|
Business Architecture
In the business sector, business architecture is a discipline that "represents holistic, multidimensional business views of: capabilities, end-to-end value delivery, information, and organizational structure; and the relationships among these business views and strategies, products, policies, initiatives, and stakeholders." In application, business architecture provides a bridge between an enterprise business model and enterprise strategy on one side, and the business functionality of the enterprise on the other side. It often enables the Strategy to Execution methodology. People who develop and maintain business architecture are known as business architects. Overview The term "business architecture" is often used to mean an architectural description of an enterprise or a business unit, an architectural model, or the profession itself. The Business Architecture Working Group of the Object Management Group (OMG) (2010) describes it as "a blueprint of the enterprise t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OMG Business Architecture Special Interest Group
The Business Architecture Special Interest Group (BASIG) is a working group on business architecture of the Object Management Group (OMG), known for their contribution to the history of business architecture. This working group was founded in 2007 as the Business Architecture Working Group (BAWG). History Foundation The 2007 announcement for the OMG Technical Meeting on Dec. 12, 2007 in Burlingame, California gave the following rationale for the foundation of a specialized working group on business architecture: In looking at the link between IT and the business, it has become apparent that there needs to be more formally defined sets of relationships between IT architecture and business architecture. In addition, the concept of business architecture is probably 10-15 years behind the maturity of the IT architecture world. For example, the relationship between business rules and processes is not apparent and the role of organizational governance is similarly disconnected. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OMG Business Architecture Working Group
The Business Architecture Special Interest Group (BASIG) is a working group on business architecture of the Object Management Group (OMG), known for their contribution to the history of business architecture. This working group was founded in 2007 as the Business Architecture Working Group (BAWG). History Foundation The 2007 announcement for the OMG Technical Meeting on Dec. 12, 2007 in Burlingame, California gave the following rationale for the foundation of a specialized working group on business architecture: In looking at the link between IT and the business, it has become apparent that there needs to be more formally defined sets of relationships between IT architecture and business architecture. In addition, the concept of business architecture is probably 10-15 years behind the maturity of the IT architecture world. For example, the relationship between business rules and processes is not apparent and the role of organizational governance is similarly disconnected. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
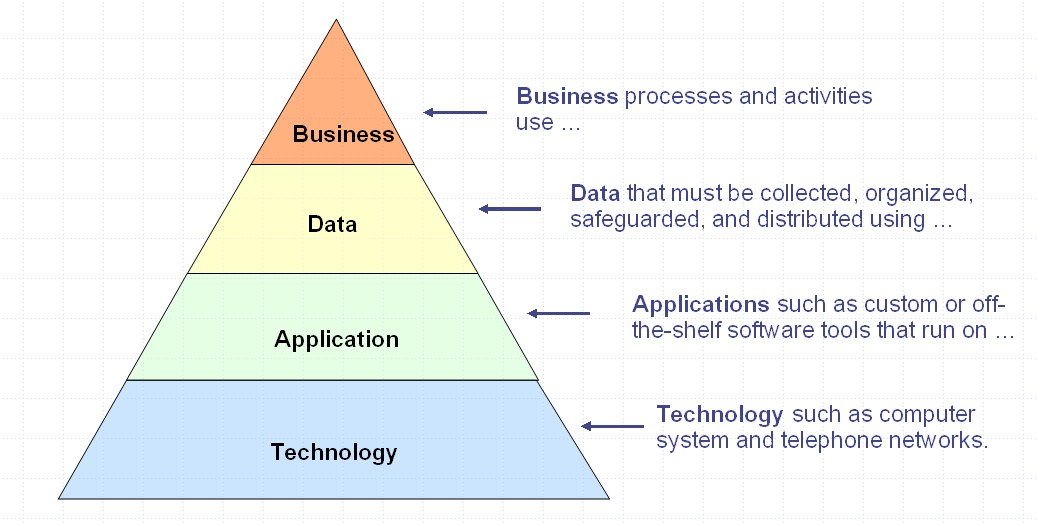
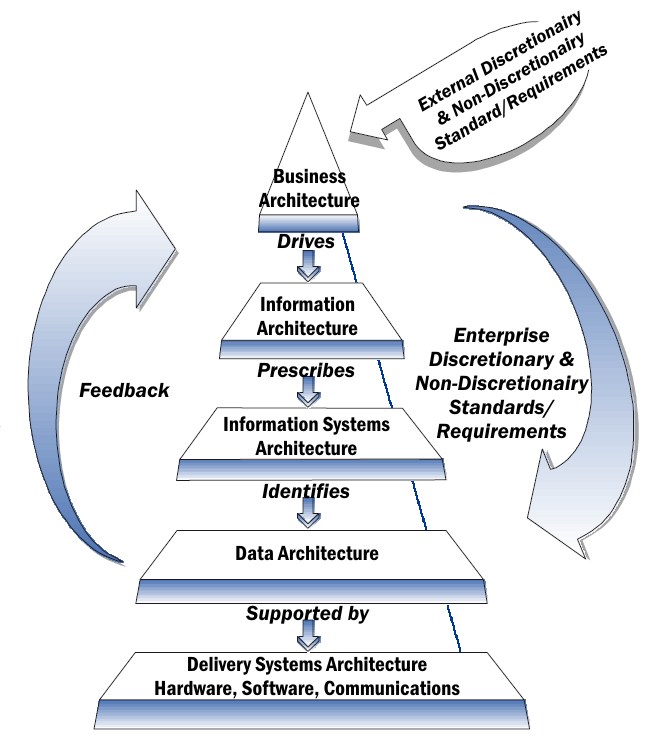
Architectural Domain
An architecture domain in enterprise architecture is a broad view of an enterprise or system. It is a partial representation of a whole system that addresses several concerns of several stakeholders. It is a description that hides other views or facets of the system described. Business, data, application and technology architectures are recognized as the core domains in the most of proposed concepts concerned with the definition of enterprise architecture. Overview Since Stephen Spewak's book called enterprise architecture planning (EAP) in 1993, and perhaps before then, it has been normal to recognise four types of architecture domain. The British Computer Society's "Reference Model for Enterprise and Solution Architecture" also follows this subdivision but additionally mentions the (single) application architecture level just below the application''s'' architecture as well as the domains of information architecture, information systems architecture, or security architectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Semantics Of Business Vocabulary And Rules
Semantics is the study of linguistic meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics relies on logic and mathematics to provide precise frameworks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
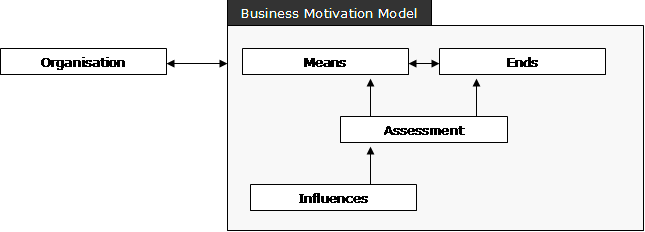
Business Motivation Model
The Business Motivation Model (BMM) in enterprise architecture provides a scheme and structure for developing, communicating, and managing business plans in an organized manner. Specifically, the Business Motivation Model does all the following: * identifies factors that motivate the establishing of business plans; * identifies and defines the elements of business plans; and * indicates how all these factors and elements inter-relate. History Initially developed by the Business Rules Group (BRG), in September 2005, the Object Management Group (OMG) voted to accept the Business Motivation Model as the subject of a Request for Comment (RFC). This meant that the OMG was willing to consider the Business Motivation Model as a specification to be adopted by the OMG, subject to comment from any interested parties. Adoption as an OMG specification carries the intention that the Business Motivation Model would, in time, be submitted to the International Organization for Standardization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Model Driven Architecture
Model-driven architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001."OMG pursues new strategic direction to build on success of past efforts" Overview Model Driven Architecture® (MDA®) "provides an approach for deriving value from models and architecture in support of the full life cycle of physical, organizational and I.T. systems". A model is a (representation of) an abstraction of a system. MDA® provides value by producing models ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
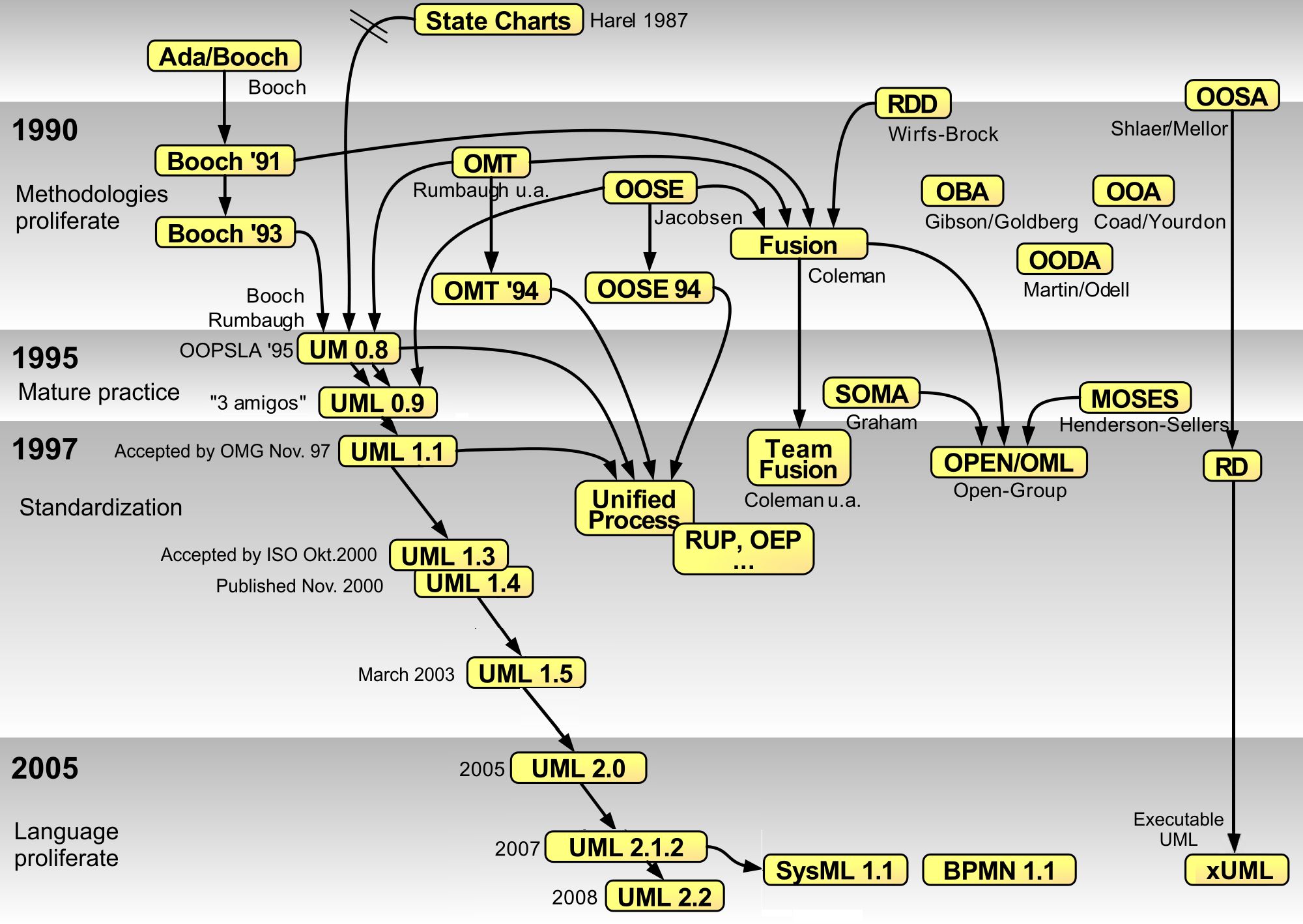
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Object Management Group
The Object Management Group (OMG®) is a computer industry Standards Development Organization (SDO), or Voluntary Consensus Standards Body (VCSB). OMG develops enterprise integration and modeling standards for a range of technologies. Business activities The goal of the OMG was a common portable and interoperable object model with methods and data that work using all types of development environments on all types of platforms. The group provides only specifications, not implementations. But before a specification can be accepted as a standard by the group, the members of the submitter team must guarantee that they will bring a conforming product to market within a year. This is an attempt to prevent unimplemented (and unimplementable) standards. Other private companies or open source groups are encouraged to produce conforming products and OMG is attempting to develop mechanisms to enforce true interoperability. OMG hosts four technical meetings per year for its members an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enterprise Architecture Framework
An enterprise architecture framework (EA framework) defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models – typically matrices and diagrams – for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support. Overview Enterprise architecture regards the enterprise as a large and complex system or system of systems. To manage the scale and complexity of this system, an architectural framework provides tools and approaches that help architects abstract from the level of detail at which builders work, to bring enterprise design tasks into focus and produce valuable architecture description d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zachman Framework
The Zachman Framework is a structured tool used in enterprise architecture to organize and understand complex business systems. It acts as an Ontology (information science), ontology, providing a clear and formal way to describe an enterprise through a two-dimensional grid. This grid combines two key perspectives: the basic questions of Five Ws, What, How, When, Who, Where, and Why, and the process of turning abstract ideas into concrete realities, known as Reification (fallacy), reification. These reification stages include identification, definition, representation, specification, configuration, and instantiation. While influential in shaping enterprise architecture, the framework is often considered theoretical, with limited direct adoption in fast-paced industries like technology, where agile methods are preferred. Unlike a methodology, the Zachman Framework does not prescribe specific steps or processes for gathering or using information. Instead, it serves as a Conceptual m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IEEE 1471
IEEE 1471 is a superseded IEEE standard for describing the architecture of a "software-intensive system", also known as software architecture. In 2011 it was superseded by ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010, ''Systems and software engineering — Architecture description''. Overview IEEE 1471 is the short name for a standard formally known as ANSI/IEEE 1471-2000, ''Recommended Practice for Architecture Description of Software-Intensive Systems.'' Within Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) parlance, this is a "recommended practice", the least normative of its standards. In 2007 this standard was adopted by ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7 as ISO/IEC 42010:2007, ''Systems and Software Engineering -- Recommended practice for architectural description of software-intensive systems''. It has long been recognized that "architecture" has a strong influence over the life cycle of a system. However, until relatively recently, hardware issues have tended to dominate architectural thinking, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Business Strategy
In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates.qn, date=June 2018 Strategic management provides overall direction to an enterprise and involves specifying the organization's objectives, developing policies and plans to achieve those objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the plans. Academics and practicing managers have developed numerous models and frameworks to assist in strategic decision-making in the context of complex environments and competitive dynamics. Strategic management is not static in nature; the models can include a feedback loop to monitor execution and to inform the next round of planning. Michael Porter identifies three principles underlying strategy: * creating a " unique a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |