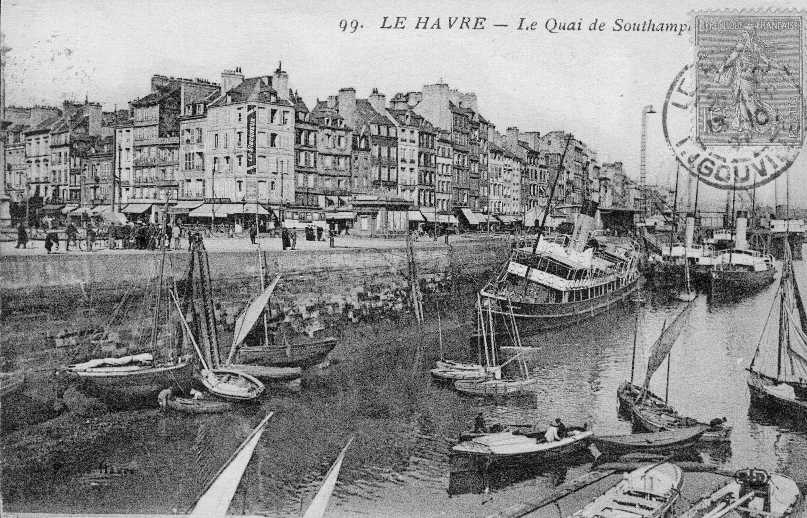|
Bad Faith (existentialism)
In the philosophy of existentialism, bad faith (''mauvaise foi'') is the psychological phenomenon whereby individuals act inauthentically, by yielding to the external pressures of society to adopt false values and disown their innate freedom as sentient human beings. Bad faith also derives from the related concepts of self-deception and ''ressentiment''. Freedom and choice A critical claim in existentialist thought is that individuals are always free to make choices and guide their lives towards their own chosen goal or "project". This claim suggests that individuals cannot escape this freedom, even in overwhelming circumstances. For instance, even an empire's colonized victims possess choices: to submit to rule, to negotiate, to commit suicide, to resist nonviolently, or to counter-attack. Although external circumstances may limit individuals (this limitation from the outside is called facticity), they cannot force a person to follow one of the remaining courses over anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existentialism
Existentialism ( ) is a form of philosophical inquiry that explores the problem of human existence and centers on human thinking, feeling, and acting. Existentialist thinkers frequently explore issues related to the meaning, purpose, and value of human existence, and the role of personal agency in transforming one's life. In the view of an existentialist, the individual's starting point is phenomenological, grounded in the immediate direct experience of life. Key concepts include " existential angst", a sense of dread, disorientation, confusion, or anxiety in the face of an apparently meaningless or absurd world, and also authenticity, courage, and human-heartedness. Existentialism is associated with several 19th- and 20th-century European philosophers who shared an emphasis on the human subject, despite often profound differences in thought. Among the earliest figures associated with existentialism are philosophers Søren Kierkegaard and Friedrich Nietzsche and novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Self
The true self (also known as real self, authentic self, original self and vulnerable self) and the false self (also known as fake self, idealized self, superficial self and pseudo self) are a psychological dualism conceptualized by English psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott. Winnicott used "true self" to denote a sense of self based on spontaneous authentic experience and a feeling of being alive, having a real self with little to no contradiction. "False self", by contrast, denotes a sense of self created as a defensive façade, which in extreme cases can leave an individual lacking spontaneity and feeling dead and empty behind an inconsistent and incompetent appearance of being real, such as in narcissism. Characteristics In his work, Winnicott saw the "true self" as stemming from self-perception in early infancy, such as awareness of tangible aspects of being alive, like blood pumping through veins and lungs inflating and deflating with breathing—what Winnicott called ''simply bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existentialist Concepts
Existentialism ( ) is a form of philosophical inquiry that explores the problem of human existence and centers on human thinking, feeling, and acting. Existentialist thinkers frequently explore issues related to the meaning, purpose, and value of human existence, and the role of personal agency in transforming one's life. In the view of an existentialist, the individual's starting point is phenomenological, grounded in the immediate direct experience of life. Key concepts include " existential angst", a sense of dread, disorientation, confusion, or anxiety in the face of an apparently meaningless or absurd world, and also authenticity, courage, and human-heartedness. Existentialism is associated with several 19th- and 20th-century European philosophers who shared an emphasis on the human subject, despite often profound differences in thought. Among the earliest figures associated with existentialism are philosophers Søren Kierkegaard and Friedrich Nietzsche and noveli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea (novel)
''Nausea'' (french: La Nausée) is a philosophical novel by the existentialist philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre, published in 1938. It is Sartre's first novel. The novel takes place in 'Bouville' (homophone of ''Boue-ville'', literally, 'Mud town') a town similar to Le Havre. It comprises the thoughts and subjective experiences—in a personal diary format—of Antoine Roquentin, a melancholy and socially isolated intellectual who is residing in Bouville ostensibly for the purpose of completing a biography on a historical figure. Roquentin's growing alienation and disillusionment coincide with an increasingly intense experience of revulsion, which he calls "the nausea", in which the people and things around him seem to lose all their familiar and recognizable qualities. Sartre's original title for the novel before publication was ''Melancholia''. The novel has been translated into English by Lloyd Alexander as ''The Diary of Antoine Roquentin'' and by Robert Baldick as ''Nausea''. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critique Of Dialectical Reason
''Critique of Dialectical Reason'' (french: Critique de la raison dialectique) is a 1960 book by the philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre, in which the author further develops the existentialist Marxism he first expounded in his essay '' Search for a Method'' (1957). ''Critique of Dialectical Reason'' and ''Search for a Method'' were written as a common manuscript, with Sartre intending the former to logically precede the latter. ''Critique of Dialectical Reason'' was Sartre's second large-scale philosophical treatise, ''Being and Nothingness'' (1943) having been the first. The book has been seen by some as an abandonment of Sartre's original existentialism, while others have seen it as a continuation and elaboration of his earlier work. It was translated into English by Alan Sheridan-Smith. The first volume, "Theory of Practical Ensembles", was first published in English in 1976; a corrected English translation was published in 1991, based on the revised French edition of 1985. The sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Poster
Mark Poster (July 5, 1941 – October 10, 2012) was Professor Emeritus of History and Film and Media Studies at UC Irvine, where he also taught in the Critical Theory Emphasis. He was pivotal to "bringing French critical theory to the U.S., and went on to analyse contemporary media." "Mark Poster 1941-2012 obituary," article 8 November 2012 by Matthew Reisz in ''Times Higher Education'' magazine, UK Early life Poster was born in New York on 5 July 1941, studied at the Wharton School and completed a PhD in history at New York University in 1968. His research interests included European ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Consciousness
In Marxist theory, false consciousness is a term describing the ways in which material, ideological, and institutional processes are said to mislead members of the proletariat and other class actors within capitalist societies, concealing the exploitation intrinsic to the social relations between classes. Friedrich Engels (1820–1895) used the term "false consciousness" in an 1893 letter to Franz Mehring to address the scenario where a subordinate class willfully embodies the ideology of the ruling class. Engels dubs this consciousness "false" because the class is asserting itself towards goals that do not benefit it. "Consciousness", in this context, reflects a class's ability to politically identify and assert its will. The subordinate class is conscious if it plays a major role in society and can assert its will due to being sufficiently unified in ideas and action. Later development Marshall I. Pomer has argued that members of the proletariat disregard the true nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Being And Nothingness
''Being and Nothingness: An Essay on Phenomenological Ontology'' (french: L'Être et le néant : Essai d'ontologie phénoménologique), sometimes published with the subtitle ''A Phenomenological Essay on Ontology'', is a 1943 book by the philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre. In the book, Sartre develops a philosophical account in support of his existentialism, dealing with topics such as consciousness, perception, social philosophy, self-deception, the existence of "nothingness", psychoanalysis, and the question of free will. While a prisoner of war in 1940 and 1941, Sartre read Martin Heidegger's '' Being and Time'' (1927), which uses the method of Husserlian phenomenology as a lens for examining ontology. Sartre attributed the course of his own philosophical inquiries to his exposure to this work. Though influenced by Heidegger, Sartre was profoundly skeptical of any measure by which humanity could achieve a kind of personal state of fulfillment comparable to the hypothetical Heidegger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ethics Of Ambiguity
''The Ethics of Ambiguity'' (french: Pour une morale de l'ambiguïté) is Simone de Beauvoir's second major non-fiction work. It was prompted by a lecture she gave in 1945, after which she claimed that it was impossible to base an ethical system on her partner Jean-Paul Sartre's major philosophical work ''Being and Nothingness'' (french: L'Être et le néant). The following year, over a six-month period, she took on the challenge, publishing the resulting text first as installments in ''Les Temps modernes'' and then, in November 1947, as a book. Contents ''The Ethics of Ambiguity'' consists of three parts and a short conclusion. Part I "Ambiguity and Freedom," lays out the philosophical underpinnings of Beauvoir's stance on ethics. She asserts that man is fundamentally free, a freedom that comes from his "nothingness," which is an essential aspect of his ability to be self-aware, to be conscious of himself: "... the nothingness which is at the heart of man is also the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existentialism And Humanism
''Existentialism Is a Humanism'' (french: L'existentialisme est un humanisme) is a 1946 work by the philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre, based on a lecture by the same name he gave at Club Maintenant in Paris, on 29 October 1945. In early translations, ''Existentialism and Humanism'' was the title used in the United Kingdom; the work was originally published in the United States as ''Existentialism'', and a later translation employs the original title. Summary Sartre asserts that the key defining concept of existentialism is that the existence of a person is prior to their essence or " existence precedes essence". Thus, Sartre rejects what he calls "deterministic excuses" and claims that people must take responsibility for their behavior. Sartre defines anguish as the emotion that people feel once they realize that they are responsible not just for themselves, but for all humanity. Anguish leads people to realize that their actions guide humanity and allows them to make judgments ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Faith
Bad faith (Latin: ''mala fides'') is a sustained form of deception which consists of entertaining or pretending to entertain one set of feelings while acting as if influenced by another."of two hearts ... a sustained form of deception which consists in entertaining or pretending to entertain one set of feelings, and acting as if influenced by another; bad faith", ''Webster's Dictionary'', 1913 It is associated with hypocrisy, breach of contract, affectation, and lip service. It may involve intentionality, intentional deceit of others, or self-deception. Some examples of bad faith include: Soldiers waving a white flag and then firing when their enemy approaches to take prisoners (cf. perfidy); a company representative who negotiates with union workers while having no intent of compromising;"Bad Faith Negotiation," Union Voice a prosecutor who argues a legal position that he knows to be false; an insurer who uses language and reasoning which are deliberately misleading in orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomie
In sociology, anomie () is a social condition defined by an uprooting or breakdown of any moral values, standards or guidance for individuals to follow. Anomie is believed to possibly evolve from conflict of belief systems and causes breakdown of social bonds between an individual and the community (both economic and primary socialization). An example is alienation in a person that can progress into a dysfunctional inability to integrate within normative situations of their social world such as finding a job, achieving success in relationships, etc. The term, commonly understood to mean ''normlessness'', is believed to have been popularized by French sociologist Émile Durkheim in his influential book ''Suicide'' (1897). Émile Durkheim suggested that Protestants exhibited a greater degree of anomie than Catholics. However, Durkheim first introduced the concept of anomie in his 1893 work ''The Division of Labour in Society''. Durkheim never used the term ''normlessness''; ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |