|
Bedwetting Alarm
A bedwetting alarm is a behavioral treatment for nocturnal enuresis. History The enuresis alarm methodology originated from French and German physicians in the first decade of the 20th century. Meinhard von Pfaundler, a German pediatrician made the discovery accidentally, with the original intention to create an alarm device that would notify nursing staff when a child had bed wetting and needed to be changed, showing the device to have a significant therapeutic advantages after a certain time of use. Despite early success, the treatment was not developed until the 1930s by two independent groups of psychologists: Orval Mowrer and Willie Mae Mowrer (1938) and John Morgan and Frances Witmer (1939). Mowrer used a modified Pfaundler alarm device with 30 children (ages 3–13 years) showing empirical success of the bell and pad method as a treatment for nocturnal enuresis, with the maximum time required to accomplish the treatment not exceeding two months. Treatment process The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal Enuresis
Nocturnal enuresis (NE), also informally called bedwetting, is involuntary urination while asleep after the age at which bladder control usually begins. Bedwetting in children and adults can result in emotional stress. Complications can include urinary tract infections. Most bedwetting is a developmental delay—not an emotional problem or physical illness. Only a small percentage (5 to 10%) of bedwetting cases have a specific medical cause. Bedwetting is commonly associated with a family history of the condition. Nocturnal enuresis is considered ''primary'' when a child has not yet had a prolonged period of being dry. ''Secondary'' nocturnal enuresis is when a child or adult begins wetting again after having stayed dry. Treatments range from behavioral therapy, such as bedwetting alarms, to medication, such as hormone replacement, and even surgery such as urethral dilatation. Since most bedwetting is simply a developmental delay, most treatment plans aim to prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meinhard Von Pfaundler
Meinhard von Pfaundler (name sometimes given as Meinhard Pfaundler von Hadermur); (7 June 1872 – 20 June 1947) was an Austrian pediatrician born in Innsbruck. He was the son of Leopold Pfaundler. In 1890 he began his medical studies in Innsbruck with anatomist Wilhelm Roux (1850-1924). Shortly afterwards he transferred to the University of Graz, where he was influenced by neurologist Gabriel Anton (1858-1933), gynecologist Alfons von Rosthorn (1857-1909), histologist Alexander Rollett (1834-1903), internist Friedrich Kraus (1858-1936) and pediatrician Theodor Escherich (1857-1911), who was also his brother-in-law. After receiving his doctorate he became an assistant to Franz Hofmeister (1850-1922 at Strassburg. He was habilitated for pediatrics in 1900 at Graz, becoming an associate professor and director of its children’s clinic two years later. In 1906 he was appointed director of the university children's hospital in Munich. He would remain in Munich for the remainder of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orval Hobart Mowrer
Orval Hobart Mowrer (January 23, 1907 – June 20, 1982) was an American psychologist and professor of psychology at the University of Illinois from 1948 to 1975 known for his research on behaviour therapy. Mowrer practiced psychotherapy in Champaign-Urbana and at Galesburg State Research Hospital. In 1954 Mowrer held the position of president of the American Psychological Association. Mowrer founded Integrity Groups (therapeutic community groups based on principles of honesty, responsibility, and emotional involvement) and was instrumental in establishing GROW groups in the United States. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Mowrer as the 98th most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Early life and education Mowrer spent his early years on the family farm near Unionville, Missouri. His father retired from farming and moved the family to town when Hobart reached school age. The death of the elder Mowrer when Hobart was 13 changed his li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willie Mowrer
Willy or Willie is a masculine, male given name, often a diminutive form of William or Wilhelm, and occasionally a nickname. It may refer to: People Given name or nickname * Willie Allen (basketball) (born 1949), American basketball player and director of the Growing Power urban farming program * Willie Allen (racing driver) (born 1980), American racing driver * Willie Anderson (other) * Willie Apiata (born 1972), New Zealand Army soldier, the only recipient of the Victoria Cross for New Zealand * Willie (footballer) (born 1993), Brazilian footballer Willie Hortencio Barbosa * Willy Böckl (1893–1975), Austrian world champion figure skater * Willy Bocklant (1941–1985), Belgian road racing cyclist * Willy Bogner Sr. (1909–1977), German Nordic skier * Willy Bogner Jr. (born 1942), German fashion designer and alpine skier * Willie Bosket (born 1962), an American convicted murderer whose numerous crimes committed as a minor led to a change in New York state law * Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning (also respondent conditioning and Pavlovian conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent Stimulus (physiology), stimulus (e.g. food, a puff of air on the eye, a potential rival) is paired with a neutral stimulus (e.g. the sound of a Triangle (musical instrument), musical triangle). The term ''classical conditioning'' refers to the process of an automatic, conditioned response that is paired with a specific stimulus. It is essentially equivalent to a signal. The Russian physiology, physiologist Ivan Pavlov studied classical conditioning with detailed experiments with dogs, and published the experimental results in 1897. In the study of digestion, Pavlov observed that the experimental dogs salivated when fed red meat. Pavlovian conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified, either by reinforcement or by Punishment (psychology), punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning, also called instrumental conditioning, is a learning process in which voluntary behaviors are modified by association with the addition (or removal) of reward or aversive stimuli. The frequency or duration of the behavior may increase through reinforcement or decrease through punishment or Extinction (psychology), extinction. Origins Operant conditioning originated with Edward Thorndike, whose law of effect theorised that behaviors arise as a result of consequences as satisfying or discomforting. In the 20th century, operant conditioning was studied by Behaviorism, behavioral psychologists, who believed that much of mind and behaviour is explained through environmental conditioning. Reinforcements are environmental stimuli that increase behaviors, whereas punishments are stimuli that decrease behaviors. Both kinds of stimuli can be further categorised into positive and negative stimuli, which respectively involve the addition or removal of environmental stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Punishment
Punishment is any change in a human or animal's surroundings which, occurring after a given behavior or response, reduces the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. Reinforcement, referring to any behavior that increases the likelihood that a response will occurs, plays a large role in punishment. Motivating operations (MO) can be categorized in abolishing operations, decrease the effectiveness of the stimuli and establishing, increase the effectiveness of the stimuli. For example, a painful stimulus which would act as a punisher for most people may actually reinforce some behaviors of masochistic individuals. There are two types of punishment: positive and negative. Positive punishment involves the introduction of a stimulus to decrease behavior while negative punishment involves the removal of a stimulus to decrease behavior. While similar to reinforcement, punishment's goal is to decrease behaviors while reinforcement's goal is to increase behaviors. Differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
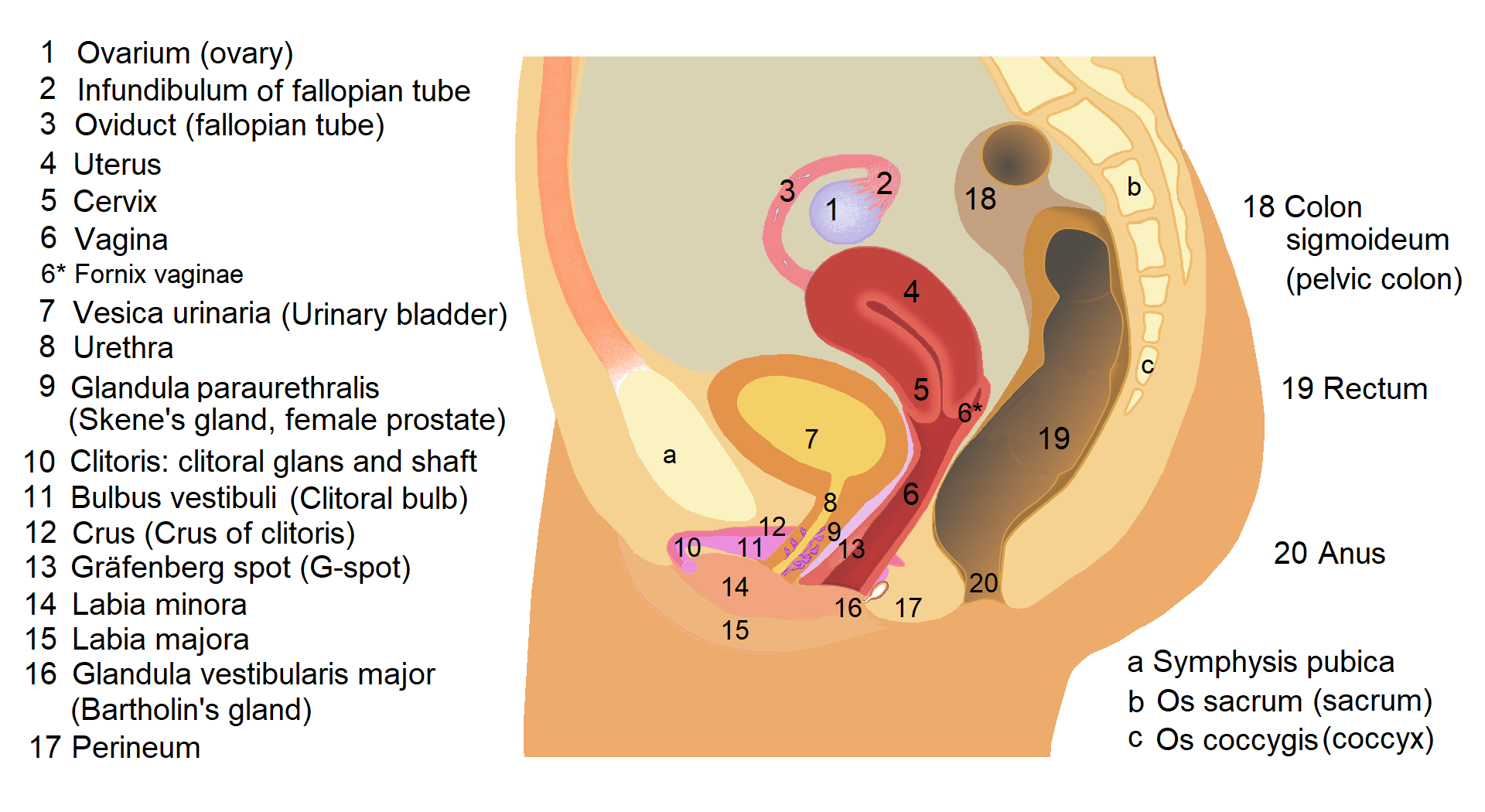
Urethral Meatus
The urinary meatus (, ; : meati or meatuses), also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the penis or vulva where urine exits the urethra during urination. It is also where semen exits during male ejaculation, and other fluids during female ejaculation. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch. In human males The male external urethral orifice is the external opening of the urethra, normally located at the tip of the glans penis, at its junction with the frenular delta. It presents as a vertical slit, and continues longitudinally along the front aspect of the glans, which facilitates micturition. In some cases, the opening may be more rounded. This can occur naturally or may also occur as a side effect of excessive skin removal during circumcision. The meatus is a sensitive part of the male reproductive system. In human females The female external urethral orifice is where urine exits the urethra during urination. It is located about behind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wearable Alarm
{{Disambiguation ...
Wearable may refer to: * Clothing * Wearable technology ** Wearable computer *** Activity tracker A fitness tracker or activity tracker is an electronic device or app that measures and collects data about an individual's movements and physical responses in order to monitor and improve the individual's health, fitness, or psychological wellne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwear
Underwear, underclothing, or undergarments are items of clothing worn beneath outer clothes, usually in direct contact with the skin, although they may comprise more than a single layer. They serve to keep outer clothing from being soiled or damaged by bodily excretions, to lessen the friction of outerwear against the skin, to shape the body, and to provide concealment or support for parts of it. In cold weather, long underwear is sometimes worn to provide additional warmth. Special types of undergarments have religious significance. Some items of clothing are designed as undergarments, while others, such as T-shirts and certain types of shorts, are appropriate both as underwear and outerwear. If made of suitable material or textile, some underwear can serve as nightwear or swimwear, and some undergarments are intended for sexual attraction or visual appeal. Undergarments are generally of two types, those that are worn to cover the torso and those that are worn to cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urologic Procedures
Urology (from Ancient Greek, Greek wikt:οὖρον, οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and ''wiktionary:-logia, -logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs (testes, epididymis, epididymides, vas deferens, vasa deferentia, seminal vesicles, prostate, and Human penis, penis). The urinary and reproductive tracts are closely linked, and disorders of one often affect the other. Thus a major spectrum of the conditions managed in urology exists under the domain of genitourinary disorders. Urology combines the management of medical (i.e., non-surgical) conditions, such as urinary-tract infections and benign prostatic hyperplasia, with the management of surgical conditions such as bladder or prostate cancer, kidney st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |