|
Boundary Scan
Boundary scan is a method for testing interconnects (wire lines) on printed circuit boards or sub-blocks inside an integrated circuit (IC). Boundary scan is also widely used as a debugging method to watch integrated circuit pin states, measure voltage, or analyze sub-blocks inside an integrated circuit. The Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) developed a specification for boundary scan testing that was standardized in 1990 as the IEEE Std. 1149.1-1990. In 1994, a supplement that contains a description of the boundary scan description language (BSDL) was added which describes the boundary-scan logic content of IEEE Std 1149.1 compliant devices. Since then, this standard has been adopted by electronic device companies all over the world. Boundary scan is now mostly synonymous with JTAG.IEEE Std 1149.1 (JTAG) Testability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
JTAG Register
JTAG (named after the Joint Test Action Group which codified it) is an industry standard for verifying designs of and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture. JTAG implements standards for on-chip instrumentation in electronic design automation (EDA) as a complementary tool to digital simulation. It specifies the use of a dedicated debug port implementing a serial communications interface for low-overhead access without requiring direct external access to the system address and data buses. The interface connects to an on-chip Test Access Port (TAP) that implements a stateful protocol to access a set of test registers that present chip logic levels and device capabilities of various parts. The Joint Test Action Group formed in 1985 to develop a method of verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture. In 1990 the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers codified the results of the effort in IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990, entitled ''Standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serial Vector Format
Serial Vector Format (SVF) is a file format that contains boundary scan vectors to be sent to an electronic circuit using a JTAG interface. Boundary scan vectors consist of the following data: * Stimulus data: This is data to be sent to a device or electronic circuit * Expected response: This is the data the device or circuit is expected to send back if there is no error * Mask data: Defines which bits in the expected response are valid; other bits of the device's response are unknown and must be ignored when comparing the expected response and the data returned from the circuit * Additional information on how to send the data (e.g. maximum clock frequency) The SVF standard was jointly developed by companies ''Texas Instruments'' and ''Teradyne''. Control over the format has been handed off to boundary-scan solution provider ''ASSET InterTech''. The most recent revision is Revision E. SVF files are used to transfer boundary scan data between tools. As an example a VHDL VH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry is the industry that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices that are built in factories operated by the industry, which are almost always partially automated. Electronic products are primarily assembled from metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) transistors and integrated circuits, the latter principally by photolithography and often on printed circuit boards. Circuit boards are assembled largely using surface-mount technology, which typically involves the automated placement of electronic parts on circuit boards using pick-and-place machines. Surface-mount technology and pick-and-place machines make it possible to assemble large numbers of circuit boards at high speed. The industry's size, the use of toxic materials, and the difficulty of recycling have led to a series of problems with electronic waste. International reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acceptance Testing
In engineering and its various subdisciplines, acceptance testing is a test conducted to determine if the requirements of a specification or contract are met. It may involve chemical tests, physical tests, or performance tests. In systems engineering, it may involve black-box testing performed on a system (for example: a piece of software, lots of manufactured mechanical parts, or batches of chemical products) prior to its delivery. In software testing, the ISTQB defines ''acceptance testing'' as: The final test in the QA lifecycle, user acceptance testing, is conducted just before the final release to assess whether the product or application can handle real-world scenarios. By replicating user behavior, it checks if the system satisfies business requirements and rejects changes if certain criteria are not met. Some forms of acceptance testing are, user acceptance testing (UAT), end-user testing, operational acceptance testing (OAT), acceptance test-driven developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Functional Testing (manufacturing)
In manufacturing, functional testing (FCT) is performed during the last phase of the production line. This is often referred to as a final quality control test, which is done to ensure that specifications are carried out by FCTs. The process of FCTs is entailed by the emulation or simulation of the environment in which a product is expected to operate. This is done so to check, and correct any issues with functionality. The environment involved with FCTs consists of any device that communicates with an DUT, the power supply of said DUT, and any loads needed to make the DUT function correctly. Functional tests are performed in an automatic fashion by production line operators using test software. In order for this to be completed, the software will communicate with any external programmable instruments such as I/O boards, digital multimeters, and communication ports. In conjunction with the test fixture, the software that interfaces with the DUT is what makes it possible for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
In-circuit Test
In-circuit testing (ICT) is an example of white box testing where an electrical probe tests a populated printed circuit board (PCB), checking for shorts, opens, resistance, capacitance, and other basic quantities which will show whether the assembly was correctly fabricated. It may be performed with a "bed of nails" test fixture and specialist test equipment, or with a fixtureless in-circuit test setup. In-Circuit Test (ICT) is a widely used and cost-efficient method for testing medium- to high-volume electronic printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs). It has maintained its popularity over the years due to its ability to diagnose component-level faults and its operational speed. Using In-Circuit Test fixtures is a very effective way of maintaining standards when carrying out tests. It can help to reduce production downtime by identifying faults early in the testing process, ensuring that defective products are removed from the production line and fixed. Fixtures for in-circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automated X-ray Inspection
Automated inspection (AXI) is a technology based on the same principles as automated optical inspection (AOI). It uses as its source, instead of visible light, to automatically inspect features, which are typically hidden from view. Automated X-ray inspection is used in a wide range of industries and applications, predominantly with two major goals: # Process optimization, i.e. the results of the inspection are used to optimize following processing steps, # Anomaly detection, i.e. the result of the inspection serve as a criterion to reject a part (for scrap or re-work). While AOI is mainly associated with electronics manufacturing (due to widespread use in printed circuit board manufacturing), AXI has a much wider range of applications. It ranges from the quality check of alloy wheels to the detection of bone fragments in processed meat. Wherever large numbers of very similar items are produced according to a defined standard, automatic inspection using advanced image processin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automated Optical Inspection
Automated optical inspection (AOI) is an automated visual inspection of printed circuit board (PCB) (or LCD, transistor) manufacture where a camera machine vision, autonomously scans the device under test for both catastrophic failure (e.g. missing component) and Product defect, quality defects (e.g. fillet size or shape or component skew). It is commonly used in the manufacturing process because it is a non-contact test method. It is implemented at many stages through the manufacturing process including bare board inspection, solder paste inspection (SPI), pre-reflow and post-re-flow as well as other stages. Historically, the primary place for AOI systems has been after solder re-flow or "post-production." Mainly because, post-re-flow AOI systems can inspect for most types of defects (component placement, solder shorts, missing solder, etc.) at one place in the line with one single system. In this way the faulty boards are reworked and the other boards are sent to the next process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Level-sensitive Scan Design
Within the field of electronics Level-sensitive scan design (LSSD) is part of an integrated circuit manufacturing test process. It is a DFT scan design method which uses separate system and scan clocks to distinguish between normal and test mode. Latches are used in pairs, each has a normal data input, data output and clock for system operation. For test operation, the two latches form a master/slave pair with one scan input, one scan output and non-overlapping scan clocks A and B which are held low during system operation but cause the scan data to be latched when pulsed high during scan. ____ , , Sin ----, S , A ------, > , , Q, ---+--------------- Q1 D1 -----, D , , CLK1 ---, > , , , ____, , ____ , , , +---, S , B -------------------, > , , Q, ------ Q2 / SOut D2 ------------------, D , CLK2 ----------------, > , , ____, In a single latch LSSD configuration, the second latch is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
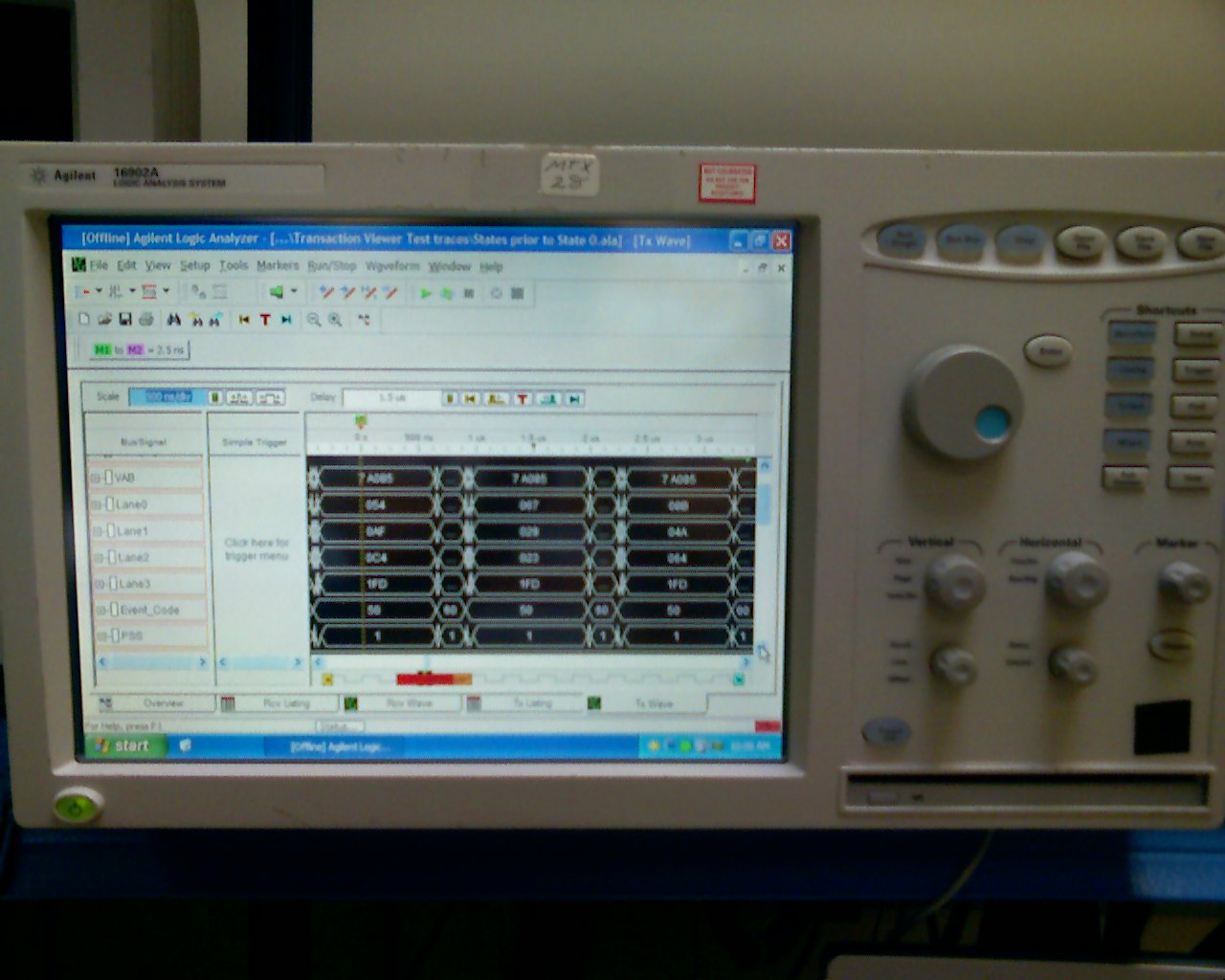
Logic Analyzer
A logic analyzer is an electronic instrument that captures and displays multiple logic signals from a digital system or digital circuit. A logic analyzer may convert the capture into timing diagrams, protocol decodes, state machine traces, opcodes, or may correlate opcodes with source-level software. Logic analyzers have advanced triggering capabilities, and are useful when a user needs to see the timing relationships between many signals in a digital system. Overview Presently, there are three distinct categories of logic analyzers available on the market: * Modular LAs, which consist of both a chassis or mainframe and logic analyzer modules. The mainframe/chassis contains the display, controls, control computer, and multiple slots into which the actual data-capturing hardware is installed. The modules each have a specific number of channels, and multiple modules may be combined to obtain a very high channel count. While modular logic analyzers are typically more expensive, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Embedded System
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Engineer
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |