|
Brilliant Cresyl Blue
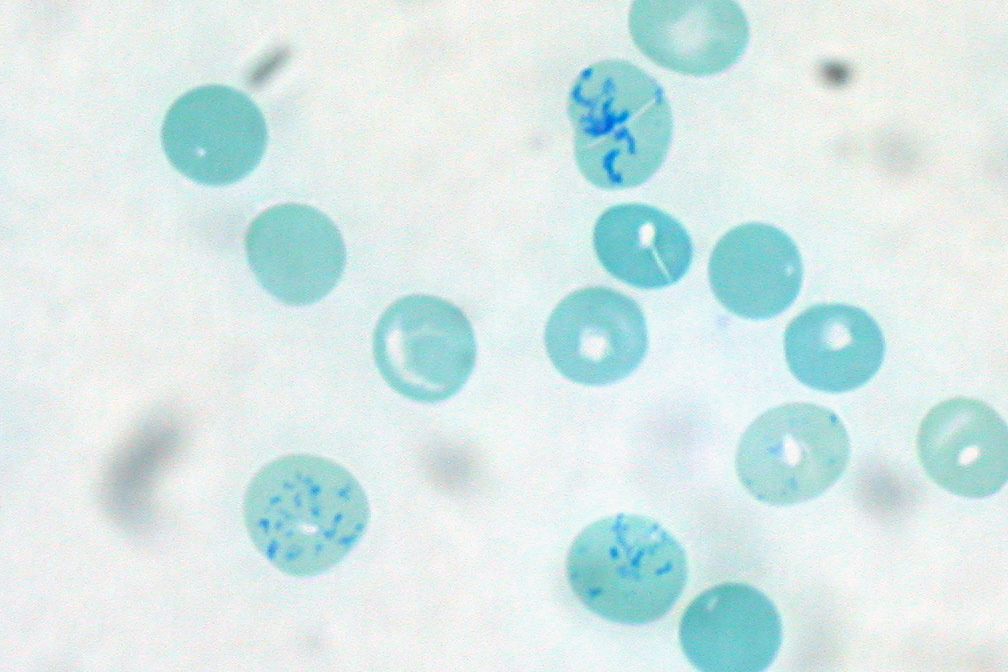
Brilliant cresyl blue is a supravital stain used for counting reticulocyte Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into ma ...s. It is classified as an oxazine dye. N95 dust masks, eye shields, and gloves must all be worn when handling the chemical. References {{heterocyclic-stub Chlorides Zinc compounds Oxazine dyes Phenoxazines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brilliant Cresyl Blue
Brilliant cresyl blue is a supravital stain used for counting reticulocyte Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into ma ...s. It is classified as an oxazine dye. N95 dust masks, eye shields, and gloves must all be worn when handling the chemical. References {{heterocyclic-stub Chlorides Zinc compounds Oxazine dyes Phenoxazines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supravital Stain
Supravital staining is a method of staining used in microscopy to examine living cells that have been removed from an organism. It differs from intravital staining, which is done by injecting or otherwise introducing the stain into the body. Thus a supravital stain may have a greater toxicity, as only a few cells need to survive it a short while. The term "vital stain" is used by some authors to refer specifically to an intravital stain, and by others interchangeably with a supravital stain, the core concept being that the cell being examined is still alive. As the cells are alive and unfixed, outside the body, supravital stains are temporary in nature. The most common supravital stain is performed on reticulocytes using new methylene blue or brilliant cresyl blue, which makes it possible to see the reticulofilamentous pattern of ribosomes characteristically precipitated in these live immature red blood cells by the supravital stains. By counting the number of such cells the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain. Clinical significance To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorescent dye that marks RNA and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine). Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a characteristic that is described by the mean corpuscular volume. The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
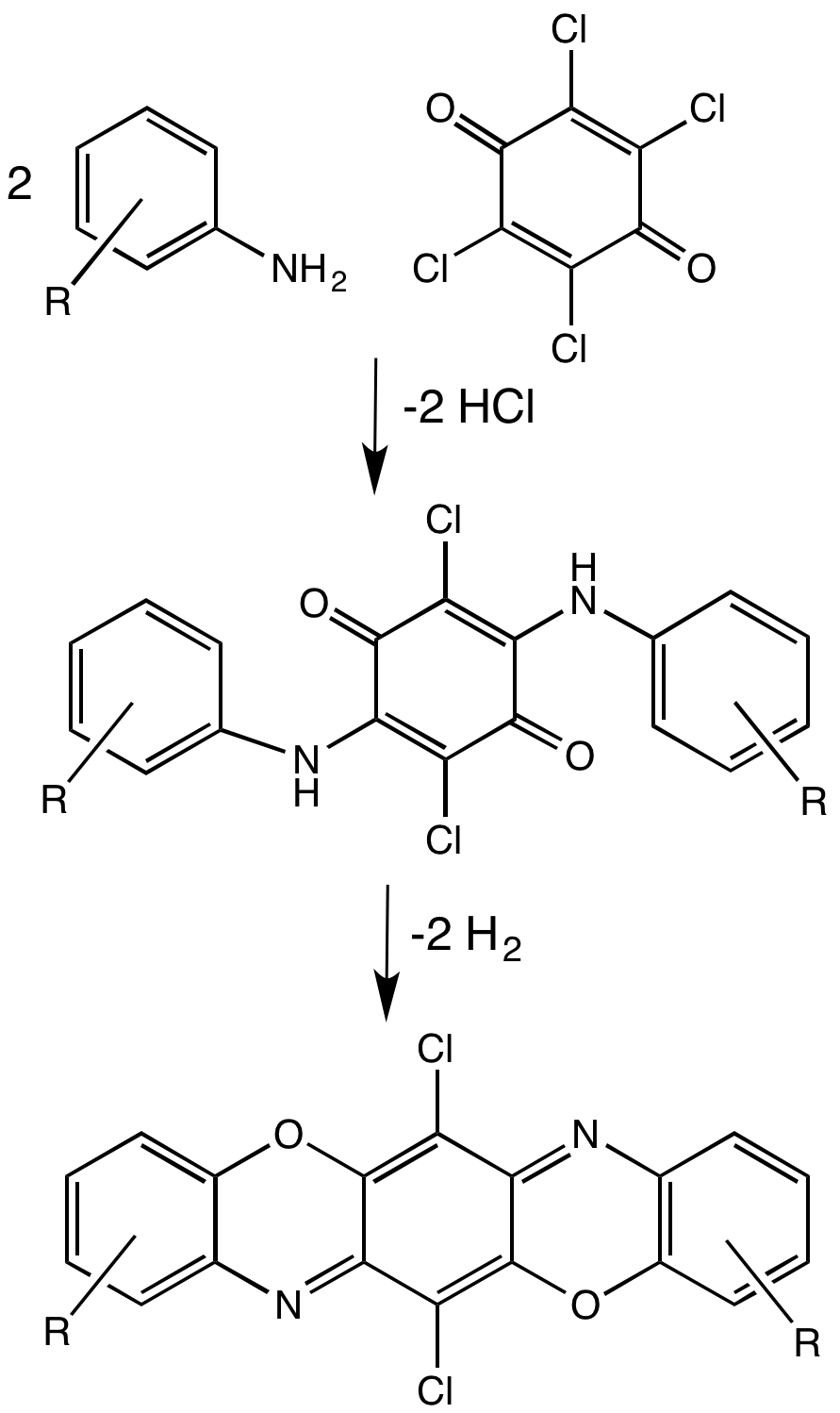
Oxazine Dye
Oxazines are heterocyclic compounds containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom in a doubly unsaturated six-membered ring. Isomers exist depending on the relative position of the heteroatoms and relative position of the double bonds. By extension, the derivatives are also referred to as oxazines; examples include ifosfamide and morpholine (tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine). A commercially available dihydro-1,3-oxazine is a reagent in the Meyers synthesis of aldehydes. Fluorescent dyes such as Nile red and Nile blue are based on the aromatic benzophenoxazine. Cinnabarine and cinnabaric acid are two naturally occurring dioxazines, being derived from biodegradation of tryptophan. Dioxazines Dioxazines are pentacyclic compounds consisting of two oxazine subunits. A commercially important example is the pigment pigment violet 23. Benzoxazines Benzoxazines are bicyclic compounds formed by the ring fusion of a benzene ring with an oxazine. Polybenzoxazines are a class of polymers formed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N95 Mask
An N95 filtering facepiece respirator, commonly abbreviated N95 respirator, is a particulate-filtering facepiece respirator that meets the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) N95 classification of air filtration, meaning that it filters at least 95% of airborne particles. This standard does not require that the respirator be resistant to oil; another standard, P95, adds that requirement. The N95 type is the most common particulate-filtering facepiece respirator. It is an example of a mechanical filter respirator, which provides protection against particulates but not against gases or vapors. An authentic N95 respirator is marked with the text "NIOSH" or the NIOSH logo, the filter class ("N95"), a "TC" approval number of the form XXX-XXXX, the approval number must be listed on the NIOSH Certified Equipment List (CEL) or the NIOSH Trusted-Source page, and it must have headbands instead of ear loops. The N95 mask filter was invented by Taiwanese-Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorides
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often very soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Less frequently, the word ''chloride'' may also form part of the "common" name of chemical compounds in which one or more chlorine atoms are covalently bonded. For example, methyl chloride, with the standard name chloromethane (see IUPAC books) is an organic compound with a covalent C−Cl bond in which the chlorine is not an anion. Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much larger th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Compounds
Zinc compounds are chemical compounds containing the element zinc which is a member of the group 12 of the periodic table. The oxidation state of zinc in most compounds is the group oxidation state of +2. Zinc may be classified as a post-transition main group element with zinc(II). Zinc compounds are noteworthy for their nondescript behavior, they are generally colorless (unlike other elements with the oxidation number +2, which are usually white), do not readily engage in redox reactions, and generally adopt symmetrical structures. General characteristics In its compounds, Zn2+ ions have an electronic configuration r3d10. As such, Zn2+ tends to have a symmetrical coordination geometry in both its complexes and compounds. In both ZnO and ZnS, (zincblende) zinc is bound tetrahedrally bound to four ligands (oxide and sulfide, respectively). Many complexes, such as ZnCl42−, are tetrahedral. Tetrahedrally coordinated zinc is found in metallo-enzymes such as carbonic anhydrase. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazine Dyes
Oxazines are heterocyclic compounds containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom in a doubly unsaturated six-membered ring. Isomers exist depending on the relative position of the heteroatoms and relative position of the double bonds. By extension, the derivatives are also referred to as oxazines; examples include ifosfamide and morpholine (tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine). A commercially available dihydro-1,3-oxazine is a reagent in the Meyers synthesis of aldehydes. Fluorescent dyes such as Nile red and Nile blue are based on the aromatic benzophenoxazine. Cinnabarine and cinnabaric acid are two naturally occurring dioxazines, being derived from biodegradation of tryptophan. Dioxazines Dioxazines are pentacyclic compounds consisting of two oxazine subunits. A commercially important example is the pigment pigment violet 23. Benzoxazines Benzoxazines are bicyclic compounds formed by the ring fusion of a benzene ring with an oxazine. Polybenzoxazines are a class of polymers formed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |