System of Units (SI) for the seven base quantities of what is now known as the International System of Quantities: they are notably a basic set from which all other SI units can be derived. The units and their physical quantities are the second for time, the metre (sometimes spelled meter) for length or distance, the kilogram for mass, the ampere for electric current, the kelvin for thermodynamic temperature, the mole for amount of substance, and the candela for luminous intensity. The SI base units are a fundamental part of modern metrology, and thus part of the foundation of modern science and technology. The SI base units form a set of mutually independent dimensions as required by dimensional analysis commonly employed in science and technology. The names and symbols of SI base units are written in lowercase, except the symbols of those named after a person, which are written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
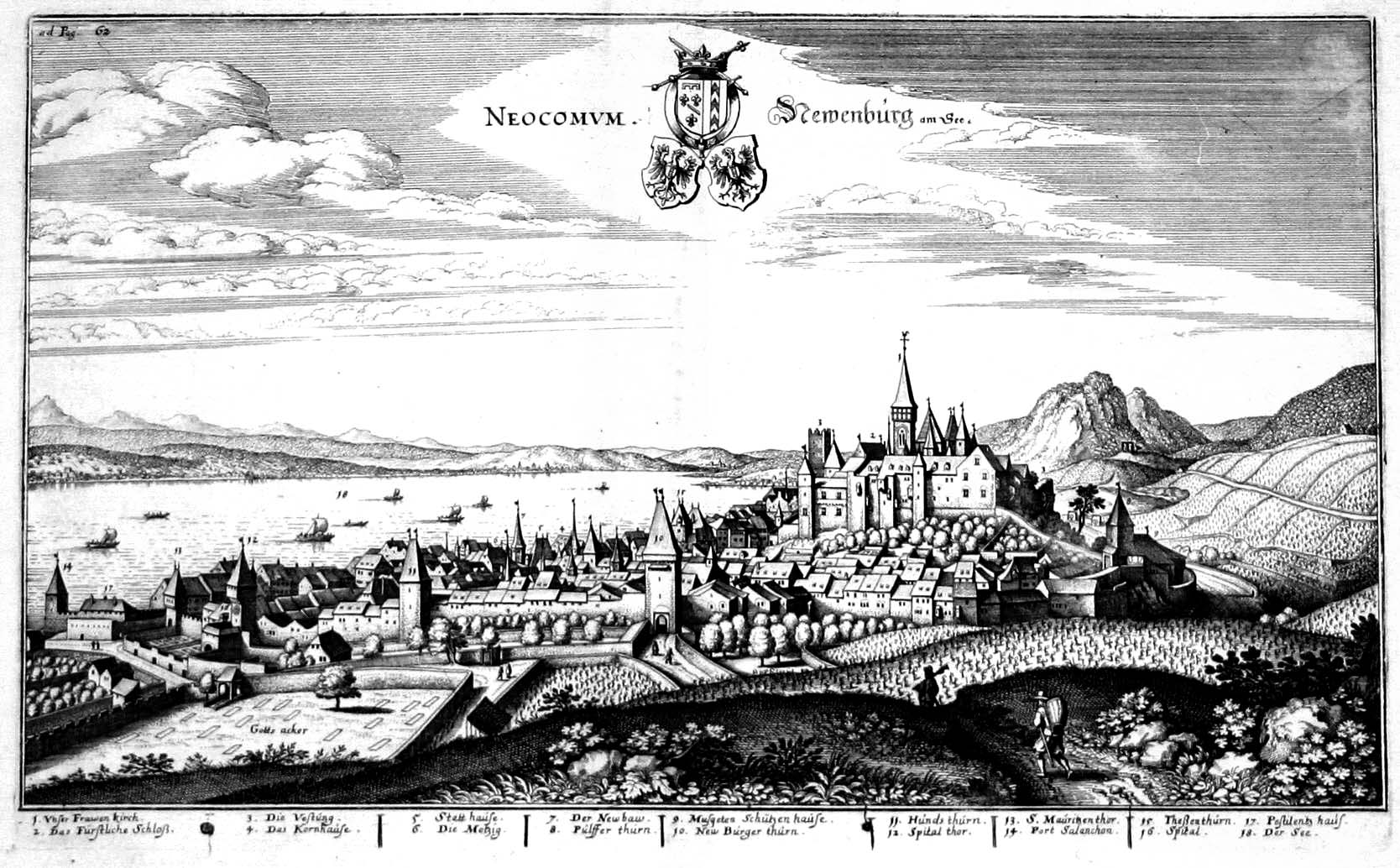
Neuchâtel
Neuchâtel (, ; ; ) is a list of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital (political), capital of the cantons of Switzerland, Swiss canton of Neuchâtel (canton), Neuchâtel on Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, Neuchâtel, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 33,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". The castle after which the city is named was built by Rudolph III of Burgundy and completed in 1011. Originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the city was absorbed into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033. The domain of the counts of Neuchatel was first referred to as a city in 1214. The city came under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1806 to 1814. In 1848, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercure De France
The () was originally a French gazette and literary magazine first published in the 17th century, but after several incarnations has evolved as a publisher, and is now part of the Éditions Gallimard publishing group. The gazette was published from 1672 to 1724 (with an interruption in 1674–1677) under the title (sometimes spelled ; 1672–1674) and (1677–1724). The title was changed to in 1724. The gazette was briefly suppressed (under Napoleon) from 1811 to 1815 and ceased publication in 1825. The name was revived in 1890 for both a literary review and (in 1894) a publishing house initially linked with the symbolist movement. Since 1995 has been part of the Éditions Gallimard publishing group. The original ''Mercure galant'' and ''Mercure de France'' The ''Mercure galant'' was founded by the writer Jean Donneau de Visé in 1672. He directed the publication until his death in 1710. The name refers to the god Mercury, the messenger of the gods; the title al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Thermometer
Mercury most commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the closest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a chemical element * Mercury (mythology), a Roman deity Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Corporation, an American aircraft manufacturer * Mercury Cyclecar Company, a defunct American car company * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company * Mercury Technologies, a financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Lyon
__NOTOC__ The Academy of Sciences, Humanities and Arts of Lyon (French: Académie des Sciences, Belles-Lettres et Arts de Lyon) is a French learned society founded in 1700. Its founders included: * Claude Brossette, lawyer, alderman of Lyons, and administrator of the Hôtel-Dieu de Lyon; * , President of the Cour des monnaies; * , future consulting physician of King Louis XIV LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ... and member of the ; * Antoine de Serre, adviser to the Cour des monnaies; * , naturalist; * Father Jean de Saint-Bonnet, professor at the Collège-lycée Ampère. * Thomas Bernard Fellon. Notable Members * Joseph D'Aquin * Jean Pouilloux See also * French art salons and academies Notes References National academies Learned societies of France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Pierre Christin
Jean-Pierre Christin (31 May 1683 – 19 January 1755) was a French physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and musician. His proposal in 1743 to reverse the Celsius thermometer scale (from water boiling at 0 degrees and ice melting at 100 degrees, to where zero represented the freezing point of water and 100 represented the boiling point of water) was widely accepted and is still in use today. Christin was born in Lyon Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north .... He was a founding member of the '' Académie des sciences, belles-lettres et arts de Lyon'' and served as its Permanent Secretary from 1713 until 1755. His thermometer was known in France before the Revolution as the thermometer of Lyon. One of these thermometers was kept at the Science Museum in London. Thermome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyne
The dyne (symbol: dyn; ) is a derived units of measurement, unit of force (physics), force specified in the centimetre–gram–second system of units, centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system of units, a predecessor of the modern International System of Units, SI. History The name dyne was first proposed as a CGS unit of force in 1873 by a Committee of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. Definition The dyne is defined as "the force required to accelerate a mass of one gram at a rate of one centimetre per second squared". An equivalent definition of the dyne is "that force which, acting for one second, will produce a change of velocity of one centimetre per second in a mass of one gram". One dyne is equal to 10 micronewtons, 10−5 newton (unit), N or to 10 nsn (nanosthenes) in the old metre–tonne–second system of units. * 1 dyn = 1 g⋅cm/s2 = 10−5 kg⋅m/s2 = 10−5 N * 1 N = 1 kg⋅m/s2 = 105 g⋅cm/s2 = 105 dyn Use The dyne per centimetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Conference On Weights And Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (abbreviated CGPM from the ) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established in 1875 under the terms of the Metre Convention through which member states act together on matters related to measurement science and measurement standards. The CGPM is made up of delegates of the governments of the member states and observers from the Associates of the CGPM. It elects the International Committee for Weights and Measures (abbreviated CIPM from the ) as the supervisory board of the BIPM to direct and supervise it. Initially the work of the BIPM concerned the kilogram and the metre, but in 1921 the scope of the Metre Convention was extended to accommodate all Physical quantity, physical measurements and hence all aspects of the metric system. In 1960 the 11th CGPM approved the title International System of Units, usually known as "SI". The General Conferenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and Navigation, marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to Calibration, calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead a long-term average of tide gauge readings at a particular reference location. The term ''above sea level'' generally refers to the height above mean sea level (AMSL). The term APSL means above present sea level, comparing sea levels in the past with the level today. Earth's radius at sea level is 6,378.137 km (3,963.191 mi) at the equator. It is 6,356.752 km (3,94 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celsius Original Thermometer Horizontal
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius temperature scale "Celsius temperature scale, also called centigrade temperature scale, scale based on 0 ° for the melting point of water and 100 ° for the boiling point of water at 1 atm pressure." (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the closely related Kelvin scale. The degree Celsius (symbol: °C) can refer to a specific point on the Celsius temperature scale or to a difference or range between two temperatures. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701–1744), who proposed the first version of it in 1742. The unit was called ''centigrade'' in several languages (from the Latin ''centum'', which means 100, and ''gradus'', which means steps) for many years. In 1948, the International Committee for Weights and Measures renamed it to honor Celsius and also to remove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries That Use Celsius
A country is a distinct part of the Earth, world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, List of states with limited recognition, state with limited recognition, Country (other)#Administrative divisions, constituent country, or dependent territory. Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are members of the United Nations. There is no universal agreement on List of sovereign states, the number of "countries" in the world, since several states have disputed sovereignty status or limited recognition, and a number of non-sovereign entities are commonly considered countries. The definition and usage of the word "country" are flexible and have changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Areas much smaller than a political entit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |