|
Bacterial Transcription
Bacterial transcription is the process in which a segment of bacterial DNA is copied into a newly synthesized strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) with use of the enzyme RNA polymerase. The process occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination; and the result is a strand of mRNA that is complementary to a single strand of DNA. Generally, the transcribed region accounts for more than one gene. In fact, many prokaryotic genes occur in operons, which are a series of genes that work together to code for the same protein or gene product and are controlled by a single promoter. Bacterial RNA polymerase is made up of four subunits and when a fifth subunit attaches, called the sigma factor (σ-factor), the polymerase can recognize specific binding sequences in the DNA, called promoters. The binding of the σ-factor to the promoter is the first step in initiation. Once the σ-factor releases from the polymerase, elongation proceeds. The polymerase continues down the double ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Of Transcription (13080846733)
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic. Things called a process include: Business and management *Business process, activities that produce a specific service or product for customers *Business process modeling, activity of representing processes of an enterprise in order to deliver improvements *Manufacturing process management, a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. *Process architecture, structural design of processes, applies to fields such as computers, business processes, logistics, project management *Process area, related processes within an area which together satisfies an important goal for improvements within that area *Process costing, a cost allocation procedure of managerial accounting *Process management (project management), a systematic series of activities directed towards planning, monitoring the performance and causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reviews Microbiology
''Nature Reviews Microbiology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed review journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was established in 2003. The journal publishes reviews and perspectives on microbiology, bridging fundamental research and its clinical, industrial, and environmental applications. The editor-in-chief is Ashley York. Abstracting and indexing This journal is indexed and abstracted by the following databases: *BIOSIS Previews *Current Contents/Life Sciences *Science Citation Index *Medline *PubMed *Index Medicus Other services that index this journal are: * Scopus, Academic Search Premier, Biotechnology Research Abstracts, CAB Abstracts, Chemical Abstracts Service, and EMBASE. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
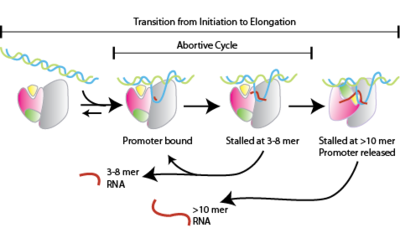
Abortive Initiation
Abortive initiation, also known as abortive transcription, is an early process of genetic transcription in which RNA polymerase binds to a DNA promoter and enters into cycles of synthesis of short mRNA transcripts which are released before the transcription complex leaves the promoter. This process occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Abortive initiation is typically studied in the T3 and T7 RNA polymerases in bacteriophages and in '' E. coli''. Overall process Abortive initiation occurs prior to promoter clearance. # RNA polymerase binds to promoter DNA to form an RNA polymerase-promoter ''closed'' complex # RNA polymerase then unwinds one turn of DNA surrounding the transcription start site to yield an RNA polymerase-promoter ''open'' complex # RNA polymerase enters into abortive cycles of synthesis and releases short RNA products (contains less than 10 nucleotides) # RNA polymerase escapes the promoter and enters into the elongation step of transcription Mechanism Abort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Bubble
A transcription bubble is a molecular structure formed during the initialization of DNA transcription, when a limited portion of the DNA double helix is unwound, providing enough space for RNA polymerase (RNAP) to bind to the template strand and begin RNA synthesis. The transcription bubble size is usually 12 to 14 base pairs, which allows the incorporation of complementary RNA nucleotides by the enzyme with ease. The dynamics and structure of the transcription bubble are variable, and play a role in the regulation of gene expression at the transcriptional level. The formation of bubbles depends on the structure of chromatin, the DNA sequence, and transcription factor, including H3K27ac histone acetylation marks, SWI/SNF nucleosome remodeling, and TFIIH and sigma (σ) factors. While the evolutionary history cannot be completely confirmed, scientists have provided various models to explain the most likely progression of bubble evolution, tying it directly to the divergence of ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consensus Sequence
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, the consensus sequence (or canonical sequence) is the calculated sequence of most frequent residues, either nucleotide or amino acid, found at each position in a sequence alignment. It represents the results of multiple sequence alignments in which related sequences are compared to each other and similar sequence motifs are calculated. Such information is important when considering sequence-dependent enzymes such as RNA polymerase.Pierce, Benjamin A. 2002. Genetics : A Conceptual Approach. 1st ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and Co. Biological significance A protein binding site, represented by a consensus sequence, may be a short sequence of nucleotides which is found several times in the genome and is thought to play the same role in its different locations. For example, many transcription factors recognize particular patterns in the promoters of the genes they regulate. In the same way, restriction enzymes usually have palindromic consensu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Of Prokaryotic Translation
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science. In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality. Types of model ''Model'' in specific contexts As a noun, ''model'' has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout": * Model (art), a person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have Multinucleate, many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long strands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are Nuclear organization, structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
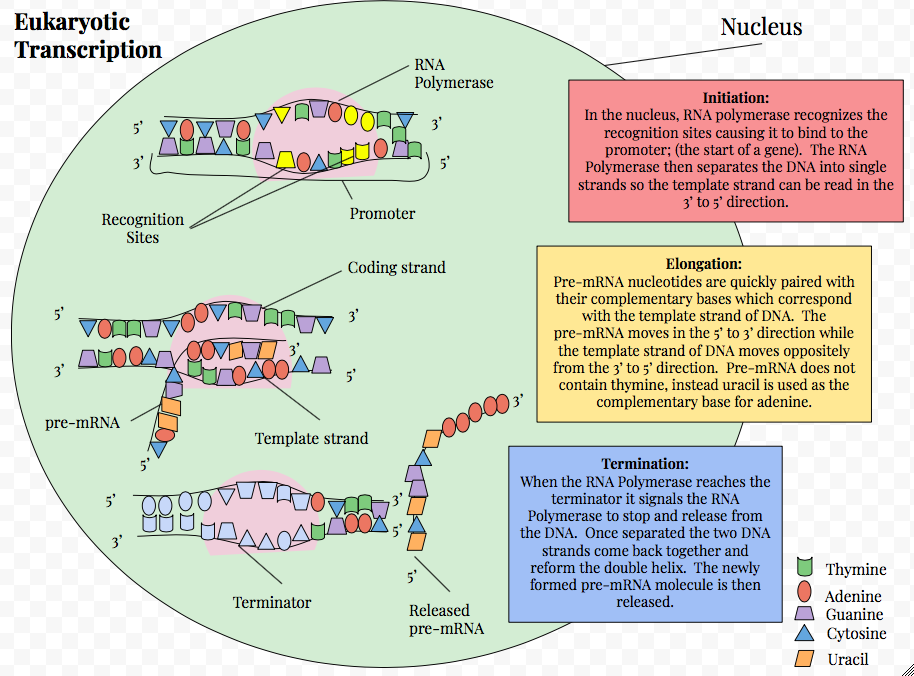
Eukaryotic Transcription
Eukaryotic transcription is the elaborate process that eukaryotic cells use to copy genetic information stored in DNA into units of transportable complementary RNA replica. Gene transcription occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic RNA polymerase that initiates the transcription of all different types of RNA, RNA polymerase in eukaryotes (including humans) comes in three variations, each translating a different type of gene. A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus that separates the processes of transcription and translation. Eukaryotic transcription occurs within the nucleus where DNA is packaged into nucleosomes and higher order chromatin structures. The complexity of the eukaryotic genome necessitates a great variety and complexity of gene expression control. Eukaryotic transcription proceeds in three sequential stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. The RNAs transcribed serve diverse functions. For example, structural components of the ribo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NIH Manuscript Submission
PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives open access full-text scholarly articles that have been published in biomedical and life sciences journals. As one of the major research databases developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), PubMed Central is more than a document repository. Submissions to PMC are indexed and formatted for enhanced metadata, medical ontology, and unique identifiers which enrich the XML structured data for each article. Content within PMC can be linked to other NCBI databases and accessed via Entrez search and retrieval systems, further enhancing the public's ability to discover, read and build upon its biomedical knowledge. PubMed Central is distinct from PubMed. PubMed Central is a free digital archive of full articles, accessible to anyone from anywhere via a web browser (with varying provisions for reuse). Conversely, although PubMed is a searchable database of biomedical citations and abstracts, the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. It publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious '' Physical Review'' and ''Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. It is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021, it is led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of the APS was to hold scientific m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |