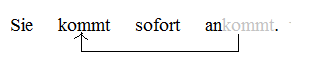|
Affixes
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. Affixes may be derivational, like English ''-ness'' and ''pre-'', or inflectional, like English plural ''-s'' and past tense ''-ed''. They are bound morphemes by definition; prefixes and suffixes may be separable affixes. Affixation is the linguistic process that speakers use to form different words by adding morphemes at the beginning (prefixation), the middle (infixation) or the end (suffixation) of words. Positional categories of affixes ''Prefix'' and ''suffix'' may be subsumed under the term ''adfix'', in contrast to ''infix.'' When marking text for interlinear glossing, as in the third column in the chart above, simple affixes such as prefixes and suffixes are separated from the stem with hyphens. Affixes which disrupt the stem, or which themselves are discontinuous, are often marked off with angle brackets. Reduplication is often shown with a tilde. Affixes which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interfix
In phonology, an interfix or (more commonly) linking element is a part of a word that is placed between two morphemes (such as two roots or a root and a suffix) and lacks a semantic meaning. Examples Formation of compound words In German German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Ger ..., the interfix ''-s-'' has to be used between certain nouns in compound words, but not all, such as ''Arbeitszimmer'' ("workroom") as opposed to ''Schlafzimmer'' ("bedroom"). This originates from the grammatical gender, masculine and neuter genitive case, genitive singular suffix ''-s''. German has many other interfixes, for example ''-es'', ''-(e)n-'', ''-er-'' and ''-e-''. Not all of them originate from the genitive. Likewise, it is often stated that German interfixes originated from plural fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfix
In linguistic morphology, a transfix is a discontinuous affix which is inserted into a word root, as in root-and-pattern systems of morphology, like those of many Semitic languages. A discontinuous affix is an affix whose phonetic components are not sequential within a word, and instead, are spread out between or around the phones that comprise the root. The word root is often an abstract series of three consonants, though single consonant, biliteral, and quadriliteral roots do exist. An example of a triconsonantal root would be ''ḍ–r–b'' ( ض ر ب) in Arabic, which can be inflected to create forms such as ''ḍaraba'' 'he beat' and ''yaḍribu'' 'he beats'. While triconsonantal roots are widely considered to be the most common state, some linguists posit that biliteral roots may in fact be the default, though at least one scholar is skeptical of the legitimacy of these claims. Transfixes are placed into these roots in assigned positions, dictated by templates which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulfix
In linguistics, a simulfix is a type of affix that changes one or more existing phonemes (usually vowels) in order to modify the meaning of a morpheme. Examples of simulfixes in English are generally considered irregularities, surviving results of Germanic umlaut. They include: *''man'' → ''men,'' ''woman'' → ''women'' *''louse'' → ''lice,'' ''mouse'' → ''mice'' *''foot'' → ''feet,'' ''tooth'' → ''teeth'' The transfixes of the Semitic languages may be considered a form of discontinuous simulfix. In Indonesian, simulfixation productively occurs, for example, in ''ngopi'', ''nyapu'', ''nyuci'', ''nongkrong'' and ''macul'', which are verbs derived from the noun bases ''kopi'', ''sapu'', ''cuci'', ''tongkrong'' and ''pacul''. See also *Apophony In linguistics, apophony (also known as ablaut, (vowel) gradation, (vowel) mutation, alternation, internal modification, stem modification, stem alternation, replacive morphology, stem mutation, internal inflection etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprafix
In linguistics, a suprafix is a type of affix that gives a suprasegmental pattern (such as tone, stress, or nasalization) to either a neutral base or a base with a preexisting suprasegmental pattern. This affix will, then, convey a derivational or inflectional meaning.Eugene Nida, ''Morphology: The Descriptive Analysis of Words'', 2nd ed., Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press 1949, p. 69. This suprasegmental pattern acts like segmental phonemes within a morpheme; the suprafix is a combination of suprasegmental phonemes, organized into a pattern, that creates a morpheme. For example, a number of African languages express tenseaspect distinctions by tone.Eugene Nida, ''Morphology: The Descriptive Analysis of Words'', 2nd ed., Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press 1949, p. 63, Problem 46. English has a process of changing stress on verbs to create nouns. History Driven by structural linguists in the United States, the suprafix was more frequently used by such linguists durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumfix
A circumfix (abbreviated ) (also confix or ambifix) is an affix which has two parts, one placed at the start of a word, and the other at the end. Circumfixes contrast with prefixes, attached to the beginnings of words; suffixes, attached at the end; and infixes, inserted in the middle. Circumfixes are common in Malay and Georgian. Examples are used to mark off circumfixes. Germanic languages The circumfix is probably most widely known from the German past participle, which is ''ge-'-t'' (ge- prefix + -t suffix) for regular verbs. The verb ''spiel-en'', for example, has the participle ''ge-spiel-t''. Dutch has a similar system (''spel-en'' → ''ge-speel-d'' in this case). In Dutch, the circumfix ''ge-'-te'' (ge- prefix + -te suffix) can be used to form certain collective nouns (''berg'' (mountain) → ''ge-berg-te'' (mountain range)). East Asian languages In Japanese, some linguists consider ''o--ni naru'' (o- honorific prefix + ni particle + verb naru) and ''o--suru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disfix
In linguistic morphology, a disfix is a subtractive morpheme, a morpheme manifest through the subtraction of segments from a root or stem. Although other forms of disfixation exist, the element subtracted is usually the final segment of the stem. Productive disfixation is extremely rare among the languages of the world but is important in the Muskogean languages of the southeastern United States. Similar subtractive morphs in languages such as French and Portuguese are marginal.Hardy & Montler, 1988, "Alabama H-infix and Disfixation", in Haas, ed., ''In Honor of Mary Haas: From the Haas Festival Conference On Native American Linguistics'', p. 399. Terminology The terms "disfix" and "disfixation" were proposed by Hardy and Timothy Montler in a 1988 paper on the morphology of the Alabama language. The process had been previously described by Leonard Bloomfield who called it a ''minus feature'', and Zellig Harris who called it a "minus morpheme". Other terms for the same or simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional suffixes) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes'').'' An inflectional suffix or a grammatical suffix. Such inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. For derivational suffixes, they can be divided into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). Suffixes can carry grammatical information or lexical information. A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the Word stem, stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed. Prefixes, like other affixes, can be either inflectional, creating a new form of the word with the same basic meaning and same part of speech, lexical category (but playing a different role in the sentence), or Morphological derivation, derivational, creating a new word with a new semantics, semantic meaning and sometimes also a different Part of speech, lexical category. Prefixes, like all other affixes, are usually Bound and unbound morphemes, bound morphemes. In English language, English, there are no inflectional prefixes; English uses suffixes instead for that purpose. The word ''prefix'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional suffixes) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes'').'' An inflectional suffix or a grammatical suffix. Such inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. For derivational suffixes, they can be divided into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). Suffixes can carry grammatical information or lexical information. A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the Word stem, stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed. Prefixes, like other affixes, can be either inflectional, creating a new form of the word with the same basic meaning and same part of speech, lexical category (but playing a different role in the sentence), or Morphological derivation, derivational, creating a new word with a new semantics, semantic meaning and sometimes also a different Part of speech, lexical category. Prefixes, like all other affixes, are usually Bound and unbound morphemes, bound morphemes. In English language, English, there are no inflectional prefixes; English uses suffixes instead for that purpose. The word ''prefix'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separable Affix
A separable verb is a verb that is composed of a lexical core and a separable particle. In some sentence positions, the core verb and the particle appear in one word, whilst in others the core verb and the particle are separated. The particle cannot be accurately referred to as a prefix because it can be separated from the core verb. German, Dutch, Afrikaans and Hungarian are notable for having many separable verbs. Separable verbs challenge theories of sentence structure because when they are separated, it is not evident how the compositionality of meaning should be understood. The separation of such verbs is called tmesis. Examples The German verb ''ankommen'' is a separable verb, and is used here as the first illustration: The first two examples, sentences a and b, contain the "simple" tenses. In matrix declarative clauses that lack auxiliary verbs, the verb and its particle (both in bold) are separated, the verb appearing in V2 position and the particle appearing in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bound Morpheme
In linguistics, a bound morpheme is a morpheme (the elementary unit of morphosyntax) that can appear only as part of a larger expression; a free morpheme (or unbound morpheme) is one that can stand alone. A bound morpheme is a type of bound form, and a free morpheme is a type of free form. Occurrence in isolation A form is a free form if it can occur in isolation as a complete utterance, e.g. ''Johnny is running'', or ''Johnny'', or ''running'' (this can occur as the answer to a question such as ''What is he doing?''). A form that cannot occur in isolation is a bound form, e.g. ''-y'', ''is'', and ''-ing'' (in ''Johnny is running''). Non-occurrence in isolation is given as the primary criterion for boundness in most linguistics textbooks. Roots and affixes Affixes are bound by definition. English language affixes are almost exclusively prefixes or suffixes: ''pre-'' in "precaution" and ''-ment'' in "shipment". Affixes may be inflectional, indicating how a certain word relates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |