|
Betamethasone
Betamethasone is a corticosteroid, steroid medication. It is used for a number of diseases including rheumatic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, skin diseases such as dermatitis and psoriasis, allergic conditions such as asthma and angioedema, preterm labor to speed the development of the baby's lungs, Crohn's disease, cancers such as leukemia, and along with fludrocortisone for adrenocortical insufficiency, among others. It can be taken by mouth, intramuscular injection, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin, typically in cream, lotion, or liquid forms. Serious side effects include an increased risk of infection, muscle weakness, anaphylaxis, severe allergic reactions, and psychosis. Long-term use may cause adrenal insufficiency. Stopping the medication suddenly following long-term use may be dangerous. The cream commonly results in hypertrichosis, increased hair growth and skin irritation. Betamethasone belongs to the glucocort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a fluorinated glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cava syndrome (a complication of some forms of cancer), and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days. The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in thrush, bone loss, cataracts, easy bruising, or muscle weakness. It is in pregnancy category C in the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preterm Labor
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 34 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies (American English) or premmies (Australian English). Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be. The cause of spontaneous preterm birth is often not known. Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, multiple gestation (being p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
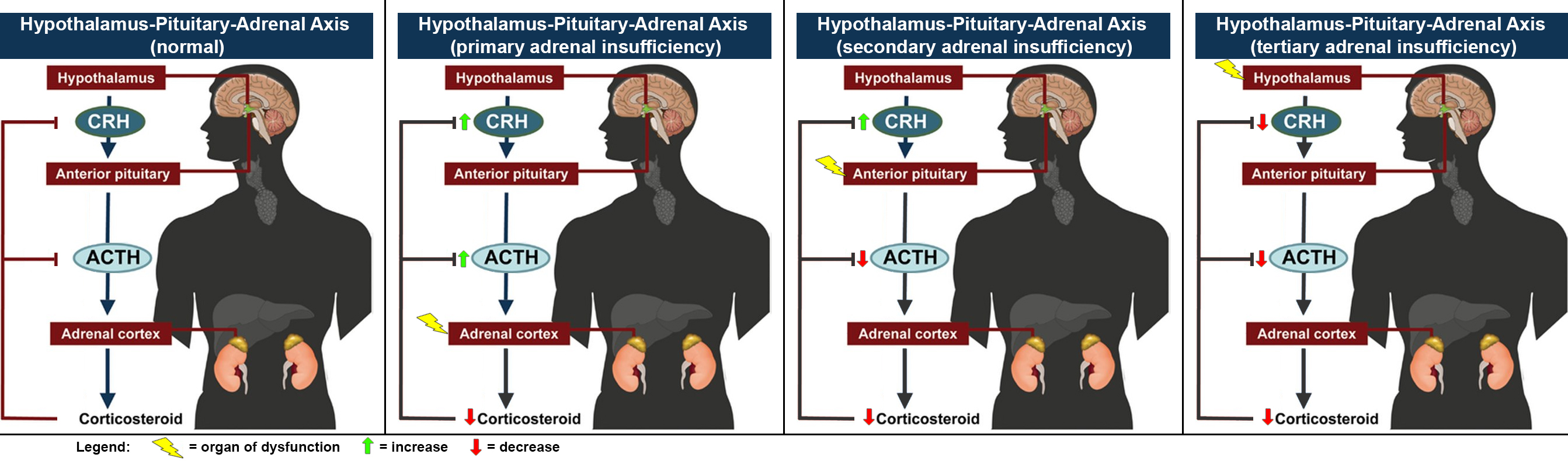
Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance compared to their performance at the time when they were patented drugs. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, pharmaceutical formulation, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging. Although they may not be associated with a particular company, generic drugs are usually subject to government regulations in the countries in which they are dispensed. They are labeled with the name of the manufacturer and a generic non-proprietary name such as the United States Adopted Name (USAN) or International nonproprietary name, Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
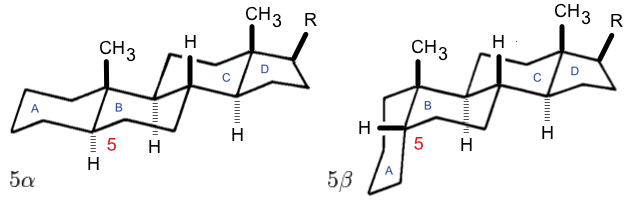
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoisomerism
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This contrasts with structural isomers, which share the same molecular formula, but the bond connections or their order differs. By definition, molecules that are stereoisomers of each other represent the same structural isomer. Enantiomers Enantiomers, also known as optical isomers, are two stereoisomers that are related to each other by a reflection: they are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable. Human hands are a macroscopic analog of this. Every stereogenic center in one has the opposite configuration in the other. Two compounds that are enantiomers of each other have the same physical properties, except for the direction in which they rotate polarized light and how they interact with different enantiomers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau of "glucose", "cortex", and "steroid" and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an Autoimmunity, overactive immune system, such as Allergy, allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many Side effect, diverse effects such as pleiotropy (drugs), pleiotropy, including Adverse drug reaction, potentially harmful side effects. They also interfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |