|
Business Metadata
Business metadata is data that adds business context to other data. It provides information authored by business people and/or used by business people. It is in contrast to technical metadata, which is data used in the storage and structure of the data in a database or system. Technical metadata includes the database table name and column name, data type, indexes referencing the data, ETL jobs involving the data, when the data was last updated, accessed, etc. Concept According to noted author and columnist Lowell Fryman, "The essence of business metadata is in reducing or eliminating the barriers of communication between human and human, as well as human and computer, so that the data conveyed from reports, information systems, or business intelligence applications can be crystal clear, can facilitate business operations, and can be leveraged for all business decision-making processes." Dan Linstedt, creator of the data vault methodology, says business metadata "...provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Metadata
Technical may refer to: * Technical (vehicle), an improvised fighting vehicle * Technical area, an area which a manager, other coaching personnel, and substitutes are allowed to occupy during a football match * Technical advisor, a person who advises the director on the convincing portrayal of a subject in a film production * Technical analysis, a discipline for forecasting the future direction of prices through the study of past market data * Technical drawing, showing how something is constructed or functions (also known as drafting) ** Technical file, a set of technical drawings * Technical death metal, a subgenre of death metal that focuses on complex rhythms, riffs, and song structures * Technical foul, an infraction of the rules in basketball usually concerning unsportsmanlike non-contact behavior * Technical geography, one of the main branches of geography * Technical rehearsal for a performance, often simply referred to as a technical * Technical support, a range of servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
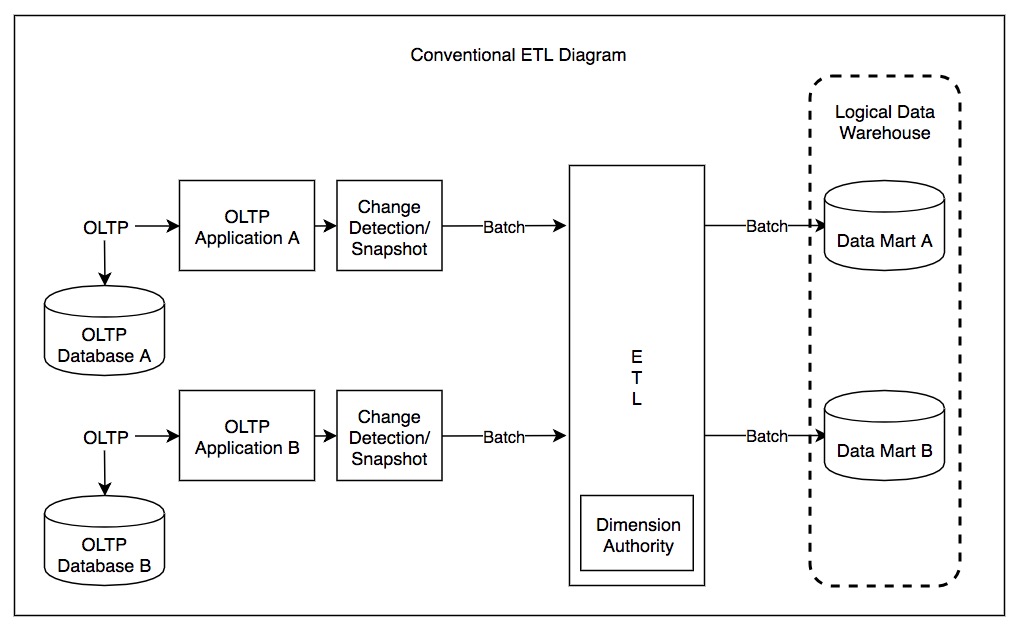
Extract, Transform, Load
Extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase computing process where data is ''extracted'' from an input source, ''transformed'' (including cleaning), and ''loaded'' into an output data container. The data can be collected from one or more sources and it can also be output to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software applications but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on recurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs. A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions. The ETL process is often used in data warehousing. ETL sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Linstedt
Daniel Linstedt is an American data architect and inventor of the data modeling method data vault for data warehouses and business intelligence. He developed the model in the 1990s and published the first version in the early 2000s. In 2012, Data Vault 2.0 was announced and it was released in 2013. In addition to data modeling, the data vault method incorporates process design, database tuning and performance improvements for ETL/ ELT, Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) and agile software development. Dan holds a Bachelor of Science in computer science from California State University, Chico. Since 2020, he has been the chief executive officer (CEO) of DataVaultAlliance Holdings LLC. Selected works * ''The Business of Data Vault Modeling'' (2010-11-19) by author Daniel Linstedt and co-authors Kent Graziano and Hans Hultgren * ''Super Charge Your Data Warehouse: Invaluable Data Modeling Rules to Implement Your Data Vault (Data Warehouse Architecture Book 1)'' (2012-05- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Vault Modeling
Datavault or data vault modeling is a database modeling method that is designed to provide long-term historical storage of data coming in from multiple operational systems. It is also a method of looking at historical data that deals with issues such as auditing, tracing of data, loading speed and resilience to change as well as emphasizing the need to trace where all the data in the database came from. This means that every row in a data vault must be accompanied by record source and load date attributes, enabling an auditor to trace values back to the source. The concept was published in 2000 by Dan Linstedt. Data vault modeling makes no distinction between good and bad data ("bad" meaning not conforming to business rules). This is summarized in the statement that a data vault stores " a single version of the facts" (also expressed by Dan Linstedt as "all the data, all of the time") as opposed to the practice in other data warehouse methods of storing "a single version of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) consists of strategies, methodologies, and technologies used by enterprises for data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of BI technologies include Financial reporting, reporting, online analytical processing, analytics, Dashboard (business), dashboard development, data mining, process mining, complex event processing, business performance management, benchmarking, text mining, Predictive Analysis, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. BI tools can handle large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help organizations identify, develop, and otherwise create new strategic business opportunities. They aim to allow for the easy interpretation of these big data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights is assumed to potentially provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability, and help them take strategic decisions. Busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgan Kaufmann
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers is a Burlington, Massachusetts (San Francisco, California until 2008) based publisher specializing in computer science and engineering content. Since 1984, Morgan Kaufmann has been publishing contents on information technology, computer architecture, data management, computer networking, computer systems, human computer interaction, computer graphics, multimedia information and systems, artificial intelligence, computer security, and software engineering. Morgan Kaufmann's audience includes the research and development communities, information technology (IS/IT) managers, and students in professional degree programs. The company was founded in 1984 by publishers Michael B. Morgan and William Kaufmann and computer scientist Nils Nilsson. It was held privately until 1998, when it was acquired by Harcourt General and became an imprint of the Academic Press, a subsidiary of Harcourt. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier in 2001; Morgan Kaufmann is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Terms
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." A business entity is not necessarily separate from the owner and the creditors can hold the owner liable for debts the business has acquired except for limited liability company. The taxation system for businesses is different from that of the corporates. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. A distinction is made in law and public offices between the term business and a company (such as a corporation or cooperative). Colloquially, the terms are used interchangeably. Corporations are distinct from sole proprietors and partnerships. Corporations are separate and unique legal entities from their shareholders; as such they provide limited liability for their owners and members. Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |