|
Broken Heart
A broken heart (also known as heartbreak or heartache) is a metaphor for the intense emotional stress or pain one feels at experiencing great loss or deep longing. The concept is cross-cultural, often cited with reference to unreciprocated or lost love. Failed romantic love or unrequited love can be extremely painful; people suffering from a broken heart may succumb to depression, grief, anxiety and, in more extreme cases, post-traumatic stress disorder. Physiology The intense pain of a broken heart is believed to be part of the survival instinct. The " social-attachment system" uses the " pain system" to encourage humans to maintain their close social relationships by causing pain when those relationships are lost. Psychologists Geoff MacDonald of the University of Queensland and Mark Leary of Wake Forest University proposed in 2005 the evolution of common mechanisms for both physical and emotional pain responses and argue that such expressions are "more than just a metaph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California
The University of California (UC) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university, research university system in the U.S. state of California. Headquartered in Oakland, California, Oakland, the system is composed of its ten campuses at University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, University of California, Davis, Davis, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, University of California, Merced, Merced, University of California, Riverside, Riverside, University of California, San Diego, San Diego, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, University of California, Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, and University of California, Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, along with numerous research centers and academic centers abroad. The system is the state's land-grant university. In 1900, UC was one of the founders of the Association of American Universities and since the 1970s seven of its campuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Trauma
Psychological trauma (also known as mental trauma, psychiatric trauma, emotional damage, or psychotrauma) is an emotional response caused by severe distressing events, such as Major trauma, bodily injury, Sexual assault, sexual violence, or other threats to the life of the subject or their loved ones; indirect exposure, such as from watching television news, may be extremely distressing and can produce an involuntary and possibly overwhelming physiological stress response, but does not always produce trauma ''per se''. Examples of distressing events include violence, rape, or a Terrorism, terrorist attack. Short-term reactions such as acute stress disorder, psychological shock and denial, psychological denial typically follow. Long-term reactions and effects include flashback (psychology), flashbacks, panic attacks, insomnia, nightmare disorder, difficulties with interpersonal relationships, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and brief psychotic disorder. Physical symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low Mood (psychology), mood and aversion to activity. It affects about 3.5% of the global population, or about 280 million people worldwide, as of 2020. Depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, feelings, and subjective well-being, sense of well-being. The pleasure or joy that a person gets from certain experiences is reduced, and the afflicted person often experiences a loss of motivation or interest in those activities. People with depression may experience sadness, feelings of dejection or hopelessness, difficulty in thinking and concentration, or a significant change in appetite or time spent sleeping; Suicidal ideation, suicidal thoughts can also be experienced. Depression can have multiple, sometimes overlapping, origins. Depression can be a symptom of some mood disorders, some of which are also commonly called ''depression'', such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and dysthymia. Additionally, depression can be a norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stressor
A stressor is a chemical or biological agent, environmental condition, external stimulus or an event seen as causing stress to an organism. Psychologically speaking, a stressor can be events or environments that individuals might consider demanding, challenging, and/or threatening individual safety.Deckers, Lambert (2018). Motivation Biological, Psychological, and Environmental. New York, NY: Routledge. pp. 208-212. . Events or objects that may trigger a stress response may include: * environmental stressors ( hypo or hyper-thermic temperatures, elevated sound levels, over-illumination, overcrowding) * daily "stress" events (e.g., traffic, lost keys, money, quality and quantity of physical activity) * life changes (e.g., divorce, bereavement) * workplace stressors (e.g., high job demand vs. low job control, repeated or sustained exertions, forceful exertions, extreme postures, office clutter) * chemical stressors (e.g., tobacco, alcohol, drugs) * social stressors (e.g., soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shame
Shame is an unpleasant self-conscious emotion often associated with negative self-evaluation; motivation to quit; and feelings of pain, exposure, distrust, powerlessness, and worthlessness. Definition Shame is a discrete, basic emotion, described as a Moral emotions, moral or social emotion that drives people to hide or deny their wrongdoings.Shein, L. (2018). "The Evolution of Shame and Guilt". PLoSONE, 13(7), 1–11. Moral emotions are emotions that have an influence on a person's decision-making skills and monitors different social behaviors. The focus of shame is on the self or the individual with respect to a perceived audience. It can bring about profound feelings of deficiency, defeat, inferiority, unworthiness, or self-loathing. Our attention turns inward; we isolate from our surroundings and withdraw into closed-off self-absorption. Not only do we feel alienated from others but also from the healthy parts of ourselves. The Social alienation, alienation from the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakup
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the ending of a Interpersonal relationship, relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping [someone]" in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a marriage, married couple, where a breakup is typically called a Legal separation, separation or divorce. When a couple engaged to be married breaks up, it is typically called a "broken engagement". People commonly think of breakups in a Romance (love), romantic aspect, however, there are also non-romantic and platonic breakups, and this type of relationship dissolution is usually caused by failure to maintain a friendship. Susie Orbach (1992) has argued that the dissolution of dating and cohabiting relationships can be as painful as or more painful than divorce because these nonmarital relationships are less socially recognized. Kamiar-K. Rueckert argues with the works of Donald Winnicott that the ability to be alone is an essentially healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bowlby
Edward John Mostyn Bowlby (; 26 February 1907 – 2 September 1990) was a British psychiatrist and psychoanalyst, notable for his interest in child development and for his pioneering work in attachment theory. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Bowlby as the 49th most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Family background Bowlby was born in London to an upper-middle-income family. He was the fourth of six children and was brought up by a nanny in the British fashion of his class at that time: the family hired a nanny who was in charge of raising the children, in a separate nursery in the house.Van Dijken, S. (1998). John Bowlby: His Early Life: A Biographical Journey into the Roots of Attachment Theory. London: Free Association Books Nanny Friend took care of the infants and generally had two other nursemaids to help her. Bowlby was raised primarily by nursemaid Minnie who acted as a mother figure to him and his siblings. His father, Sir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time (magazine)
''Time'' (stylized in all caps as ''TIME'') is an American news magazine based in New York City. It was published Weekly newspaper, weekly for nearly a century. Starting in March 2020, it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on March 3, 1923, and for many years it was run by its influential co-founder, Henry Luce. A European edition (''Time Europe'', formerly known as ''Time Atlantic'') is published in London and also covers the Middle East, Africa, and, since 2003, Latin America. An Asian edition (''Time Asia'') is based in Hong Kong. The South Pacific edition, which covers Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands, is based in Sydney. Since 2018, ''Time'' has been owned by Salesforce founder Marc Benioff, who acquired it from Meredith Corporation. Benioff currently publishes the magazine through the company Time USA, LLC. History 20th century ''Time'' has been based in New York City since its first issue published on March 3, 1923 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kübler-Ross Model
According to the model of the five stages of grief, or the Kübler-Ross model, those experiencing sudden grief following an abrupt realization (shock) go through five emotions: denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. Critics of the model have warned against using it too literally. Introduced as "The Five Stages of Death" by Swiss-American psychiatrist Elisabeth Kübler-Ross in 1969, this model has been known by various names, including "The Five Stages of Loss", "The Kübler-Ross Model", the "Kübler-Ross Grief Cycle", the "Grief Cycle", "The Seven Stages of Grief", and the "Kübler-Ross Change Curve". History The model was introduced by Kübler-Ross in her 1969 book ''On Death and Dying'', and was inspired by her work with terminally ill patients. Motivated by the lack of instruction in medical schools on the subject of death and dying, Kübler-Ross examined death and those faced with it at the University of Chicago's medical school. Kübler-Ross's project evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
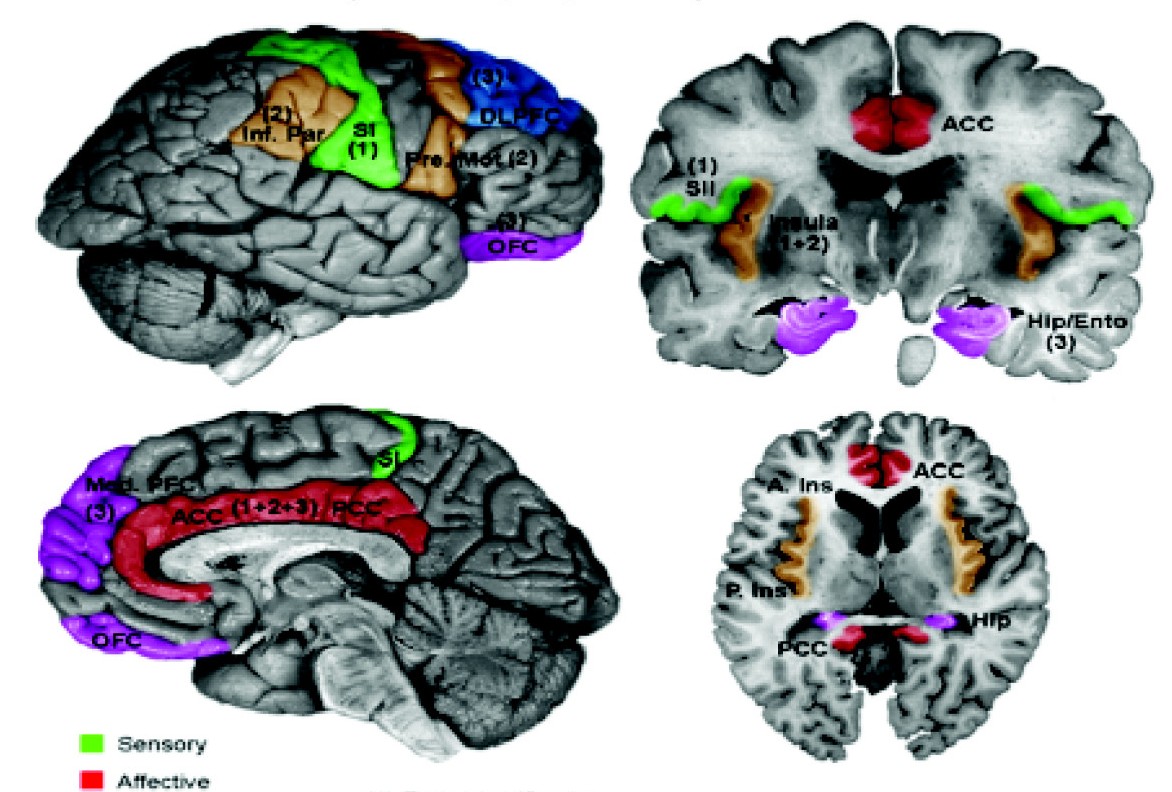
Insular Cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere, hemisphere of the mammalian brain. The insulae are believed to be involved in consciousness and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to emotion or the regulation of the body's homeostasis. These functions include compassion, empathy, taste, perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning, interpersonal relationships, and awareness of homeostatic emotions such as Hunger (physiology), hunger, pain and fatigue. In relation to these, it is involved in psychopathology. The insular cortex is divided by the central sulcus of the insula, into two parts: the anterior insula and the posterior insula in which more than a dozen field areas have been identified. The cortical area overlying the insula toward the lateral su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Somatosensory Cortex
The human secondary somatosensory cortex (S2, SII) is a region of sensory cortex in the parietal operculum on the ceiling of the lateral sulcus. Region S2 was first described by Adrian in 1940, who found that feeling in cats' feet was not only represented in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1) but also in a second region adjacent to S1. In 1954, Penfield and Jasper evoked somatosensory sensations in human patients during neurosurgery by electrically stimulating the ceiling of the lateral sulcus, which lies adjacent to S1, and their findings were confirmed in 1979 by Woolsey et al. using evoked potentials and electrical stimulation. Experiments involving ablation of the second somatosensory cortex in primates indicate that this cortical area is involved in remembering the differences between tactile shapes and textures. Functional neuroimaging studies have found S2 activation in response to light touch, pain, visceral sensation, and tactile attention. In monkeys, apes and homin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |