|
Bufotoxin
Bufotoxins are a family of toxic steroid lactones or substituted tryptamines of which some may or may not be toxic. They occur in the parotoid glands, skin, and poison of many toads ( genus ''Bufo'') and other amphibians, and in some plants and mushrooms. The exact composition varies greatly with the specific source of the toxin. It can contain 5-MeO-DMT, bufagins, bufalin, bufotalin, bufotenin, bufothionine, dehydrobufotenine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Some authors have also used the term ''bufotoxin'' to describe the conjugate of a bufagin with suberylarginine. The toxic substances found in toads can be divided by chemical structure in two groups: #bufadienolides, which are cardiac glycosides (e.g., bufotalin, bufogenin) # tryptamine-related substances (e.g., bufotenin) Toads known to secrete bufotoxin include the following: *'' Bufo alvarius'' *''Bufo americanus'' *''Bufo arenarum'' *''Bufo asper'' *''Bufo blombergi'' *''Bufo boreas'' *''Bufo bufo' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Bufo
The common toad, European toad, or in Anglophone parts of Europe, simply the toad (''Bufo bufo'', from Latin ''bufo'' "toad"), is a frog found throughout most of Europe (with the exception of Ireland, Iceland, and some Mediterranean islands), in the western part of North Asia, and in a small portion of Northwest Africa. It is one of a group of closely related animals that are descended from a common ancestral line of toads and which form a species complex. The toad is an inconspicuous animal as it usually lies hidden during the day. It becomes active at dusk and spends the night hunting for the invertebrates on which it feeds. It moves with a slow, ungainly walk or short jumps, and has greyish-brown skin covered with wart-like lumps. Although toads are usually solitary animals, in the breeding season, large numbers of toads converge on certain breeding ponds, where the males compete to mate with the females. Eggs are laid in gelatinous strings in the water and later hatch out int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufotoxin
Bufotoxins are a family of toxic steroid lactones or substituted tryptamines of which some may or may not be toxic. They occur in the parotoid glands, skin, and poison of many toads ( genus ''Bufo'') and other amphibians, and in some plants and mushrooms. The exact composition varies greatly with the specific source of the toxin. It can contain 5-MeO-DMT, bufagins, bufalin, bufotalin, bufotenin, bufothionine, dehydrobufotenine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Some authors have also used the term ''bufotoxin'' to describe the conjugate of a bufagin with suberylarginine. The toxic substances found in toads can be divided by chemical structure in two groups: #bufadienolides, which are cardiac glycosides (e.g., bufotalin, bufogenin) # tryptamine-related substances (e.g., bufotenin) Toads known to secrete bufotoxin include the following: *'' Bufo alvarius'' *''Bufo americanus'' *''Bufo arenarum'' *''Bufo asper'' *''Bufo blombergi'' *''Bufo boreas'' *''Bufo bufo' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Toad
The Asiatic toad or Chusan Island toad (''Bufo gargarizans'') is a species of toad endemic to East Asia. The species was previously classified as ''Bufo bufo gargarizans'', a subspecies of the common toad. Distribution and habitat It is common in China (specifically Anhui, Fujian, Gansu, Guizhou, Hebei, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Inner Mongolia, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Jilin, Qinghai, Shaanxi, Shandong, Shanxi, Sichuan, and Zhejiang) and portions of the Russian Far East (up north to the Amur River valley and on Sakhalin Island, and east to Transbaikalia in Siberia), but relatively rare on the Korean Peninsula. Asiatic toads are also found on the Miyako Islands of southern Japan, although they have been extirpated from some islands in recent years, possibly including Okinawa. The Miyako subspecies, '' Bufo gargarizans miyakonis'', is also known as the Miyako toad. The Asiatic toad avoids dense forests, but is found in most other habitats, including grasslands, open forests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotoid Gland
The parotoid gland (alternatively, paratoid gland) is an external skin gland on the back, neck, and shoulder of toads and some frogs and salamanders. It can secrete a number of milky alkaloid substances (depending on the species) known collectively as bufotoxins, which act as neurotoxins to deter predation. These cutaneous glands are called parotoid as they are somewhat similarly positioned to mammalian parotid gland, although the latter have a different function, excreting saliva within the mouth rather than externally excreted defensive chemicals. A study of the parotoid glands of the Colorado River toad in 1976 found that the parotoid glands were "composed of numerous lobules", each of which is a separate unit with a lumen surrounded by a double cell layer. The cell layers have interlocking microvilli. The study found that the outer cell layer resembled smooth muscle cells, with some organelles hypothesised to "function in some aspects of venom synthesis, active cellular tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Americanus
The American toad (''Anaxyrus americanus'') is a common species of toad found throughout Canada and the eastern United States. It is divided into three subspecies: the eastern American toad (''A. a. americanus''), the dwarf American toad (''A. a. charlesmithi'') and the rare Hudson Bay toad (''A. a. copei''). Recent taxonomic treatments place this species in the genus ''Anaxyrus'' instead of ''Bufo''. Tadpoles The eggs of the American toad are laid in two strings and can hatch in 2–14 days. When hatched the tadpoles are recognizable by their skinny tails in relation to the size of their black bodies. They may advance to adulthood in 50–65 days. When metamorphosis is completed, the "toadlets" may stay in the water for a short period of time before they become mostly land based. Often entire groups of tadpoles reach the ''toadlet'' stage at once and a mass migration to higher ground takes place usually to shaded areas of mid range and upland forests bordering the marshes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Boreas
The western toad (''Anaxyrus boreas'') is a large toad species, between long, native to western North America. ''A. boreas'' is frequently encountered during the wet season on roads, or near water at other times. It can jump a considerable distance for a toad. Breeding occurs between March and July in mountainous areas, and as early as January in lower-elevation regions. The female lays up to 17,000 eggs stuck together in strings that adhere to vegetation and other objects along water edges. Description It has a white or cream dorsal stripe, and is dusky gray or greenish dorsally with skin glands concentrated within the dark blotches. Its parotoid glands are oval, widely separated, and larger than the upper eyelids. It has a mottled venter and horizontal pupils but lacks cranial crests. Compared to females, males have smoother skin, reduced dorsal blotching, and nuptial pads (thickened skin) on their forefeet during breeding season. In juveniles of this species, the dorsal strip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Blombergi
Blomberg's toad (''Rhaebo blombergi''), also known as the Colombian giant toad, is a very large species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in rainforests at altitudes between in western Colombia ( Chocó, Valle del Cauca, Cauca, and Nariño Departments) and northwestern Ecuador (Carchi, Esmeraldas, and Imbabura Provinces). It has been recorded in Florida in 1963, apparently because of pet escape or release, but did not get established. Etymology This species epithet commemorates Swedish explorer Rolf Blomberg who collected the type series. Description ''Rhaebo blombergi'' is one of the world's largest toads: males measure and females in snout–to–vent length. Life history Fecundity of captive individuals has been 15,000–80,000 eggs of in diameter. Captive individuals have an average lifespan of ten years, with the maximum reported age of 28 years. Habitat and conservation ''Rhaebo blombergi'' inhabit closed lowland tropical rainforest. They breed in pool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Asper
The Asian giant toad (''Phrynoidis asper''), sometimes referred to as the river toad, is a species of true toad native to Mainland Southeast Asia and the Greater Sundas. It is a medium-large toad, but it is easily confused with its larger relative, the giant river toad (''P. juxtasper''). Description ''Phrynoidis asper'' is generally a dark grey, green, black or brown in color, and is heavily covered in tubercles. Females can reach up to in snout–to–vent Vent or vents may refer to: Science and technology Biology *Vent, the cloaca region of an animal * Vent DNA polymerase, a thermostable DNA polymerase Geology *Hydrothermal vent, a fissure in a planet's surface from which geothermally heated wate ... length and males up to . They can be commonly found near stream and rivers. Photos File:Giant Asian Toad (Phrynoidis aspera) (8688768164).jpg File:River Toad Phrynoidis aspera (7920853968).jpg File:River Toad (Phrynoidis aspera) (6731222373).jpg References *Frogs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufo Arenarum
''Rhinella arenarum'' is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae that is found in southern Brazil and Uruguay; can also occur in Paraguay. It is also found in Argentina from the Chubut Province northward, Bolivia , image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ... east of the Andes. ''Rhinella arenarum'' inhabits small ponds or bogs with stagnant water, in dry, temperate habitats, mostly in open areas. It is locally common. While it is collected for educational and scientific uses and also suffers from road kills, it in general is not threatened. Fossils representing this species are known with certainty from the late Pliocene up to the Holocene of central Argentina. References arenarum Amphibians described in 1867 Amphibians of Brazil Amphibians of Bolivia Amphibians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado River Toad
The Colorado River toad (''Incilius alvarius''), formerly known as the Sonoran Desert toad, is found in northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It exudes toxins from glands within its skin that have psychoactive properties. Description The Colorado River toad can grow to about long and is the largest toad in the United States apart from the non-native cane toad (''Rhinella marina''). It has a smooth, leathery skin and is olive green or mottled brown in color. Just behind the large golden eye with horizontal pupil is a bulging kidney-shaped parotoid gland. Below this is a large circular pale green area which is the tympanum or ear drum. By the corner of the mouth there is a white wart and there are white glands on the legs. All these glands produce toxic secretions. Its call is described as, "a weak, low-pitched toot, lasting less than a second." Dogs that have attacked toads have suffered paralysis or even death. Raccoons have learned to pull a toad away from a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
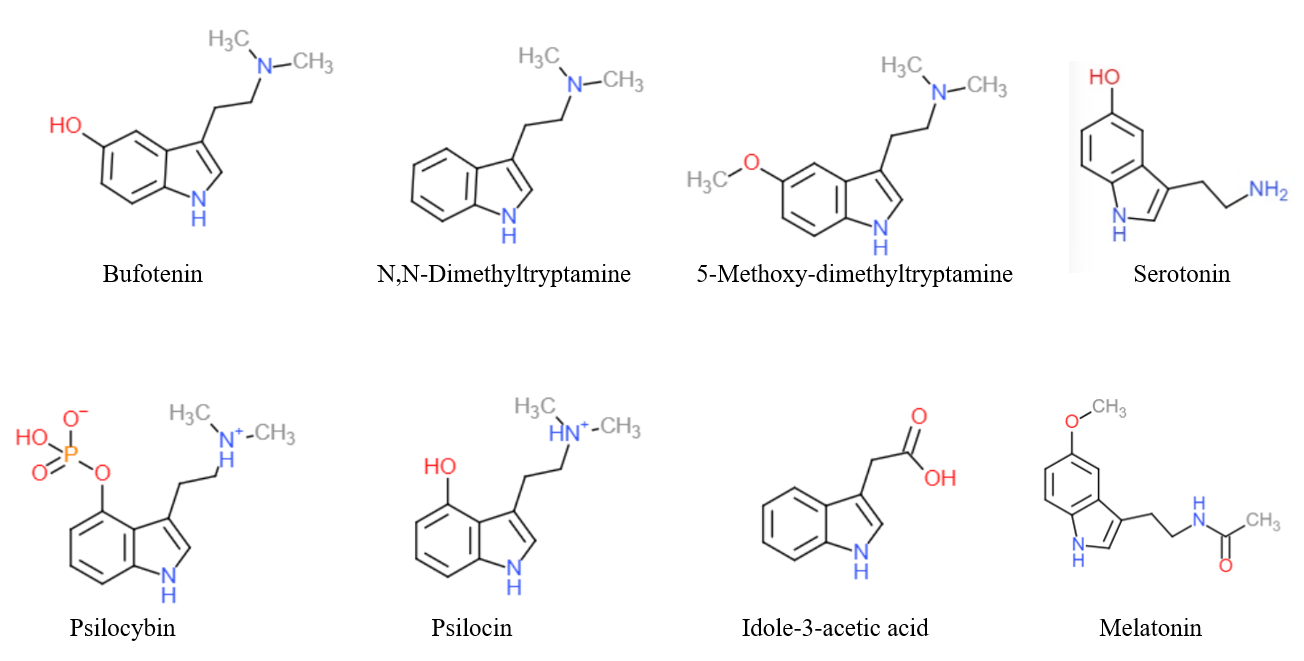
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(7046220291).jpg)