|
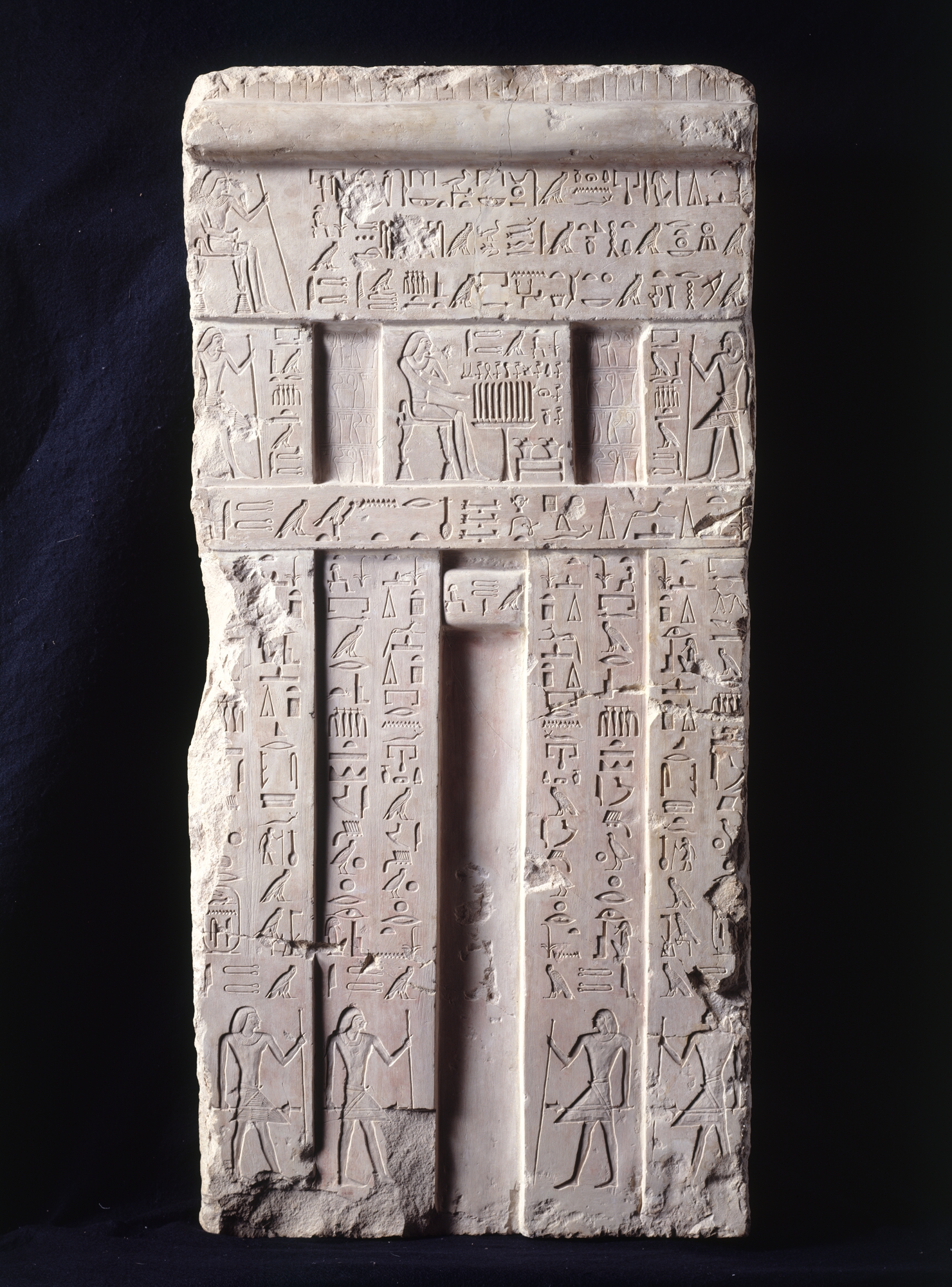
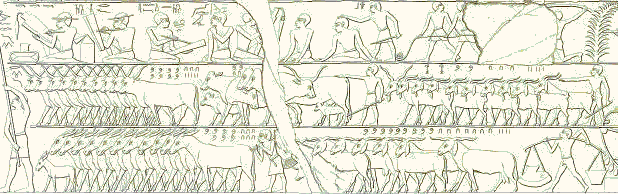
Cattle Count
In ancient Egypt, the cattle count was one of the two main means of evaluating the amount of taxes to be levied, the other one being the height of the annual inundation. A very important economic event, the cattle count was controlled by high officials, and was connected to several cultic feasts. In addition it served as a means of dating other events, with the entire year when it occurred being called "year of the Xth cattle count under the person of the king Y". The frequency of cattle counts varied through the history of ancient Egypt; in the Old Kingdom it was most likely biennial, i.e. occurring every two years, and became more frequent subsequently. Process and purpose To perform the cattle count, all chattel (including productive livestock such as cows and oxen, sheep, pigs, goats and donkeys) were rounded up and counted. Following the count, the percentage of chattel to be taxed by the state would be calculated. The cattle count was performed in every nome of Egypt. Frau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Narmer
Narmer (, may mean "painful catfish", "stinging catfish", "harsh catfish", or "fierce catfish"; ) was an ancient Egyptian king of the Early Dynastic Period, whose reign began at the end of the 4th millennium BC. He was the successor to the Protodynastic king Ka. Many scholars consider him the unifier of Egypt and founder of the First Dynasty, and in turn the first king of a unified Egypt. He also had a prominently noticeable presence in Canaan, compared to his predecessors and successors. Neithhotep is thought to be his queen consort or his daughter. A majority of Egyptologists believe that Narmer was the same person as Menes. Historical identity Although highly interrelated, the questions of "who was Menes?" and "who unified Egypt?" are actually two separate issues. Narmer is often credited with the unification of Egypt by means of the conquest of Lower Egypt by Upper Egypt. Menes is traditionally considered the first king/pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, and is identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories'', a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars, among other subjects such as the rise of the Achaemenid dynasty of Cyrus. He has been described as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero, and the " Father of Lies" by others. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus was criticized in his times for his inclusion of "legends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turin King List
The Turin King List, also known as the Turin Royal Canon, is an ancient Egyptian hieratic papyrus thought to date from the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses II (r. 1279–1213 BC), now in the Museo Egizio (Egyptian Museum) in Turin. The papyrus is the most extensive list available of kings compiled by the ancient Egyptians, and is the basis for most Egyptian chronology before the reign of Ramesses II. The list includes the names of 138 kings. Other sources say that there were originally 223 names of kings in the document, of which 126 have survived (sometimes only partially). 97 names have been lost. Creation and use The papyrus is believed to date from the reign of Ramesses II, during the middle of the New Kingdom, or the 19th Dynasty. The beginning and ending of the list are now lost; there is no introduction, and the list does not continue after the 19th Dynasty. The composition may thus have occurred at any subsequent time, from the reign of Ramesses II to as late as the 20th Dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literature, literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Great Pyramid Of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. Built , over a period of about 26 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only wonder that has remained largely intact. It is the most famous monument of the Giza pyramid complex, which is part of the World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site "Memphis, Egypt, Memphis and its Memphite Necropolis, Necropolis". It is situated at the northeastern end of the line of the three main pyramids at Giza. Initially standing at , the Great Pyramid was the world's List of tallest buildings and structures#History, tallest human-made structure for more than 3,800 years. Over time, most of the smooth white limestone casing was removed, which lowered the pyramid's height to the current ; what is seen today is the underlying core structure. The ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fourth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to c. 2498 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other countries is officially documented. The Fourth Dynasty heralded the height of the pyramid-building age. The peaceful rule of the Third Dynasty of Egypt, Third Dynasty allowed artistic expressions to flourish. Building experiments done by King Sneferu led to the evolution of mastaba tombs into the smooth sided pyramids like those seen on the Giza Plateau. No other period in Egyptian history equaled the accomplishments achieved during the Fourth Dynasty.Egypt: Land and Lives of the Pharaohs Revealed, (2005), pp. 80–90, Global Book Publishing: Australia Rulers Summary of Listed Kings Sneferu Sneferu, lauded as "Bringer of Beauty", "Master of All Justice", and "Ruler of Lower and Upper Nile", was the first pharaoh of the fourt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Khufu
Khufu or Cheops (died 2566 BC) was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period (26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his father Sneferu as king. He is generally accepted as having commissioned the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, but many other aspects of his reign are poorly documented.Thomas Schneider: ''Lexikon der Pharaonen''. Albatros, Düsseldorf 2002, , page 100–104. The only completely preserved portrait of the king is a Khufu Statuette, small ivory figurine found in a temple ruin of a later period at Abydos, Egypt, Abydos in 1903. All other reliefs and statues were found in fragments, and many buildings of Khufu are lost. Everything known about Khufu comes from inscriptions in his necropolis at Giza pyramid complex, Giza and later documents. For example, Khufu is the main character noted in the Westcar Papyrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sixth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Sixth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty VI), along with the Third Dynasty of Egypt, Third, Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth and Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty, constitutes the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of Dynastic Egypt. History The Sixth Dynasty is considered by many authorities as the last dynasty of the Old Kingdom, although ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt'' includes Seventh Dynasty of Egypt, Dynasties VII and Eighth Dynasty of Egypt, VIII as part of the Old Kingdom. Manetho writes that these kings ruled from Memphis, Egypt, Memphis, since their pyramids were built at Saqqara, very close one to another. By the Fifth Dynasty, the religious institution had established itself as the dominant force in society; a trend of growth in the bureaucracy and the priesthood, and a decline in the pharaoh's power had been established during Neferirkare Kakai's reign. During Djedkare Isesi's rule, officials were endowed with greater authority—evidenced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pepi I
Pepi I Meryre (also Pepy I; died 2283 BC) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, king, third king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled for over 40 years from the 24th to the 23rd century BC, toward the end of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period. He was the son of Teti, the founder of the dynasty, and ascended the throne only after the brief intervening reign of the shadowy Userkare. His mother was Iput, who may have been a daughter of Unas, the final ruler of the preceding Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty. Pepi I, who had at least six consorts, was succeeded by his son Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, with whom he may have shared power in a coregency at the very end of his reign. Pepi II, Pepi II Neferkare, who might also have been Pepi I's son, succeeded Merenre. Several difficulties accumulated during Pepi's reign, beginning with the possible murder of his father and the ensuing reign of Userkare. Later, probably after his twentieth year of reign, Pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old Kingdom Of Egypt
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, under whom the art of pyramid-building was perfected, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who commissioned the construction of the Giza pyramid complex, pyramids at Giza. Ancient Egypt, Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" Egyptian chronology, periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The Periodization of Ancient Egypt, concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptology, Egyptologist Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen, Baron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |