|
Catalase-positive
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one catalase molecule can convert millions of hydrogen peroxide molecules to water and oxygen each second. Catalase is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 amino acids long. It contains four iron-containing heme groups that allow the enzyme to react with hydrogen peroxide. The optimum pH for human catalase is approximately 7, and has a fairly broad maximum: the rate of reaction does not change appreciably between pH 6.8 and 7.5. The pH optimum for other catalases varies between 4 and 11 depending on the species. The optimum temperature also varies by species. Structure Human catalase forms a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar Loew
Oscar Loew (2 April 1844 – 26 January 1941) was a German agricultural chemist, active in Germany, the United States, and Japan in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Biography Loew was born in Marktredwitz, Bavaria, where his father was a pharmacist. He studied at the University of Munich under the noted chemist Justus von Liebig; he was Liebig's last student. Loew was an assistant in plant physiology at the City College of New York and participated in four expeditions to the southwestern United States in 1882 before returning to Munich, Germany, where he collaborated with Carl Nägeli. Loew became associate professor at Munich University in 1886. In 1893, he was recruited by the Meiji government of Japan as a foreign advisor, and travelled to Tokyo, where he remained until 1898. Loew served as instructor at Tokyo Imperial University between 1893 and 1907, succeeding Oskar Kellner as professor of agricultural chemistry there. He trained many notable Japanese chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
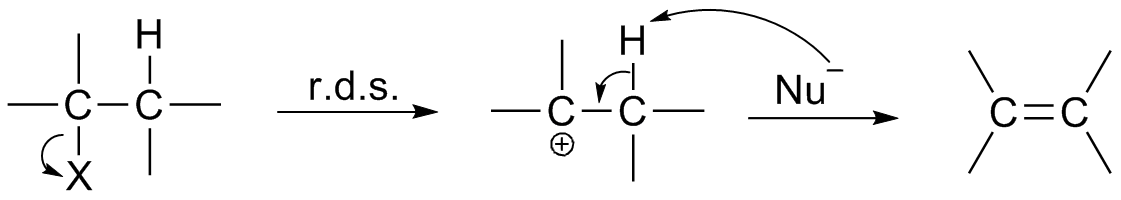
Reaction Intermediates
In chemistry, a reaction intermediate, or intermediate, is a molecular entity arising within the sequence of a stepwise chemical reaction. It is formed as the reaction product of an elementary step, from the reactants and/or preceding intermediates, but is consumed in a later step. It does not appear in the chemical equation for the overall reaction. For example, consider this hypothetical reaction: :A + B → C + D If this overall reaction comprises two elementary steps thus: :A + B → X :X → C + D then X is a reaction intermediate. The phrase ''reaction intermediate'' is often abbreviated to the single word ''intermediate'', and this is IUPAC's preferred form of the term. But this shorter form has other uses. It often refers to reactive intermediates. It is also used more widely for chemicals such as cumene which are traded within the chemical industry but are not generally of value outside it. IUPAC definition The IUPAC Gold Book defines an ''intermediate'' as a comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Amine, α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under Physiological condition, biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential amino acid, essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is Genetic code, encoded by the Genetic code, codons CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by Albrecht Kossel and Sven Gustaf Hedin in 1896. The name stems from its discovery in tissue, from ''histós'' "tissue". It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to histamine, a vital inflammatory agent in immune responses. The acyl radical (chemistry), radical is histidyl. Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is encoded by the codons AAU and AAC. The one-letter symbol N for asparagine was assigned arbitrarily, with the proposed mnemonic asparagi''N''e; History Asparagine was first isolated in 1806 in a crystalline form by French chemists Louis Nicolas Vauquelin and Pierre Jean Robiquet (then a young assistant). It was isolated from asparagus juice, in which it is abundant, hence the chosen name. It was the first amino acid to be isolated. Three years later, in 1809, Pierre Jean Robiquet identified a substance from l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding site'', and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate, the ''catalytic site''. Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |