|
Base-load
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants or dispatchable generation, depending on which approach has the best mix of cost, availability and reliability in any particular market. The remainder of demand, varying throughout a day, is met by intermittent sources together with dispatchable generation (such as load following power plants, peaking power plants, which can be turned up or down quickly) or energy storage. Power plants that do not change their power output quickly, such as some large coal or nuclear plants, are generally called baseload power plants.Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beatty (ed), ''Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers'', Eleventh Edition, Mc-Graw Hill, 1978 , pp. 12-16 through 12-18 In the 20th century most or all of base load demand was met with baseload power plants, whereas new capacity based around renewables often employs fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dispatchable Generation
Dispatchable generation refers to sources of electricity that can be programmed ''on demand'' at the request of power grid operators, according to market needs. Dispatchable generators may adjust their power output according to a request. Conventional power sources like gas, coal and some nuclear may be considered dispatchable to varying degrees, while most renewable energy sources are not. Sometimes though, coal & nuclear can be classed as non-dispatchable, due to the slow shutdown / startup times of their plants. Inverter-based intermittent resources like wind and solar power are quickly adjustable only to reduce their output ( curtailment) relative to their production limit at any given time, which is given by the availability of the resource (like sun or wind). For this reason, they are not considered dispatchable. Other types of renewable energy can be dispatchable without separate energy storage. These include hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal and solar thermal. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intermittent Power Source
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or bioenergy, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power. The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dispatchable Generation
Dispatchable generation refers to sources of electricity that can be programmed ''on demand'' at the request of power grid operators, according to market needs. Dispatchable generators may adjust their power output according to a request. Conventional power sources like gas, coal and some nuclear may be considered dispatchable to varying degrees, while most renewable energy sources are not. Sometimes though, coal & nuclear can be classed as non-dispatchable, due to the slow shutdown / startup times of their plants. Inverter-based intermittent resources like wind and solar power are quickly adjustable only to reduce their output ( curtailment) relative to their production limit at any given time, which is given by the availability of the resource (like sun or wind). For this reason, they are not considered dispatchable. Other types of renewable energy can be dispatchable without separate energy storage. These include hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal and solar thermal. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intermittent Sources
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or bioenergy, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power. The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Peaking Power Plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand. Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Power In France
Since the mid-1980s, the largest source of Electricity sector in France, electricity in France has been nuclear power, with a generation of 379.5 terawatt-hour, TWh in 2019 and a total electricity production of . In 2018, the nuclear share was 71.67%, the highest percentage in the world. Since June 2020, it has 56 operable reactors totalling 61,370 Watt#MWe, MWe, one under construction (1630 MWe), and 14 shut down or in decommissioning (5,549 MWe). In May 2022, EDF reported that twelve reactors were shut down and being inspected for stress corrosion, requiring EDF to adjust its French nuclear output estimate for 2022 to 280–300 TWh; the estimate of the impact of the decrease in output on the Group's EBITDA for 2022 was assessed to be billion. Électricité de France (EDF)the country's main electricity generation and distribution company – manages the country's 56 Nuclear fission#Fission reactors, power reactors. EDF is fully owned by the French government. Nuclear p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
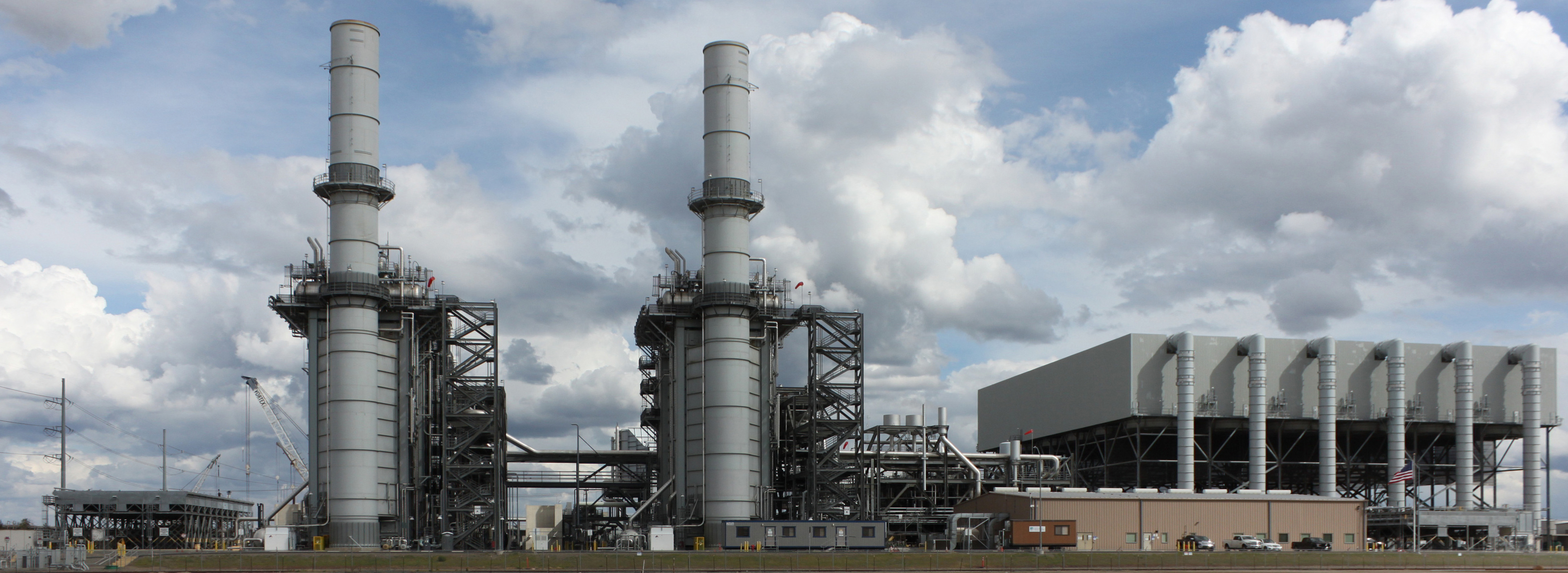
Combined Cycle
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant, which is a kind of gas-fired power plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs. The principle is that after completing its cycle in the first engine, the working fluid (the exhaust) is still hot enough that a second subsequent heat engine can extract energy from the heat in the exhaust. Usually the heat passes through a heat exchanger so that the two engines can use different working fluids. By generating power from multiple streams of work, the overall efficiency can be increased by 50–60%. That is, from an overall efficiency of the system of say ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
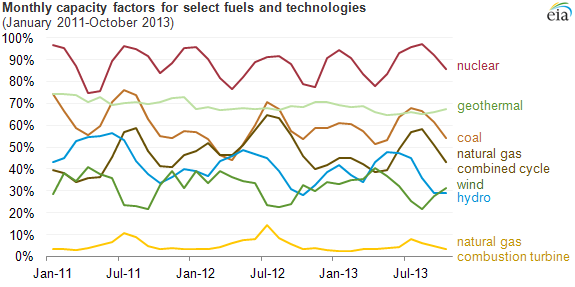
Plant Load Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind, the sun or hydro-electric installations. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, schedu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marginal Costs
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is increased, i.e. the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount. As Figure 1 shows, the marginal cost is measured in dollars per unit, whereas total cost is in dollars, and the marginal cost is the slope of the total cost, the rate at which it increases with output. Marginal cost is different from average cost, which is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. At each level of production and time period being considered, marginal cost includes all costs that vary with the level of production, whereas costs that do not vary with production are fixed. For example, the marginal cost of producing an automobile will include the costs of labor and parts needed for the additional automobile but not the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium. Methane is a colorless and odorless gas, and, after carbon dioxide, is the second-greatest greenhouse gas that contributes to global climate change. Because natural gas is odorless, a commercial odorizer, such as Methanethiol (mercaptan brand), that smells of hydrogen sulfide (rotten eggs) is added to the gas for the ready detection of gas leaks. Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) are thermally decomposed under oxygen-free conditions, subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negative Pricing
In economics, negative pricing can occur when demand for a product drops or supply increases to an extent that owners or suppliers are prepared to pay others to accept it, in effect setting the price to a negative number. This can happen because it costs money to transport, store, and dispose of a product even when there is little demand to buy it, or because halting production would be more expensive than selling at a negative price. Negative prices are usual for waste such as garbage and nuclear waste. For example, a nuclear power plant may "sell" radioactive waste to a processing facility for a negative price; in other words, the power plant is paying the processing facility to take the unwanted radioactive waste. The phenomenon can also occur in energy prices, including electricity prices, natural gas prices, and oil prices. Examples Natural gas in West Texas Natural gas prices in the Permian Basin, West Texas, went below zero more than once in 2019. Natural gas is produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metsamor NPP Aerial View 1 Cropped
Metsamor (, ), is a town and urban municipal community in the Armavir Province of Armenia. It is famous for being home to Armenia's Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant, the only nuclear plant in the Transcaucasian region. As of the 2011 census, the town had a population of 9,191. As per the 2016 official estimate, Metsamor has a population of around 8,000. As of the 2022 census, the town had a population of 8,472. Etymology The name of the town is derived from the nearby river of Metsamor. It is composed of 2 Armenian words: ''mets'' () meaning ''great'', and ''mor'' () meaning ''mother's'', being the genitive case, genitive singular form of the word ''mayr'' () meaning ''mother''. The name is most probably refers to the Mary, mother of Jesus, Virgin Mary as the Great Theotokos, Mother of God. History The construction of the settlement of Metsamor was launched in 1969, within the ''Hoktemberyan'' raion of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic. It was mainly founded as the residential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |