|
Brevetoxin
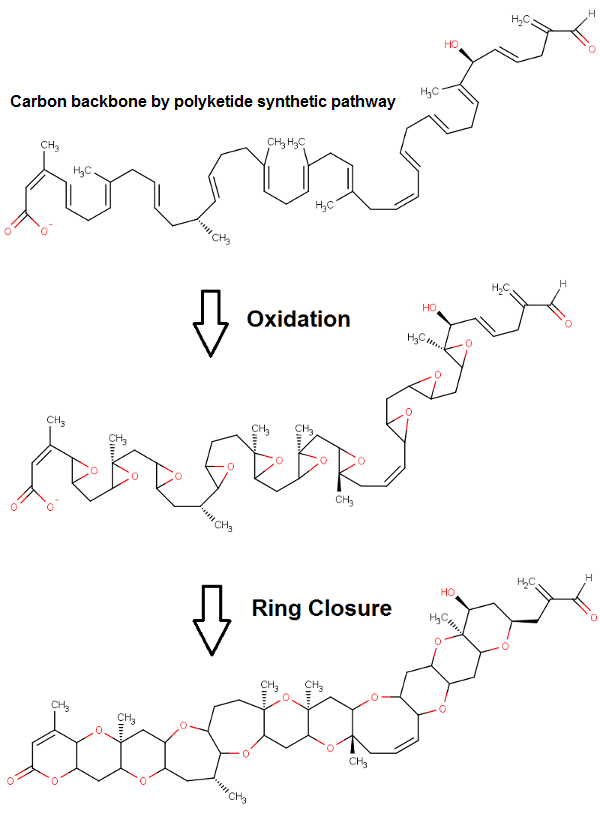
Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as ''Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, leading to disruption of normal neurological processes and causing the illness clinically described as neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP). Although brevetoxins are most well-studied in ''K. brevis'', they are also found in other species of '' Karenia'' and at least one large fish kill has been traced to brevetoxins in '' Chattonella''. Other Brevetoxins: *Brevetoxin-5 (PbTx-5): like PbTx-2, but acetylated hydroxyl group in position 38. *Brevetoxin-6 (PbTx-6): like PbTx-2, but double bond 27-28 is epoxidated. Brevetoxin-B was synthesized in 1995 by K. C. Nicolaou and coworkers in 123 steps with 91% average yield (final yield ~9·10−6) and in 2004 in a total of 90 steps with an average 93% yield for each step (0.14% overall). K. C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevetoxin B
Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as '' Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, leading to disruption of normal neurological processes and causing the illness clinically described as neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP). Although brevetoxins are most well-studied in ''K. brevis'', they are also found in other species of '' Karenia'' and at least one large fish kill has been traced to brevetoxins in '' Chattonella''. Other Brevetoxins: *Brevetoxin-5 (PbTx-5): like PbTx-2, but acetylated hydroxyl group in position 38. *Brevetoxin-6 (PbTx-6): like PbTx-2, but double bond 27-28 is epoxidated. Brevetoxin-B was synthesized in 1995 by K. C. Nicolaou and coworkers in 123 steps with 91% average yield (final yield ~9·10−6) and in 2004 in a total of 90 steps with an average 93% yield for each step (0.14% overall). K. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevetoxin A
Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as '' Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, leading to disruption of normal neurological processes and causing the illness clinically described as neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP). Although brevetoxins are most well-studied in ''K. brevis'', they are also found in other species of '' Karenia'' and at least one large fish kill has been traced to brevetoxins in '' Chattonella''. Other Brevetoxins: *Brevetoxin-5 (PbTx-5): like PbTx-2, but acetylated hydroxyl group in position 38. *Brevetoxin-6 (PbTx-6): like PbTx-2, but double bond 27-28 is epoxidated. Brevetoxin-B was synthesized in 1995 by K. C. Nicolaou and coworkers in 123 steps with 91% average yield (final yield ~9·10−6) and in 2004 in a total of 90 steps with an average 93% yield for each step (0.14% overall). K. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB) (or excessive algae growth) is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are sometimes defined as only those algal blooms that produce toxins, and sometimes as any algal bloom that can result in severely lower oxygen levels in natural waters, killing organisms in marine or fresh waters. Blooms can last from a few days to many months. After the bloom dies, the microbes that decompose the dead algae use up more of the oxygen, generating a " dead zone" which can cause fish die-offs. When these zones cover a large area for an extended period of time, neither fish nor plants are able to survive. Harmful algal blooms in marine environments are often called "red tides". It is sometimes unclear what causes specific HABs as their occurrence in some locations appears to be entirely natural, while in others they appear to be a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning
Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) is caused by the consumption of brevetoxins, which are marine toxins produced by the dinoflagellate ''Karenia brevis'' (among several others). These toxins can produce a series of gastrointestinal and neurological effects. Outbreaks of NSP commonly take place following harmful algal bloom (HAB) events, commonly referred to as "Florida red tide" (given that blooms are more commonplace along the coasts of Florida and Texas, especially during late summer and early fall). Algal blooms are a naturally-occurring phenomenon, however their frequency has been increasing in recent decades at least in-part due to human activities, climate changes, and the eutrophication (over-abundance of plant nutrients as a result of agricultural runoff, deforestation, river bed erosion, etc.) of marine waters. HABs have been occurring for all of documented history, evidenced by the Native Americans' understanding of the dangers of shellfish consumption during periods o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karenia Brevis
''Karenia brevis'' is a microscopic, single-celled, photosynthetic organism in the genus '' Karenia''. It is a marine dinoflagellate commonly found in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. It is the organism responsible for the "Florida red tides" that affect the Gulf coasts of Florida and Texas in the U.S., and nearby coasts of Mexico. ''K. brevis'' has been known to travel great lengths around the Florida peninsula and as far north as the Carolinas. Each cell has two flagella that allow it to move through the water in a spinning motion. ''K. brevis'' is unarmored, and does not contain peridinin. Cells are between 20 and 40 μm in diameter. ''K. brevis'' naturally produces a suite of potent neurotoxins collectively called brevetoxins, which cause gastrointestinal and neurological problems in other organisms and are responsible for large die-offs of marine organisms and seabirds. History ''Karenia brevis'' was named for Dr. Karen A. Steidinger in 2001, and was previously kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karenia (dinoflagellate)
''Karenia'' is a genus that consists of unicellular, photosynthetic, planktonic organisms found in marine environments. The genus currently consists of 12 described species. They are best known for their dense toxic algal blooms and red tides that cause considerable ecological and economical damage; some ''Karenia'' species cause severe animal mortality. One species, ''Karenia brevis'', is known to cause respiratory distress and neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) in humans. Taxonomy The genus ''Karenia'' is named for Dr. Karen Steidinger for her exceptional contributions to dinoflagellate research. She has spent many decades researching ''Karenia brevis''. 12 species have been described in the genus ''Karenia'' thus far: * '' Karenia asterichroma'' * ''Karenia bicuneiformis'' * ''Karenia brevis'' * '' Karenia brevisulcata'' * '' Karenia concordia'' * '' Karenia cristata'' * '' Karenia digitata'' * '' Karenia longicanalis'' * ''Karenia mikimotoi'' * ''Karenia papilionacea'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyether Toxins
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattonella
''Chattonella'' is a genus of marine raphidophytes associated with red tides. A technique using monoclonal antibodies can be used to identify the genus, while the RAPD reaction can be used to distinguish between different species within the genus. It includes the species ''Chattonella antiqua'', a bloom forming alga responsible for large scale fish deaths due to the synthesis of toxic compounds related to brevetoxin Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as ''Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, le .... References Heterokont genera Ochrophyta {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-gated Sodium Channel
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the channel for such ions, i.e. either a voltage-change ("voltage-gated", "voltage-sensitive", or "voltage-dependent" sodium channel; also called "VGSCs" or "Nav channel") or a binding of a substance (a ligand) to the channel ( ligand-gated sodium channels). In excitable cells such as neurons, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel Toxins
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel Openers
A sodium channel opener is a type of drug which facilitates ion transmission through sodium channels. Examples include toxins, such as aconitine, veratridine, batrachotoxin, robustoxin, palytoxin and ciguatoxins and insecticides (DDT and pyrethroids), which activate voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs), and solnatide (AP301), which activates the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). See also * Sodium channel blocker Sodium channel blockers are drugs which impair the conduction of sodium ions (Na+) through sodium channels. Extracellular The following naturally-produced substances block sodium channels by binding to and occluding the extracellular pore opening ... References {{pharmacology-stub Ion channel openers Sodium channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |