|
Cave Of Septum Pellucidum
The cave of septum pellucidum (CSP), cavum septi pellucidi, or cavity of septum pellucidum is a slit-like space in the septum pellucidum that is present in fetuses but usually fuses during infancy. The septum pellucidum is a thin, laminated translucent vertical membrane in the midline of the brain separating the anterior horns of the right and left lateral ventricles. It lies posterior to the corpus callosum. Persistence of the cave of septum pellucidum after infancy has been loosely associated with neural maldevelopment and several mental disorders that correlate with decreased brain tissue. The cave of septum pellucidum is bounded anteriorly by the genu of the corpus callosum, superiorly by the body of the corpus callosum, posteriorly by the anterior limb and pillars of the fornix, inferiorly by the anterior commissure and the rostrum of the corpus callosum, and laterally by the leaflets of the septum pellucidum. In prenatal development of the fetus, the laminae of the septum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavum Vergae
The cavum Vergae is a posterior extension of the cavum septi pellucidi The cave of septum pellucidum (CSP), cavum septi pellucidi, or cavity of septum pellucidum is a slit-like space in the septum pellucidum that is present in fetuses but usually fuses during infancy. The septum pellucidum is a thin, laminated tran ..., an anomaly that is found in a small percentage of human brains. It was first described by Andrea Verga. {{neuroanatomy-stub Brain Ventricular system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fornix Of The Brain
The fornix (from ; : fornices) is a C-shaped bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that acts as the major output tract of the hippocampus. The fornix also carries some afferent fibers to the hippocampus from structures in the diencephalon and basal forebrain. The fornix is part of the limbic system. While its exact function and importance in the physiology of the brain are still not entirely clear, it has been demonstrated in humans that surgical transection—the cutting of the fornix along its body—can cause memory loss. There is some debate over what type of memory is affected by this damage, but it has been found to most closely correlate with recall memory rather than recognition memory. This means that damage to the fornix can cause difficulty in recalling long-term information such as details of past events, but it has little effect on the ability to recognize objects or familiar situations. Structure The fibers begin in the hippocampus on each side of the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Drago
Ivan Vasilyevich Drago (, ) is a fictional character from the ''Rocky'' film series. He first appears in the 1985 film ''Rocky IV'', in which he is the main antagonist and rival of Rocky Balboa and is also responsible for the death of Apollo Creed after brutally defeating him in their match. He also appears in the 2018 film ''Creed II'', in which he is the main antagonist and serves as the trainer to his son Viktor played by a real Romanian kickboxer. He is portrayed by Swedish-American actor and real-life martial artist Dolph Lundgren in both films. A poll of former heavyweight champions and prominent boxing writers ranked Drago as the third-best fighter in the ''Rocky'' film series. Character biography Ivan Drago is an Olympic gold medalist and a boxing champion from the Soviet Union, who had an amateur record of 100–0–0 wins (100 KO). Drago is carefully fitted and trained to be the consummate fighter. His heart rate and punching power are constantly measured via com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Balboa (character)
Robert "Rocky" Balboa (also known by his ring name the Italian Stallion) is a fictional character and the titular protagonist of the Rocky (franchise), ''Rocky'' franchise. The character was created by Sylvester Stallone, who has also portrayed him in eight of the nine films in the franchise. He is depicted as a working class or poor Italian Americans, Italian-American from the slums of Philadelphia who started out as a club fighter and "enforcer" for a local Philadelphia Mafia, Philly Mafia loan shark. He is portrayed as overcoming the obstacles that had occurred in his life and in his career as a professional Boxer (boxing), boxer. While the story of his first film was partly inspired by a Muhammad Ali vs. Chuck Wepner, 1975 fight between underdog Chuck Wepner and heavyweight champion Muhammad Ali (which nearly went the 15 round distance despite the odds), the inspiration for the name, iconography and fighting style came from boxing legend Rocky Marciano, Rocco Francis "Rocky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky V
''Rocky V'' is a 1990 American sports drama film directed by John G. Avildsen and written by and starring Sylvester Stallone. It is the sequel to '' Rocky IV'' (1985) and the fifth installment in the ''Rocky'' franchise. It also stars Talia Shire, Burt Young, Sage Stallone in his film debut, Tommy Morrison, and Burgess Meredith. In the film, a financially struggling Rocky Balboa (Stallone) agrees to train protégé Tommy Gunn (Morrison) at the gym once owned by Balboa's trainer, Mickey Goldmill (Meredith). Development for the film began in 1989, after Stallone completed the screenplay. Avildsen, who directed the first installment, was soon confirmed to return and principal photography began in January 1990, being largely filmed on location around Philadelphia. The filmmakers encountered creative differences with United Artists and were disallowed to include darker elements of Stallone's original screenplay, who had envisioned ''Rocky V'' as the final film in the franchise. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia Pugilistica
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated trauma to the head. The encephalopathy symptoms can include behavioral problems, mood problems, and problems with thinking. The disease often gets worse over time and can result in dementia. Most documented cases have occurred in athletes involved in striking-based combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, mixed martial arts, and contact sports such as rugby union, rugby league, American football, Australian rules football, professional wrestling, and ice hockey. It is also an issue in association football (soccer), but largely as a result of heading the ball rather than player contact. Other risk factors include being in the military (combat arms), prior domestic violence, and repeated banging of the head. The exact amount of trauma required for the condition to occur is unknown, and as of 2025 definitive diagnosis can only occur at autopsy. The disease is classified as a tauopathy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisocial Personality Disorder
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) is a personality disorder defined by a chronic pattern of behavior that disregards the rights and well-being of others. People with ASPD often exhibit behavior that conflicts with social norms, leading to issues with interpersonal relationships, employment, and legal matters. The condition generally manifests in childhood or early adolescence, with a high rate of associated conduct problems and a tendency for symptoms to peak in late adolescence and early adulthood. The prognosis for ASPD is complex, with high variability in outcomes. Individuals with severe ASPD symptoms may have difficulty forming stable relationships, maintaining employment, and avoiding criminal behavior, resulting in higher rates of divorce, unemployment, homelessness, and incarceration. In extreme cases, ASPD may lead to violent or criminal behaviors, often escalating in early adulthood. Research indicates that individuals with ASPD have an elevated risk of suicide, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Brain Injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumatic brain injury. TBI can also be characterized based on mechanism (closed head injury, closed or penetrating head injury) or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death. Causes include Falling (accident), falls, vehicle collisions, and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration of the brain within the skull or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster, traffic collision, or other threats on a person's life or well-being. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress (medicine), distress to Psychological trauma, trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event and can include triggers such as misophonia. Young children are less likely to show distress, but instead may express their memories through play (activity), play. Most people who experience traumatic events do not develop PTSD. People who experience interpersonal violence such as rape, other sexual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms Prodrome, develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and rarely resolve. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood disorder, mood, anxiety disorder, anxiety, and substance use disorders, substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). About 0.3% to 0.7% of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septal Nuclei
The septal area (medial olfactory area), consisting of the lateral septum and medial septum, is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum. The septal nuclei are located in this area. The septal nuclei are composed of medium-size neurons which are classified into dorsal, ventral, medial, and caudal groups. The septal nuclei receive reciprocal connections from the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, midbrain, habenula, cingulate gyrus, and thalamus. The septal nuclei are essential in generating the theta rhythm of the hippocampus. The septal area (medial olfactory area) has no relation to the sense of smell, but it is considered a pleasure zone in animals. The septal nuclei play a role in reward and reinforcement along with the nucleus accumbens. In the 1950s, Olds & Milner showed that rats with electrodes implanted in this area will self-stimulate repeatedly (e.g., press a bar to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
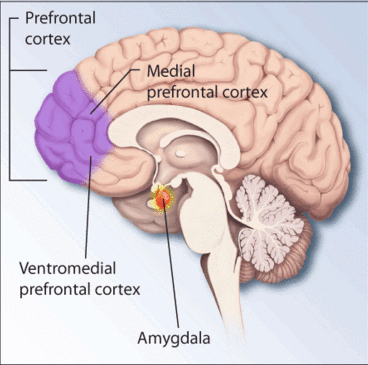
Amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In Primate, primates, it is located lateral and medial, medially within the temporal lobes. It consists of many nuclei, each made up of further subnuclei. The subdivision most commonly made is into the Basolateral amygdala, basolateral, Central nucleus of the amygdala, central, cortical, and medial nuclei together with the intercalated cells of the amygdala, intercalated cell clusters. The amygdala has a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, decision-making, and emotions, emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression). The amygdala was first identified and named by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure Thirteen Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei have been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |