|
Boulangerite
Boulangerite is an uncommon monoclinic orthorhombic sulfosalt mineral, lead antimony sulfide, formula Pb5Sb4S11. It was named in 1837 in honor of French mining engineer Charles Boulanger (1810–1849),http://www.mindat.org/min-738.html Mindat and had been a valid species since pre- IMA. It was first described prior to 1959, and is now grandfathered.http://webmineral.com/data/Boulangerite.shtml Webmineral data Properties Boulangerite was considered to be a really rare mineral until later they found numerous ore deposits of said mineral. Nowadays it is considered as an uncommon mineral, which is rather cheap, with a color of light blue to black to grey. The dust of the mineral is black. Pseudohexagonal shape is common for this mineral. It forms rings rarely. It is the homeotype of lopatkaite. The strong subcell is orthorhombic, and has a halved c. It forms small, elongated prismic or fine, needle-like crystals. Each crystal can grow up to a few centimeters, and crystals can on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in sedimentary exhalative, Mississippi-Valley type, and volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfides), calcite, dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque black variety with a high iron content. Crystal habit and structure Sphalerite crystallizes in the face-centered cubic zincblende crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio. China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are roasting followed by reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron. The largest applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin, which have improved properties for solders, bullets, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy plates in lead–acid batteries. Antimony trioxide is a prominent additive f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumosite
Plumosite is a questionable mineral. Most of the time, it can refer to any feather ore, i.e. any ore that forms fine capillaries within the surrounding rock. Older specimens could be either boulangerite, jamesonite or zinkenite Zinkenite is a steel-gray metallic sulfosalt mineral composed of lead antimony sulfide Pb9 Sb22 S42. Zinkenite occurs as acicular needle-like crystals. It was first described in 1826 for an occurrence in the Harz Mountains, Saxony-Anhalt, Germa ... (Pb2Sb2S5, sulfosalt mineral). References Mineralogy {{Mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfosalt Minerals
Sulfosalt minerals are sulfide minerals with the general formula , where *A represents a metal such as copper, lead, silver, iron, and rarely mercury, zinc, vanadium *B usually represents semi-metal such as arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and rarely germanium, or metals like tin and rarely vanadium *X is sulfur or rarely selenium and/or tellurium. The Strunz classification includes the sulfosalts in a ''sulfides and sulfosalts'' superclass. A group which have similar appearing formulas are the sulfarsenides (for example cobaltite (Co,Fe)AsS). In sulfarsenides the arsenic substitutes for sulfide anions whereas in the sulfosalts the arsenic substitutes for a metal cation.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut (1985). ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York . About 200 sulfosalt minerals are known. Examples include: File:Proustite (long prismatic crystal) - Chanarcillo, Copiapo Province, Atacama Region, Chile.jpg, As illustrated by this specimen of prous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apuan Alps
The Apuan Alps ( it, Alpi Apuane) are a mountain range in northern Tuscany, Italy. They are included between the valleys of the Serchio and Magra rivers, and, to the northwest, the Garfagnana and Lunigiana, with a total length of approximately . The name derives from the Apuani Ligures tribe that lived there in ancient times. The mountain range is known for its Carrara marble. Due to its extraction height environmental impact, the No Cav movement strongly opposes this activity. Geology and geography The chain formed out of sea sediments in the middle Triassic period, somewhat earlier than the rest of the Apennines, and on a rather different geological structure. Over time, these sediments hardened into limestone, dolomite, sandstone, and shale. Harsh pressure approximately 25 million years ago transformed the limestone in many places into the Carrara marble (named for the nearby city of Carrara) for which the range is renowned. Erosion carved much of the remaining sedimentar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide. Chemical properties The sulfide ion, S2−, does not exist in aqueous alkaline solutions of Na2S. Instead sulfide converts to hydrosulfide: :S2− + H2O → SH− + OH− Upon treatment with an acid, sulfide salts convert to hydrogen sulfide: :S2− + H+ → SH− :SH− + H+ → H2S Oxidation of sulfide is a complicated process. Depending on the conditions, the oxidation can produce elemental sulfur, polysulfides, polythionates, sulfite, or sulfate. Metal sulfides react with halogens, forming sulfur and metal salts. :8 MgS + 8 I2 → S8 + 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenopyrite
Arsenopyrite ( IMA symbol: Apy) is an iron arsenic sulfide (FeAsS). It is a hard ( Mohs 5.5-6) metallic, opaque, steel grey to silver white mineral with a relatively high specific gravity of 6.1. When dissolved in nitric acid, it releases elemental sulfur. When arsenopyrite is heated, it produces sulfur and arsenic vapor. With 46% arsenic content, arsenopyrite, along with orpiment, is a principal ore of arsenic. When deposits of arsenopyrite become exposed to the atmosphere, the mineral slowly converts into iron arsenates. Arsenopyrite is generally an acid-consuming sulfide mineral, unlike iron pyrite which can lead to acid mine drainage. The crystal habit, hardness, density, and garlic odour when struck are diagnostic. Arsenopyrite in older literature may be referred to as ''mispickel'', a name of German origin. Arsenopyrite also can be associated with significant amounts of gold. Consequently, it serves as an indicator of gold bearing reefs. Many arsenopyrite gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhotine
Pyrrhotite is an iron sulfide mineral with the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2). It is a nonstoichiometric variant of FeS, the mineral known as troilite. Pyrrhotite is also called magnetic pyrite, because the color is similar to pyrite and it is weakly magnetic. The magnetism decreases as the iron content increases, and troilite is non-magnetic.Vaughan, D. J.; Craig, J. R. "Mineral Chemistry of Metal Sulfides" Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 1978. . Structure Pyrrhotite exists as a number of polytypes of hexagonal or monoclinic crystal symmetry; several polytypes often occur within the same specimen. Their structure is based on the NiAs unit cell. As such, Fe occupies an octahedral site and the sulfide centers occupy trigonal prismatic sites. Materials with the NiAs structure often are non-stoichiometric because they lack up to 1/8th fraction of the metal ions, creating vacancies. One of such structures is pyrrhotite-4C (Fe7S8). Here "4" indicates that iron vacanci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siderite
Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). It takes its name from the Greek word σίδηρος ''sideros,'' "iron". It is a valuable iron mineral, since it is 48% iron and contains no sulfur or phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium and manganese commonly substitute for the iron resulting in the siderite- smithsonite, siderite-magnesite and siderite- rhodochrosite solid solution series. Siderite has Mohs hardness of 3.75-4.25, a specific gravity of 3.96, a white streak and a vitreous lustre or pearly luster. Siderite is antiferromagnetic below its Néel temperature of 37 K which can assist in its identification. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system, and are rhombohedral in shape, typically with curved and striated faces. It also occurs in masses. Color ranges from yellow to dark brown or black, the latter being due to the presence of manganese. Siderite is commonly found in hydrothermal veins, and is associated with barite, fluorite, galena, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
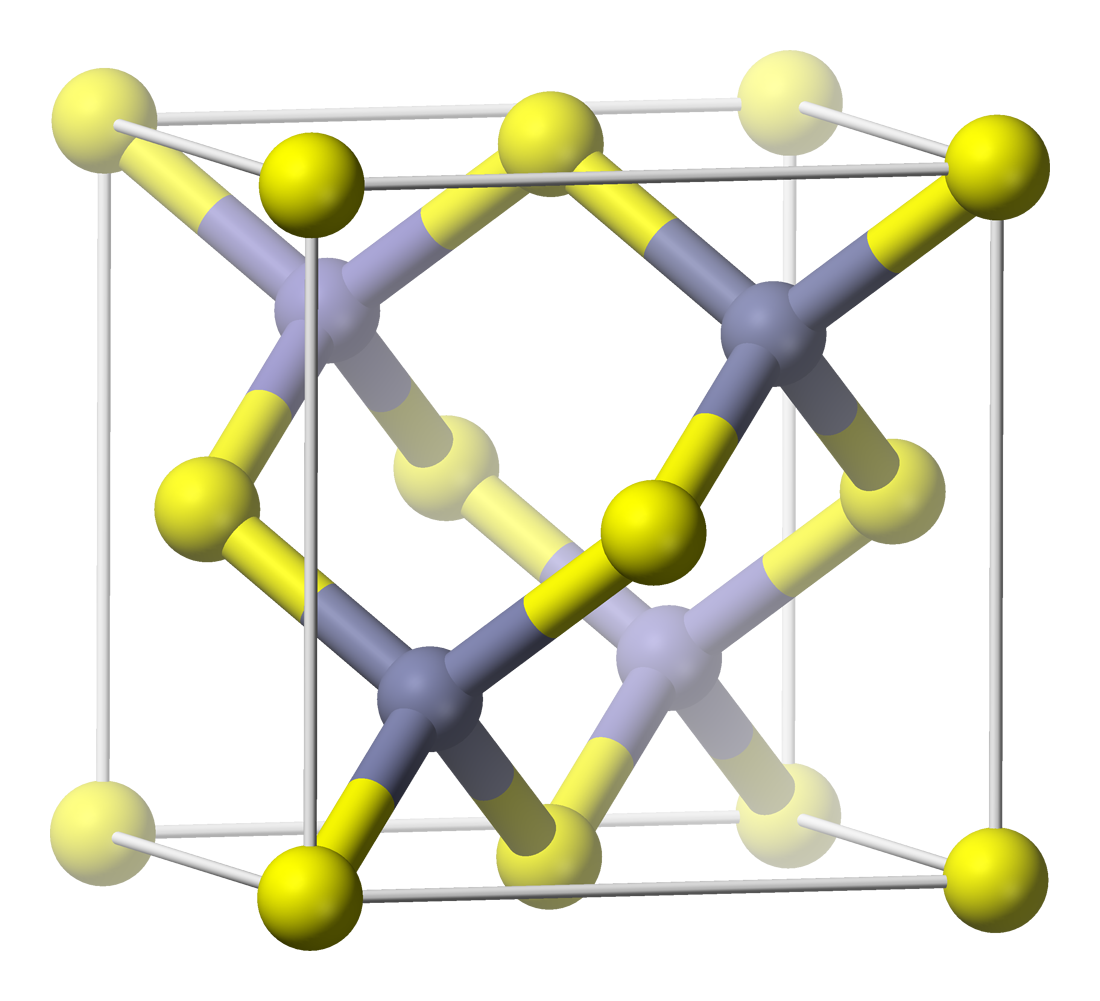
Galenite
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver. Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system often showing octahedral forms. It is often associated with the minerals sphalerite, calcite and fluorite. Occurrence Galena is the main ore of lead, used since ancient times, since lead can be smelted from galena in an ordinary wood fire. Galena typically is found in hydrothermal veins in association with sphalerite, marcasite, chalcopyrite, cerussite, anglesite, dolomite, calcite, quartz, barite, and fluorite. It is also found in association with sphalerite in low-temperature lead-zinc deposits within limestone beds. Minor amounts are found in contact metamorphic zones, in pegmatites, and disseminated in sedimentary rock. In some deposits the galena contains up to 0.5% silver, a byproduct tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lode
In geology, a lode is a deposit of metalliferous ore that fills or is embedded in a fissure (or crack) in a rock formation or a vein of ore that is deposited or embedded between layers of rock. The current meaning (ore vein) dates from the 17th century, being an expansion of an earlier sense of a "channel, watercourse" in late Middle English, which in turn is from the 11th-century meaning of ''lode'' as a ‘course, way’. The generally accepted hydrothermal model of lode deposition posits that metals dissolved in hydrothermal solutions (hot spring fluids) deposit the gold or other metallic minerals inside the fissures in the pre-existing rocks. Lode deposits are distinguished primarily from placer deposits, where the ore has been eroded out from its original depositional environment and redeposited by sedimentation. A third process for ore deposition is as an evaporite. A stringer lode is one in which the rock is so permeated by small veinlets that rather than mining th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

