|
Boron Nitride Nanotube
Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) are a polymorph of boron nitride. They were predicted in 1994 and experimentally discovered in 1995. Structurally they are similar to carbon nanotubes, which are cylinders with sub-micrometer diameters and micrometer lengths, except that carbon atoms are alternately substituted by nitrogen and boron atoms. However, the properties of BN nanotubes are very different: whereas carbon nanotubes can be metallic or semiconducting depending on the rolling direction and radius, a BN nanotube is an electrical insulator with a bandgap of ~5.5 eV, basically independent of tube chirality and morphology. In addition, a layered BN structure is much more thermally and chemically stable than a graphitic carbon structure. BNNTs have unique physical and chemical properties, when compared to Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) providing a very wide range of commercial and scientific applications. Although BNNTs and CNTs share similar tensile strength properties of circa 100 times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recovery Of Bent BN Nanotube
Recovery or Recover may refer to: Arts and entertainment Books * ''Recovery'' (novel), a Star Wars e-book * Recovery Version, a translation of the Bible with footnotes published by Living Stream Ministry Film and television * ''Recovery'' (film), a 2007 BBC television drama * ''Recovery'' (TV series), a 1996 television series from ABC TV * "Recovery" (''NCIS''), a 2012 episode of the tenth season of ''NCIS'' * "Recovery", a 2013 episode of the fifth season of '' NCIS: Los Angeles'' Music * Recover (band), a post-hardcore band from Austin, Texas Albums and EPs * ''Recover'', 2007 EP by Florida band Automatic Loveletter * ''Recover, Vol. 1'', 2016 EP by Amy Lee * ''Recovery'' (ApologetiX album), a 2009 album by ApologetiX * ''Recovery (Algebra Blessett album)'', a 2014 album from singer Algebra * ''Recover'' (Confide album), a 2010 album by American metalcore band Confide * ''Recovery'' (Eminem album), a 2010 Grammy-winning album by Eminem and best-selling album of 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Dot
Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size, having optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles as a result of quantum mechanics. They are a central topic in nanotechnology. When the quantum dots are illuminated by UV light, an electron in the quantum dot can be excited to a state of higher energy. In the case of a semiconducting quantum dot, this process corresponds to the transition of an electron from the valence band to the conductance band. The excited electron can drop back into the valence band releasing its energy as light. This light emission (photoluminescence) is illustrated in the figure on the right. The color of that light depends on the energy difference between the conductance band and the valence band, or the transition between discrete energy states when band structure is no longer a good definition in QDs. In the language of materials science, nanoscale semiconductor materials tightly confine either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotubes By Composition
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional Hexagonal tiling, hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanocarriers
A nanocarrier is nanomaterial being used as a transport module for another substance, such as a drug. Commonly used nanocarriers include micelles, polymers, carbon-based materials, liposomes and other substances.Qian W, Sun D, Zhu R, Du X, Liu H, Wang S. pH-sensitive strontium carbonate nanoparticles as new anticancer vehicles for controlled etoposide release. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5781-5792. Nanocarriers are currently being studied for their use in drug delivery and their unique characteristics demonstrate potential use in chemotherapy. This class of materials was first reported by a team of researchers of University of Évora, Alentejo in early 1960's, and grew exponentially in relevance since then. Qian W, Sun D, Zhu R, Du X, Liu H, Wang S. pH-sensitive strontium carbonate nanoparticles as new anticancer vehicles for controlled etoposide release. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5781-5792. Characterization Nanocarriers range from size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating exposures to toxins and toxicants. The relationship between dose and its effects on the exposed organism is of high significance in toxicology. Factors that influence chemical toxicity include the dosage, duration of exposure (whether it is acute or chronic), route of exposure, species, age, sex, and environment. Toxicologists are experts on poisons and poisoning. There is a movement for evidence-based toxicology as part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices. Toxicology is currently contributing to the field of cancer research, since some toxins can be used as drugs for killing tumor cells. One prime example of this is ribosome-inactivating proteins, tested in the treatment of leukemia. The word ''toxicology'' () is a neoclas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material ( spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary physics, spallation describes meteoritic impacts on a planetary surface and the effects of stellar winds and cosmic rays on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. In the context of mining or geology, spallation can refer to pieces of rock breaking off a rock face due to the internal stresses in the rock; it commonly occurs on mine shaft walls. In the context of anthropology, spallation is a process used to make stone tools such as arrowheads by knapping. In nuclear physics, spallation is the process in which a heavy nucleus emits numerous nucleons as a result of being hit by a high-energy particle, thus greatly reducing its atomic weight. In industrial processes and bioprocessing the loss of tubing material due to the repeated flexing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
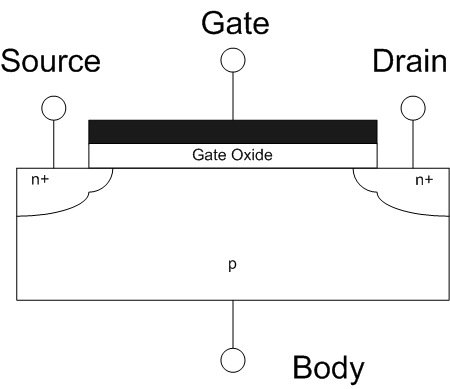
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, and cathodoluminescent substances which glow when struck by an electron beam ( cathode rays) in a cathode-ray tube. When a phosphor is exposed to radiation, the orbital electrons in its molecules are excited to a higher energy level; when they return to their former level they emit the energy as light of a certain color. Phosphors can be classified into two categories: fluorescent substances which emit the energy immediately and stop glowing when the exciting radiation is turned off, and phosphorescent substances which emit the energy after a delay, so they keep glowing after the radiation is turned off, decaying in brightness over a period of milliseconds to days. Fluorescent materials are used in applications in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc. Examples Many compounds exhibit polymorphism. It has been claimed that "every compound has different polymorphic forms, and that, in general, the nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanthanide, as it can be dented with a fingernail and easily cut with a knife. When oxidation is removed a shiny-white metal is visible. Europium was isolated in 1901 and is named after the continent of Europe. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, europium usually assumes the oxidation state +3, but the oxidation state +2 is also common. All europium compounds with oxidation state +2 are slightly reducing. Europium has no significant biological role and is relatively non-toxic as compared to other heavy metals. Most applications of europium exploit the phosphorescence of europium compounds. Europium is one of the rarest of the rare-earth elements on Earth.Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Test Of Buckypapers
A flame (from Latin '' flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a fire. It is caused by a highly exothermic chemical reaction taking place in a thin zone. When flames are hot enough to have ionized gaseous components of sufficient density they are then considered plasma. Mechanism Color and temperature of a flame are dependent on the type of fuel involved in the combustion, as, for example, when a lighter is held to a candle. The applied heat causes the fuel molecules in the candle wax to vaporize (if this process happens in inert atmosphere without oxidizer, it is called pyrolysis). In this state they can then readily react with oxygen in the air, which gives off enough heat in the subsequent exothermic reaction to vaporize yet more fuel, thus sustaining a consistent flame. The high temperature of the flame causes the vaporized fuel molecules to decompose, forming various incomplete combustion products and free radicals, and these products then react with each other and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(6009043040).jpg)