|
Brayer
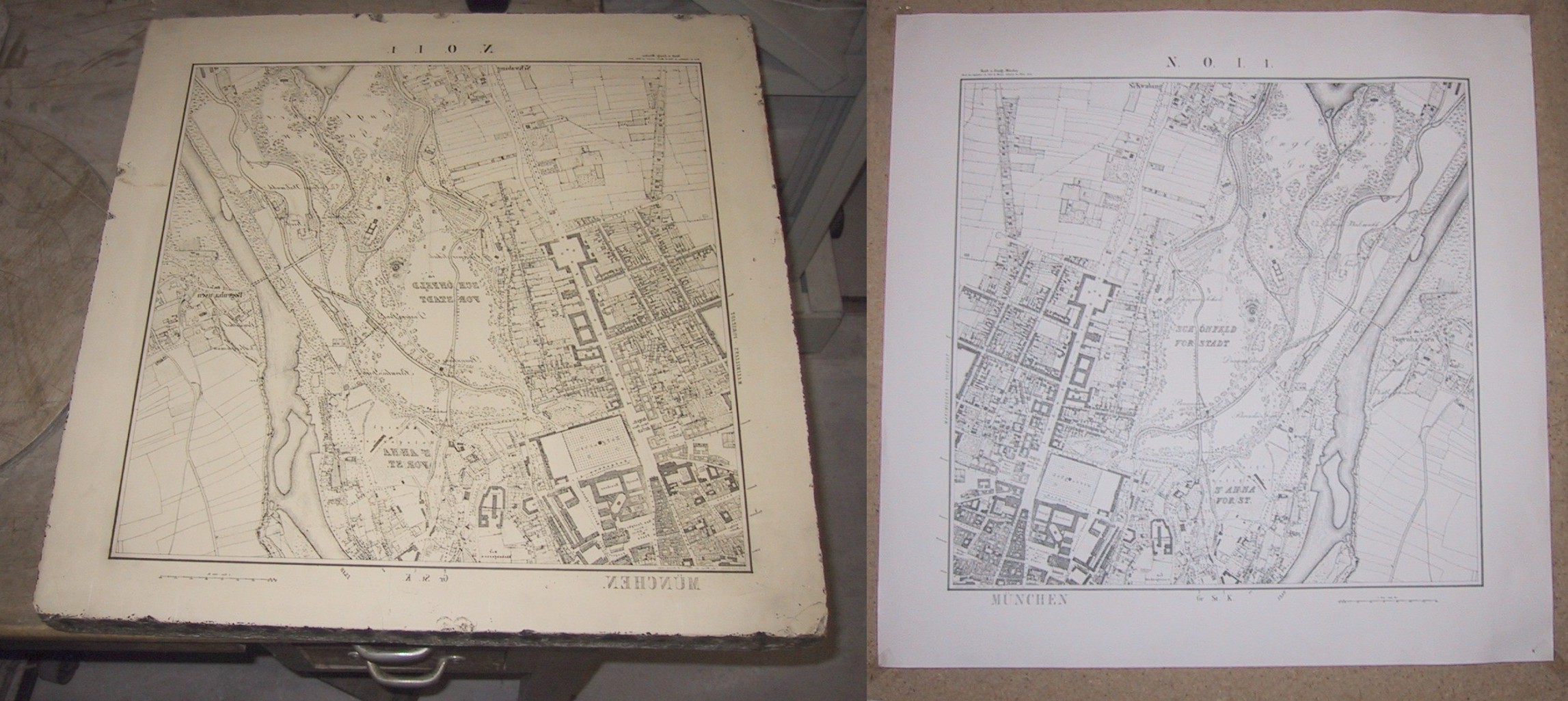
A brayer is a hand-tool used historically in printing and printmaking to break up and "rub out" (spread) ink, before it was "beaten" using Ink ball, inking balls or composition rollers. A brayer consists of a short wooden cylinder with a handle fitted to one end; the other, flat end is used to rub the ink. History The word is derived from the verb to "bray", meaning "to break, pound, or grind small, as in a mortar". In the late nineteenth century the term was applied in the United States to a small hand-roller, "used for spreading ink on the inking table, and for applying it to the distributing plates or rollers connected with presses". Such small rollers were sold as "brayers" from at least 1912 and later in the century the term was applied in the U.S. to hand-rollers of all sorts and sizes. It retains its original meaning in Europe. Materials Brayers in the original sense were generally made of wood (though Southward refers to their being made of "wood or glass").John South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating work of art, artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine (Printer (computing), a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Prints are created by transferring ink from a Matrix (printing), matrix to a sheet of paper or other material, by a variety of techniques. Common types of matrices include: metal plates for engraving, etching and related intaglio printing techniques; stone, aluminum, or polymer for lithography; blocks of wood for woodcuts and wood engravings; and linoleum for linocuts. Screens made of silk or synthetic fabrics are used for the screen printing process. Other types of matrix substrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Printing
Relief printing is a family of printing methods where a printing block, plate or matrix (printing), matrix, which has had ink applied to its non-recessed surface, is brought into contact with paper. The non-recessed surface will leave ink on the paper, whereas the recessed areas will not. A printing press may not be needed, as the back of the paper can be rubbed or pressed by hand with a simple tool such as a brayer or roller. In contrast, in Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printing, the ''recessed'' areas are printed. Relief printing is one of the traditional families of printmaking techniques, along with the Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio and planographic printing, planographic families, though modern developments have created others. The relief family of techniques In the relief family of printing, the matrix was historically made Subtractive manufacturing, subtractively, by removing material from the surface of areas not intended to be printed. The remaining surface wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating work of art, artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine (Printer (computing), a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Prints are created by transferring ink from a Matrix (printing), matrix to a sheet of paper or other material, by a variety of techniques. Common types of matrices include: metal plates for engraving, etching and related intaglio printing techniques; stone, aluminum, or polymer for lithography; blocks of wood for woodcuts and wood engravings; and linoleum for linocuts. Screens made of silk or synthetic fabrics are used for the screen printing process. Other types of matrix substrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ink Ball
An ink ball, inking ball, or dabber is a tool used in printmaking and letterpress printing to apply ink to the plate or type to be printed. Ink balls had been used since the dawn of the printing press in the 15th century. In printmaking, they were used individually, to make the ink smooth and applying it. In letterpress printing, they were used in pairs: ink was placed on one of the two balls, which were then held together and worked around until a proper thickness, consistency, and uniformity was reached. The inker then "beat" the type to apply the ink, making sure to get neither too much nor too little ink on the form. An ink ball consists of a piece of specially-treated sheepskin stuffed with wool, with wooden cupped rod as a handle ("stock"). After the invention of composition (a mixture of glue, molasses, and tar) in the early 19th century, some ink balls began to be made from that until they faded from use. By the mid- to late-19th century, they had been largely supers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Printing
Relief printing is a family of printing methods where a printing block, plate or matrix (printing), matrix, which has had ink applied to its non-recessed surface, is brought into contact with paper. The non-recessed surface will leave ink on the paper, whereas the recessed areas will not. A printing press may not be needed, as the back of the paper can be rubbed or pressed by hand with a simple tool such as a brayer or roller. In contrast, in Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printing, the ''recessed'' areas are printed. Relief printing is one of the traditional families of printmaking techniques, along with the Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio and planographic printing, planographic families, though modern developments have created others. The relief family of techniques In the relief family of printing, the matrix was historically made Subtractive manufacturing, subtractively, by removing material from the surface of areas not intended to be printed. The remaining surface wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paint Roller
A paint roller is a paint Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are ... application tool used for painting large flat surfaces rapidly and efficiently. The paint roller typically consists of two parts: a "roller frame," and a "roller cover." The roller cover absorbs the paint and transfers it to the painted surface, the roller frame attaches to the roller cover. A painter holds the roller by the handle section. The roller frame is reusable. It is possible to clean and reuse a roller cover, but it is also typically disposed of after use. The roller cover is a cylindrical core with a pile fabric covering secured to the cylindrical core. Foam rubber rollers are also produced. There are both foam and fabric roller covers that can be purchased without a frame, to replace worn o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baren (printing Tool)
Baren (馬連、馬楝) ' is a disk-like hand tool with a flat bottom and a knotted handle used in Japanese woodblock printing. It is used to burnish (firmly rub) the back of a sheet of paper, lifting ink from the block. Construction A traditional (''hon)'' baren is made of layers. A flat coil of braided cord forms the core. This is placed on a disk (''ategawa'') consisting of 30–40 sheets of high-grade long-fibred hosokawa paper, wrapped in tissue and black lacquer. This is covered by a thin bamboo sheath (''takenokawa'') twisted in such a manner as to form the handle on the top. According to Hiroshi Yoshida's manual ''Japanese Woodblock Printing'' (1939) the Phyllostachys bambusoides, madake species of bamboo, grown in Kyushu, southwest Japan, is considered the best one to use. The bamboo-sheath covering the baren may need to be renewed after a day's printing. Rewrapping requires great skill; a printer's ability is sometimes judged by their competence carrying out this wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrapbooking
Scrapbooking is a method of preserving, presenting, and arranging personal and family history in the form of a book, box, or card. Typical memorabilia include photographs, printed media, and artwork. Scrapbook albums are often decorated and frequently contain extensive journal entries or written descriptions. Scrapbooking started in the United Kingdom in the nineteenth century. History In the 15th century, commonplace books, popular in England, emerged as a way to compile information that included recipes, quotations, letters, poems, and more. Each commonplace book was unique to its creator's particular interests. Friendship albums became popular in the 16th century. These albums were used much like modern day yearbooks, where friends or patrons would enter their names, titles and short texts or illustrations at the request of the album's owner. These albums were often created as souvenirs of European tours and would contain local memorabilia including coats of arms or works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paint
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based, and each has distinct characteristics. Primitive forms of paint were used tens of thousands of years ago in cave paintings. Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted (such as a house). History Paint was used in some of the earliest known human artworks. Some cave paintings drawn with red or yellow ochre, hematite, manganese oxide, and charcoal may have been made by early ''Homo sapiens'' as long as 40,000 years ago. Paint may be even older. In 2003 and 2004, South African archeologists reported finds in Blombos Cave of a 100,000-y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the miscibility, immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for sheet music, musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design''. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146, .Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. ''Typographic Design: Form and Communication'', Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 11. Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for printmaking, fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Traditionally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offset Printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithography, lithographic process, which is based on the repulsion of oil and water, the offset technique employs a flat (planographic printing, planographic) image carrier. Ink rollers transfer ink to the image areas of the image carrier, while a water roller applies a water-based film to the non-image areas. The modern "web" process feeds a large reel of paper through a large press machine in several parts, typically for several meters, which then prints continuously as the paper is fed through. Development of the offset press came in two versions: in 1875 by Robert Barclay of England for printing on tinplate, tin and in 1904 by Ira Washington Rubel of the United States for printing on paper. Rubel's contemporary in Continental Europe was Kašpar Hermann, the author of the off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio (printmaking)
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally copper, or in recent times zinc, sheets called plates are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. The word "intaglio" describes prints created from plates where the ink-bearing regions are recessed beneath the plate's surface. Though brass, zinc, and other materials are occasionally utilized, copper is the most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |