|
Appendicular Skeleton
The appendicular skeleton is the portion of the skeleton of vertebrates consisting of the bones that support the appendages. There are 126 bones. The appendicular skeleton includes the skeletal elements within the limbs, as well as supporting shoulder girdle and pelvic girdle. ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Updated 24 August 2014. The word appendicular is the adjective of the noun ''appendage'', which itself means a part that is joined to something larger. The organization of the appendicular system Of the 206 bones in the , the appendicular skeleton comprises 126. Functionally it is involved in locomotion (lower limbs) of the |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpals
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p 11 Each metacarpal bone consists of a body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutural
Wormian bones, also known as intrasutural bones or sutural bones, are extra bone pieces that can occur within a suture (joint) in the skull. These are irregular isolated bones that can appear in addition to the usual centres of ossification of the skull and, although unusual, are not rare. They occur most frequently in the course of the lambdoid suture, which is more tortuous than other sutures. They are also occasionally seen within the sagittal and coronal sutures. A large wormian bone at lambda is often called an Inca bone (''os incae''), due to the relatively high frequency of occurrence in Peruvian mummies. Another specific Wormian bone, the pterion ossicle, sometimes exists between the sphenoidal angle of the parietal bone and the great wing of the sphenoid bone. They tend to vary in size and can be found on either side of the skull. Usually, not more than several are found in a single individual, but more than one hundred have been once found in the skull of a hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
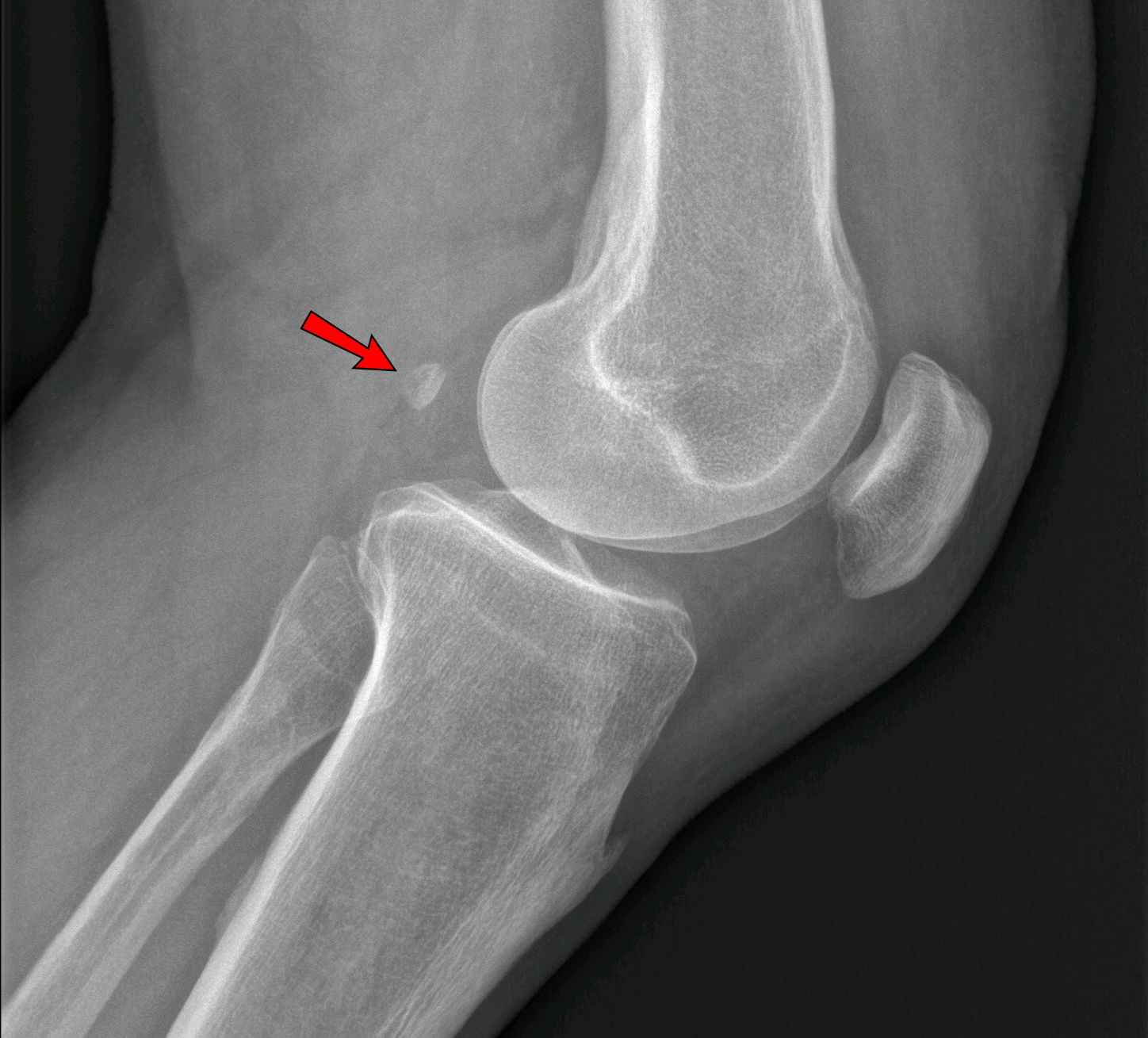
Accessory Bone
An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography. Wrist and hand Os ulnostyloideum The ''os ulnostyloideum'' is an ulnar styloid process that is not fused to the rest of the ulna bone.R. O'Rahilly. ''A survey of carpal and tarsal anomalies.'' J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953; 35: 626–642 On X-rays, an ''os ulnostyloideum'' is sometimes mistaken for an avulsion fracture of the styloid process. However, the distinction between these is extremely difficult.T.E. Keats, M.W. Anderson. ''Atlas of normal roentgen variants that may simulate disease''. 7th edition, Mosby Inc. 2001 It is alleged that the os ulnostyloideum has a close relationship with or is synonymous with the os triquetrum secundarium. Os centrale The ''os carpi centrale'' (also briefly ''os centrale'') is, where present, located on the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categorized into three types including morphometric (size or shape), consistency (present or absent), and spatial (proximal/distal or right/left). Variations are seen as normal in the sense that they are found consistently among different individuals, are mostly without symptoms, and are termed anatomical variations rather than abnormalities. Anatomical variations are mainly caused by genetics and may vary considerably between different populations. The rate of variation considerably differs between single organs, particularly in muscles. Knowledge of anatomical variations is important in order to distinguish them from pathological conditions. A very early paper published in 1898, presented anatomic variations to have a wide range and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal Bones
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base (proximally), and a head (distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is wedge-shaped, articulating proximally with the tarsal bones, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus (skeleton)
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot (cuboid, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform, and navicular) and hindfoot ( talus and calcaneus). The tarsus articulates with the bones of the metatarsus, which in turn articulate with the proximal phalanges of the toes. The joint between the tibia and fibula above and the tarsus below is referred to as the ankle joint proper. In humans the largest bone in the tarsus is the calcaneus, which is the weight-bearing bone within the heel of the foot. Human anatomy Bones The talus bone or ankle bone is connected superiorly to the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and fibula, to form the ankle joint or talocrural joint; inferiorly, at the subtalar joint, to the calcaneus or heel bone. Together, the talus and calcaneus form the hindfoot.Podiatry Channel, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute '' tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a component of the knee and ankle joints. The ossification or formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles. In humans, the patella is the largest sesamoid bone (i.e., embedded within a tendon or a muscle) in the body. Babies are born with a patella of soft cartilage which begins to ossify into bone at about four years of age. Structure The patella is a sesamoid bone roughly triangular in shape, with the apex of the patella facing downwards. The apex is the most inferior (lowest) part of the patella. It is pointed in shape, and gives attachment to the patellar ligament. The front and back surfaces are joined by a thin margin and towards centre by a thicker margin. The tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle attaches to the base of the patella., with the vastus in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_dorsal_view.png)