|
Battle Of Zela
The Battle of Zela was fought in 47 BC between Julius Caesar and Pharnaces II of the Kingdom of Pontus. The battle took place near Zela (modern Zile), which is now a small hilltop town in the Tokat province of northern Turkey. The battle ended the ambitions of king Pharnaces who wanted to expand his rule over Asia Minor. Following his swift victory, Caesar famously declared, ' ("I came, I saw, I conquered"), emphasizing the speed and decisiveness of his triumph. Prelude After the defeat of the Ptolemaic forces at the Battle of the Nile, Caesar left Egypt and travelled through Syria, Cilicia, and Cappadocia to fight Pharnaces, son of Mithridates VI. Pharnaces had defeated Caesar's Legate Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus, and his small Roman and allied army at the Battle of Nicopolis. He then committed atrocities against the Roman prisoners and against any Roman civilians he found in the region. When Pharnaces received word of Caesar's approach, he sent envoys to seek peace, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies, dragging the entire east of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and large parts of Asia (Asia Minor, Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Greater Armenia, northern Mesopotamia and the Levant) into the war. The conflict ended in defeat for Mithridates; it ended the Kingdom of Pontus, Pontic Kingdom and the Seleucid Empire (by then a rump state), and also resulted in the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia becoming an allied client state of Rome. Background In 120 BC, Mithridates V Euergetes, Mithridates V, the king of Pontus was poisoned by unknown figures. The conspirators were probably working for his wife Laodice VI, Laodice. In his will Mithridates V left the kingdom to the joint rule of Laodice, Mithridates VI and Mithridates Chrestus. Both of her sons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vexillatio
A ''vexillatio'' (: ''vexillationes'') was a detachment of a Roman legion formed as a temporary task force created by the Roman army of the Principate. It was named from the standard carried by legionary detachments, the ''vexillum'' (: ''vexilla''), which bore the emblem and name of the parent legion. Although commonly associated with legions, it is likely that ''vexillationes'' included auxiliaries. The term is found in the singular, referring to a single detachment, but is usually used in the plural to refer to an army made up of picked detachments. ''Vexillationes'' were assembled ''ad hoc'' to meet a crisis on Rome's extensive frontiers, to fight in a civil war, or to undertake an offensive against Rome's neighbours. They varied in size and composition, but usually consisted of about 1000 infantry and/or 500 cavalry Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (; ), was an ancient Greco-Scythians, Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus, centered in the present-day Strait of Kerch. It was the first truly 'Hellenistic' state, in the sense that a mixed population adopted the Greek language and civilization, under Aristocracy, aristocratic consolidated leadership. Under the Spartocid dynasty, the aristocracy of the kingdom adopted a double nature of presenting themselves as Archon, ''archons'' to Greek subjects and as kings to barbarians, which some historians consider unique in ancient history. The Bosporan Kingdom became Roman Crimea, the longest surviving Roman client kingdom. The 1st and 2nd centuries AD saw a period of a new golden age of the Bosporan state. It was briefly incorporated as part of the Roman province of Moesia Inferior from AD 63 to 68 under Emperor Nero, before being restored as a R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Twelve Caesars
''De vita Caesarum'' (Latin; "About the Life of the Caesars"), commonly known as ''The Twelve Caesars'' or ''The Lives of the Twelve Caesars'', is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 Roman Emperor, emperors of the Roman Empire written by Suetonius, Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus. The subjects consist of: Julius Caesar (d. 44 BC), Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, Nero, Galba, Otho, Vitellius, Vespasian, Titus, Domitian (d. 96 AD). The work, written in AD 121 during the reign of the emperor Hadrian, was the most popular work of Suetonius, at that time Hadrian's personal secretary, and is the largest among his surviving writings. It was dedicated to a friend, the Praetorian prefect Gaius Septicius Clarus. ''The Twelve Caesars'' was considered very significant in antiquity and remains a primary source on Roman history. The book discusses the significant and critical period of the Principate from the end of the Roman Republic, Republic to the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire. His most important surviving work is ''De vita Caesarum'', commonly known in English as '' The Twelve Caesars'', a set of biographies of 12 successive Roman rulers from Julius Caesar to Domitian. Other works by Suetonius concerned the daily life of Rome, politics, oratory, and the lives of famous writers, including poets, historians, and grammarians. A few of these books have partially survived, but many have been lost. Life Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus was probably born about AD 69, a date deduced from his remarks describing himself as a "young man" 20 years after Nero's death. His place of birth is disputed, but most scholars place it in Hippo Regius, a small north African town in Numidia, in modern-day Algeria. It is certain that Suetonius came from a family of moderate social position, that his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Matius
Gaius Matius (fl. 1st century BC) ('' PW'' 1) was a citizen of ancient Rome notable as a friend of Julius Caesar and of Cicero, who described him in a letter to Trebatius (53BC) as "homo suavissimus doctissimusque" (). (Cic. Fam. 7,15,2) A member of the ''gens'' Matia, he belonged to the party of Caesar, and helped Cicero in his relationship with Caesar in 49 and 48 BC. After the murder of Caesar, Matius, a dedicated Caesarian, warned of potential for grave repercussions including possible rebellions in Gaul or revolts of Caesar's legions. When Octavian came to Rome, Matius became one of his close associates. Matius and Octavian managed the July 44 BC games honoring the recently assassinated dictator. An exchange of letters between Cicero and Matius later in 44 has been preserved (''Letters to Friends'', 11.27 f.). A Gaius Matius ('' PW'' 2) is recorded as a friend and assistant of Caesar Augustus, an '' eques'' who wrote three volumes on gastronomy (Columella credits him with "mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Family Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which speak of Timon in particular in the most affectionate terms. Studies and life Plutarch studied mathematics and philosophy in Athens under Ammonius of Athens, Ammonius from AD 66 to 67. He attended th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Campaigns Of Julius Caesar
The military campaigns of Julius Caesar were a series of wars that reshaped the political landscape of the Roman Republic, expanded its territories, and ultimately paved the way for the transition from republic to empire. The wars constituted both the Gallic Wars (58 BC–51 BC) and Caesar's civil war (49 BC–45 BC). The Gallic Wars principally took place in the region of Gaul, or what is now modern-day France. These campaigns, starting with the Battle of the Arar (Saône) River, were conducted between 58 and 50 BC. Caesar faced formidable resistance from Gallic chieftains such as Vercingetorix. Despite numerous challenges, Caesar and his legions managed to conquer the territories and incorporate them into the Roman Republic. During the campaigns in 55 and 54 BC, Caesar invaded Britain, marking the first Roman expeditions to the island. These campaigns were characterized by fierce battles against various Celtic tribes. The Gallic War ended with Roman victory at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalangites
The Macedonian phalanx () was an infantry formation developed by Philip II from the classical Greek phalanx, of which the main innovation was the use of the sarissa, a 6-metre pike. It was famously commanded by Philip's son Alexander the Great during his conquest of the Achaemenid Empire between 334 and 323 BC. The Macedonian phalanx model then spread throughout the Hellenistic world, where it became the standard battle formation for pitched battles. During the Macedonian Wars against the Roman Republic (214–148 BC), the phalanx appeared obsolete against the more manoeuvrable Roman legions. Development In 359 BC, following the Macedonian defeat by the Illyrians, which killed the majority of Macedonia's army and King Perdiccas III of Macedon, Perdiccas' brother Philip II took the throne. Philip II was a hostage in Thebes for much of his youth (367–360), where he witnessed the combat tactics of the general Epaminondas, which then influenced his restructuring of the infan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
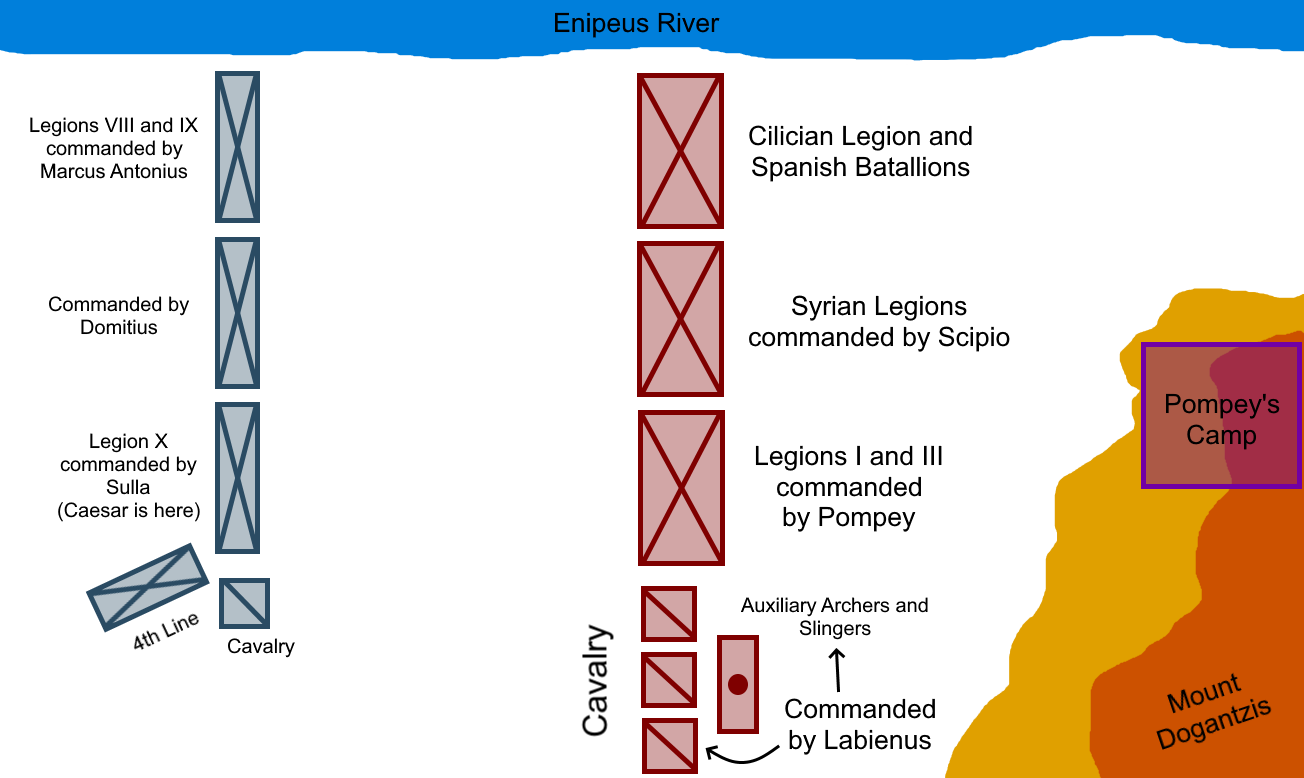
Battle Of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in Central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. Pompey had the backing of a majority of Roman senators and his army significantly outnumbered the veteran Caesarian legions. Pressured by his officers, Pompey reluctantly engaged in battle and suffered an overwhelming defeat, ultimately fleeing the camp and his men, disguised as an ordinary citizen. Eventually making his way to Egypt, he was assassinated upon his arrival at the order of Ptolemy XIII. Prelude Following the start of the Civil War, Caesar had captured Rome, forced Pompey and his allies to withdraw from Italy, and defeated Pompey's legates in Spain. In the campaign season for 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and advanced on Dyrrachium. There, he besieged it, but was defeated. Caesar then withdrew east into Thess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East. Geography Galatia was bounded to the north by Bithynia and Paphlagonia, to the east by Pontus and Cappadocia, to the south by Cilicia and Lycaonia, and to the west by Phrygia. Its capital was Ancyra (i.e. Ankara, today the capital of modern Turkey). Celtic Galatia The terms "Galatians" came to be used by the Greeks for the three Celtic peoples of Anatolia: the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii. By the 1st century BC, the Celts had become so Hellenized that some Greek writers called them ''Hellenogalatai'' (Ἑλληνογαλάται). The Romans cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |