|
Capital Formation
Capital formation is a concept used in macroeconomics, national accounts and financial economics. Occasionally it is also used in corporate accounts. It can be defined in three ways: *It is a specific statistical concept, also known as net investment, used in national accounts statistics, econometrics and macroeconomics. In that sense, it refers to a measure of the ''net additions'' to the (physical) capital stock and flow, stock of a country (or an economic sector) in an accounting interval, or, a measure of the amount by which the total physical capital stock ''increased'' during an accounting period. To arrive at this measure, standard valuation principles are used. *It is used also in economic theory, as a modern general term for capital accumulation, referring to the total "stock of capital" that has been formed, or to the growth of this total capital stock. *In a much broader or vaguer sense, the term "capital formation" has in more recent times been used in financial economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) is a component of the expenditure on gross domestic product (GDP) that indicates how much of the new value added in an economy is invested rather than consumed. It measures the value of acquisitions of new or existing fixed assets by the business sector, governments, and "pure" households (excluding their unincorporated enterprises) minus disposals of fixed assets. GFCF is a macroeconomic concept used in official national accounts such as the United Nations System of National Accounts (UNSNA), National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA), and the European System of Accounts (ESA). The concept dates back to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) studies of Simon Kuznets of capital formation in the 1930s, and standard measures for it were adopted in the 1950s. GFCF is called "gross" fixed capital formation because the measure does not make any adjustments to deduct the consumption of fixed capital (depreciation of fixed assets) from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Value
Market value or OMV (open market valuation) is the price at which an asset would trade in a competitive auction setting. Market value is often used interchangeably with ''open market value'', ''fair value'' or '' fair market value'', although these terms have distinct definitions in different standards, and differ in some circumstances. Definition International Valuation Standards defines market value as "the estimated amount for which a property should exchange on the date of valuation between a willing buyer and a willing seller in an arm’s-length transaction after proper marketing wherein the parties had each acted knowledgeably, prudently, and without compulsion". Market value is a concept distinct from market price, which is "the price at which one can transact", while market value is "the true underlying value" according to theoretical standards. The concept is most commonly invoked in inefficient markets or disequilibrium situations where prevailing market prices a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replacement Cost
The term replacement cost or replacement value refers to the amount that an entity would have to pay to replace an asset at the present time, according to its current worth. In the insurance industry, "replacement cost" or "replacement cost value" is one of several methods of determining the value of an insured item. Replacement cost is the actual cost to replace an item or structure at its pre-loss condition. This may not be the "market value" of the item, and is typically distinguished from the "actual cash value" payment which includes a deduction for depreciation. For insurance policies for property insurance, a contractual stipulation that the lost asset must be actually repaired or replaced before the replacement cost can be paid is common. This prevents overinsurance, which contributes to arson and insurance fraud.Thomas JE, Wilson B. (2005). The Indemnity Principle: Evolution from a Financial to a Functional Paradigm]. ''Journal of Risk Management & Insurance''Free full-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Cost
The historical cost of an asset at the time it is acquired or created is the value of the costs incurred in acquiring or creating the asset, comprising the consideration paid to acquire or create the asset plus transaction costs. Historical cost accounting involves reporting assets and liabilities at their historical costs, which are not updated for changes in the items' values. Consequently, the amounts reported for these balance sheet items often differ from their current economic or market values. While use of historical cost measurement is criticised for its lack of timely reporting of value changes, it remains in use in most accounting systems during periods of low and high inflation and deflation. During hyperinflation, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) require financial capital maintenance in units of constant purchasing power in terms of the monthly CPI as set out in IAS 29, Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies. Various adjustments to hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lease
A lease is a contractual arrangement calling for the user (referred to as the ''lessee'') to pay the owner (referred to as the ''lessor'') for the use of an asset. Property, buildings and vehicles are common assets that are leased. Industrial or business equipment are also leased. In essence, a lease agreement is a contract between two parties: the lessor and the lessee. The lessor is the legal owner of the asset, while the lessee obtains the right to use the asset in return for regular rental payments. The lessee also agrees to abide by various conditions regarding their use of the property or equipment. For example, a person leasing a car may agree to the condition that the car will only be used for personal use. The term rental agreement can refer to two kinds of leases: * A lease in which the asset is tangible property. Here, the user '' rents'' the asset (e.g. land or goods) ''let out'' or ''rented out'' by the owner (the verb ''to lease'' is less precise because it c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
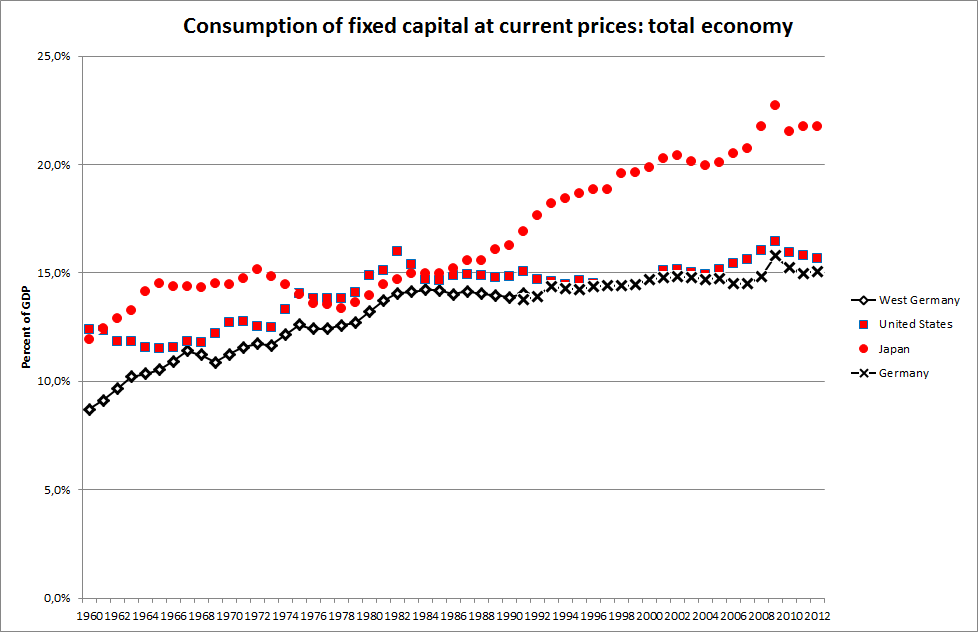
Consumption Of Fixed Capital
Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process of generating new output, and because unlike depreciation it is not valued at historic cost but at current market value (so-called "economic depreciation"); CFC may also include other expenses incurred in using or installing fixed assets beyond actual depreciation charges. Normally the term applies only to ''producing'' enterprises, but sometimes it applies also to real estate assets. CFC refers to a depreciation charge (or "write-off") against the gross income of a producing enterprise, which reflects the decline in value of fixed capital being operated with. Fixed assets will decline in value after they are purchased for use in production, due to wear and tear, changed market valuation and possibly market obsolescence. Thus, CFC represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Conference On Trade And Development
UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development but rebranded to its current name on the occasion of its 60th anniversary in 2024. It reports to both the General Assembly and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). UNCTAD is composed of 195 member states and works with non-governmental organizations worldwide; its permanent secretariat is at UNOG in Geneva, Switzerland. The primary objective of UNCTAD is to formulate policies relating to all aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance and technology. It was created in response to concerns among developing countries that existing international institutions like GATT (since replaced by the World Trade Organization), the International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Capital
Financial capital (also simply known as capital or equity in finance, accounting and economics) is any Economic resources, economic resource measured in terms of money used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy what they need to make their products or to provide their services to the sector of the economy upon which their operation is based (e.g. retail, corporate, investment banking). In other words, financial capital is internal retained earnings generated by the entity or funds provided by lenders (and Investor, investors) to businesses in order to purchase real capital equipment or services for producing new Goods and services, goods or services. In contrast, real capital comprises physical goods that assist in the production of other goods and services (e.g. shovels for gravediggers, sewing machines for tailors, or machinery and tooling for factories). IFRS concepts of capital maintenance ''Financial capital'' generally refers to saved-up financial Wealth (economics), we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream. In finance, the purpose of investing is to generate a Return (finance), return on the invested asset. The return may consist of a capital gain (profit) or loss, realised if the investment is sold, unrealised capital appreciation (or depreciation) if yet unsold. It may also consist of periodic income such as dividends, interest, or rental income. The return may also inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development. The World Bank is the collective name for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Association (IDA), two of five international organizations owned by the World Bank Group. It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. After a slow start, its first loan was to France in 1947. In its early years, it primarily focused on rebuilding Europe. Over time, it focused on providing loans to developing world countries. In the 1970s, the World Bank re-conceptualized its mission of facilitating development as being oriented around poverty reduction. For the last 30 years, it has included NGOs and environmental groups in its loan portfolio. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of last resort to national governments, and a leading supporter of exchange-rate economic stability, stability. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and poverty reduction, reduce poverty around the world." Established in July 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference, primarily according to the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it started with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary systems, international monetary system after World War II. In its early years, the IMF primarily focused on facilitating fixed exchange rates across the developed worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |